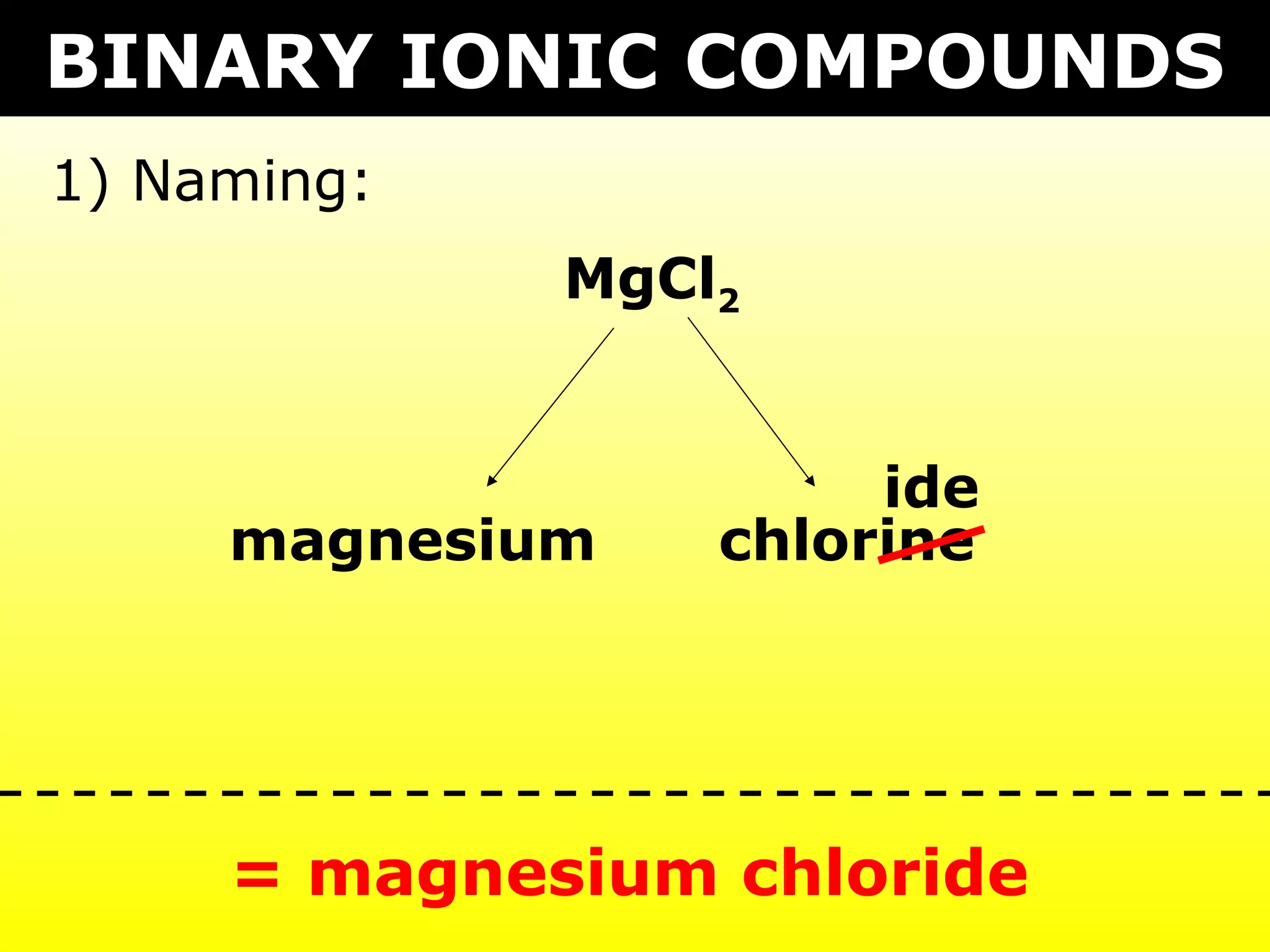
