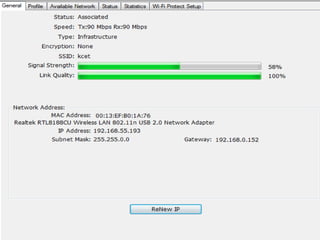
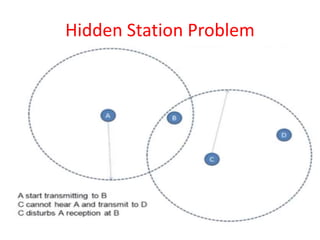
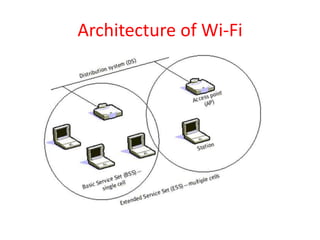
Wi-Fi allows devices to connect to the internet wirelessly using radio waves. It provides data transfer rates up to 600 Mbps within a coverage distance of about 100 meters. Multiple devices can connect to a Wi-Fi network through a router, unlike Bluetooth which only supports 7 devices. Wi-Fi networks use SSIDs to identify the network and access points to connect wireless devices to wired networks. Common standards include 802.11a, b, g, and n which provide higher data rates and backward compatibility. Security measures for Wi-Fi include MAC address filtering and WEP encryption.