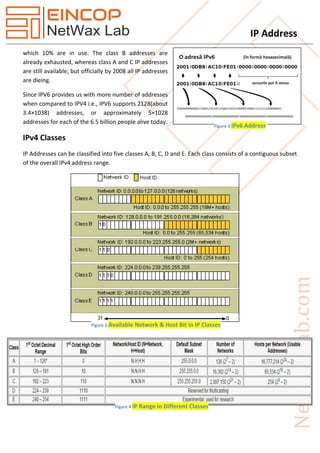
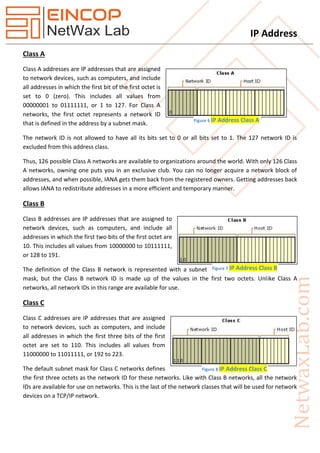
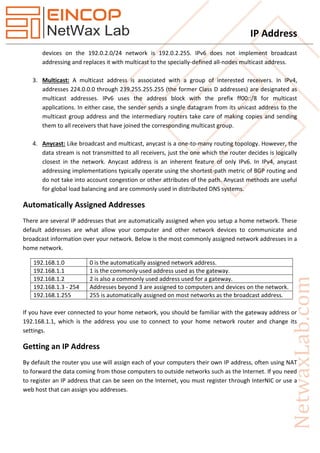
An IP address uniquely identifies a device on a network for communication, with IPv4 and IPv6 being the two main versions, where IPv4 uses 32 bits and IPv6 uses 128 bits. IPv4 has various classes (A to E) defining different address ranges and functionalities, whereas IPv6 significantly expands the address space. IP addressing methods include unicast, broadcast, multicast, and anycast, with additional mechanisms like NAT being utilized for address management in networks.