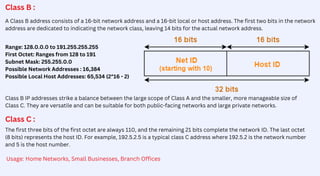
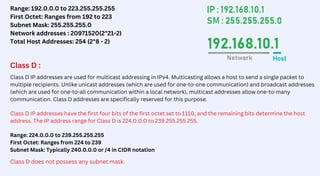
The document explains IP addresses, their classes, and subnetting. It details the two main types of IP addresses, IPv4 and IPv6, and outlines the importance of subnetting for network efficiency and security. Additionally, it categorizes IP addresses into classes A, B, C, D, and E, explaining their characteristics and typical usage scenarios.