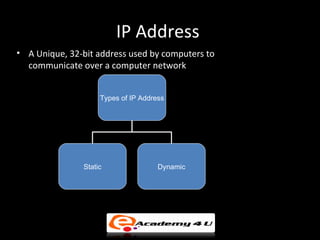
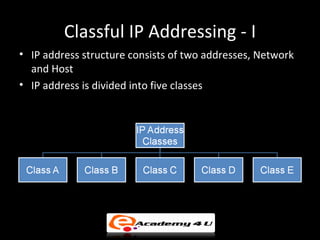
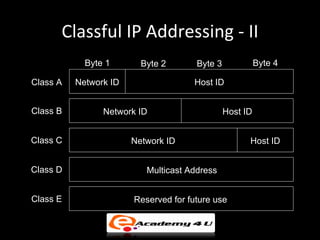
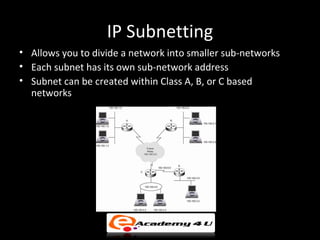
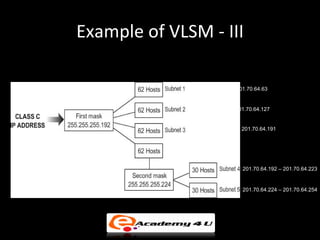
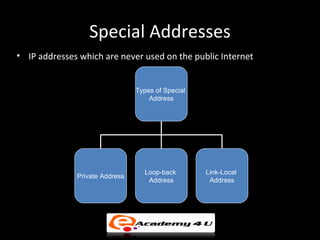
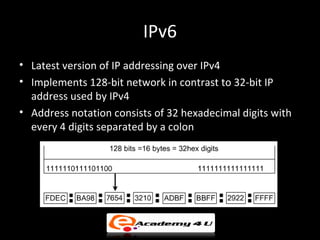
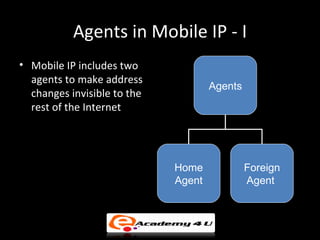
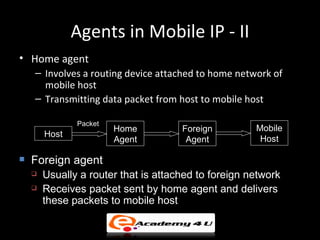
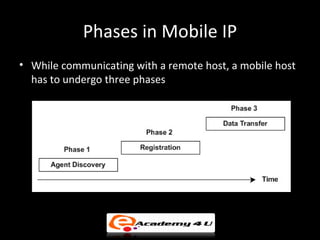
IP addressing provides a unique identifier for devices on a network. There are two main types - static and dynamic. IP addresses are 32-bit numbers divided into network and host portions. Classes A, B, and C determine the portions. Subnetting and CIDR allow flexible allocation. Special addresses like private and link-local are never used publicly. IPv6 uses 128-bit addressing. Tools like ping, tracert, and pathping test network connectivity. Mobile IP uses home and care-of addresses to maintain connectivity as devices move between networks, with home and foreign agents facilitating address changes. Inefficiency can occur via double crossing or triangle routing.