There are several types of IP addresses including public, private, static, and dynamic addresses. Public IP addresses are associated with an entire network while private IP addresses uniquely identify devices within a home network. Static IP addresses never change while dynamic IP addresses are temporary and change each time a device connects.
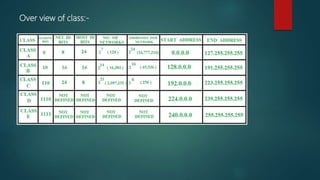
IP addresses are also classified based on version (IPv4 or IPv6), address space (A, B, C, D, E classes), and function (unicast, multicast, broadcast, anycast). Key differences between classes include the number of bits used for network vs. host identification and the total number of possible networks. Specific rules govern how network and host IDs are assigned to ensure unique identification of devices.