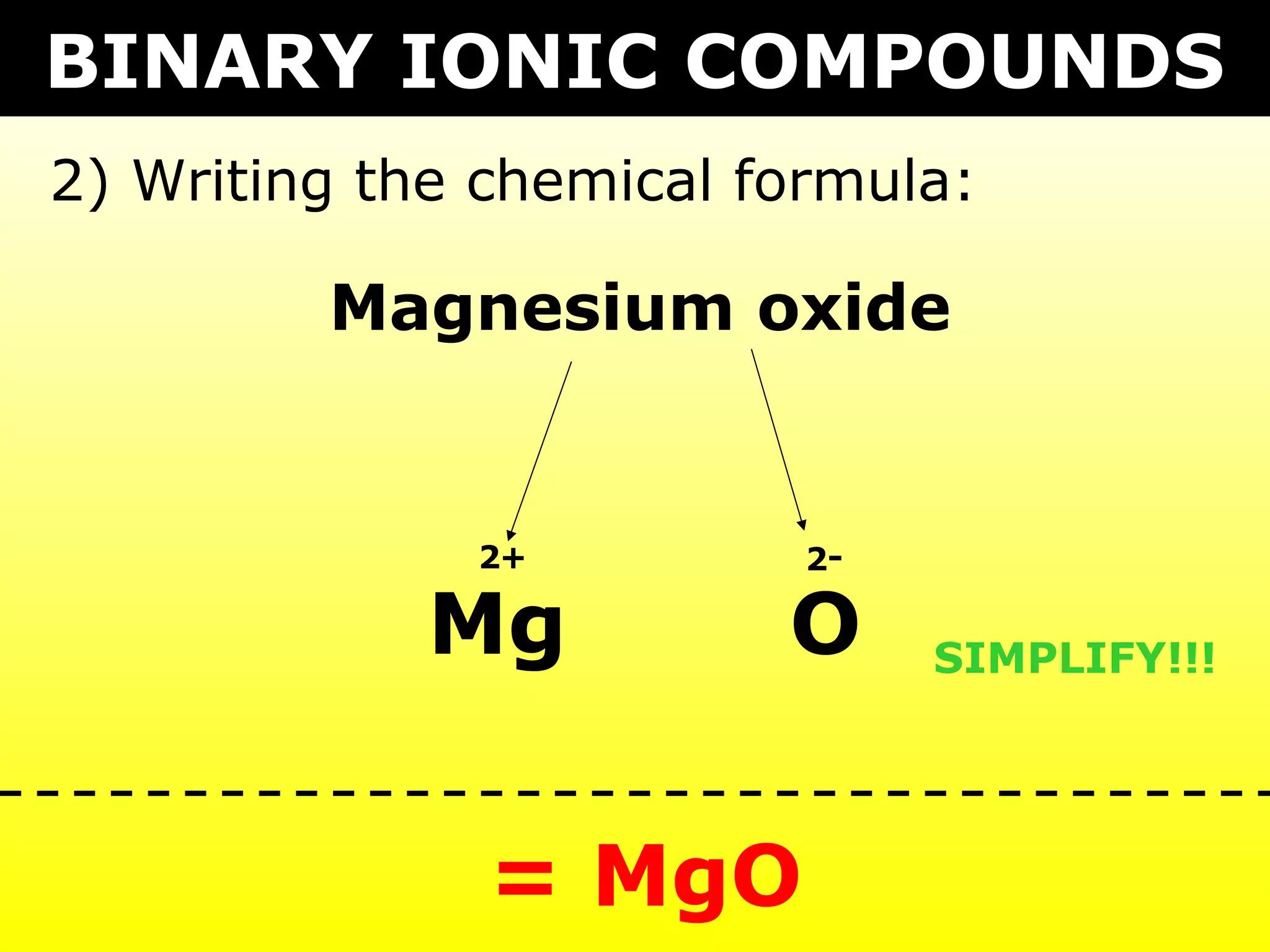
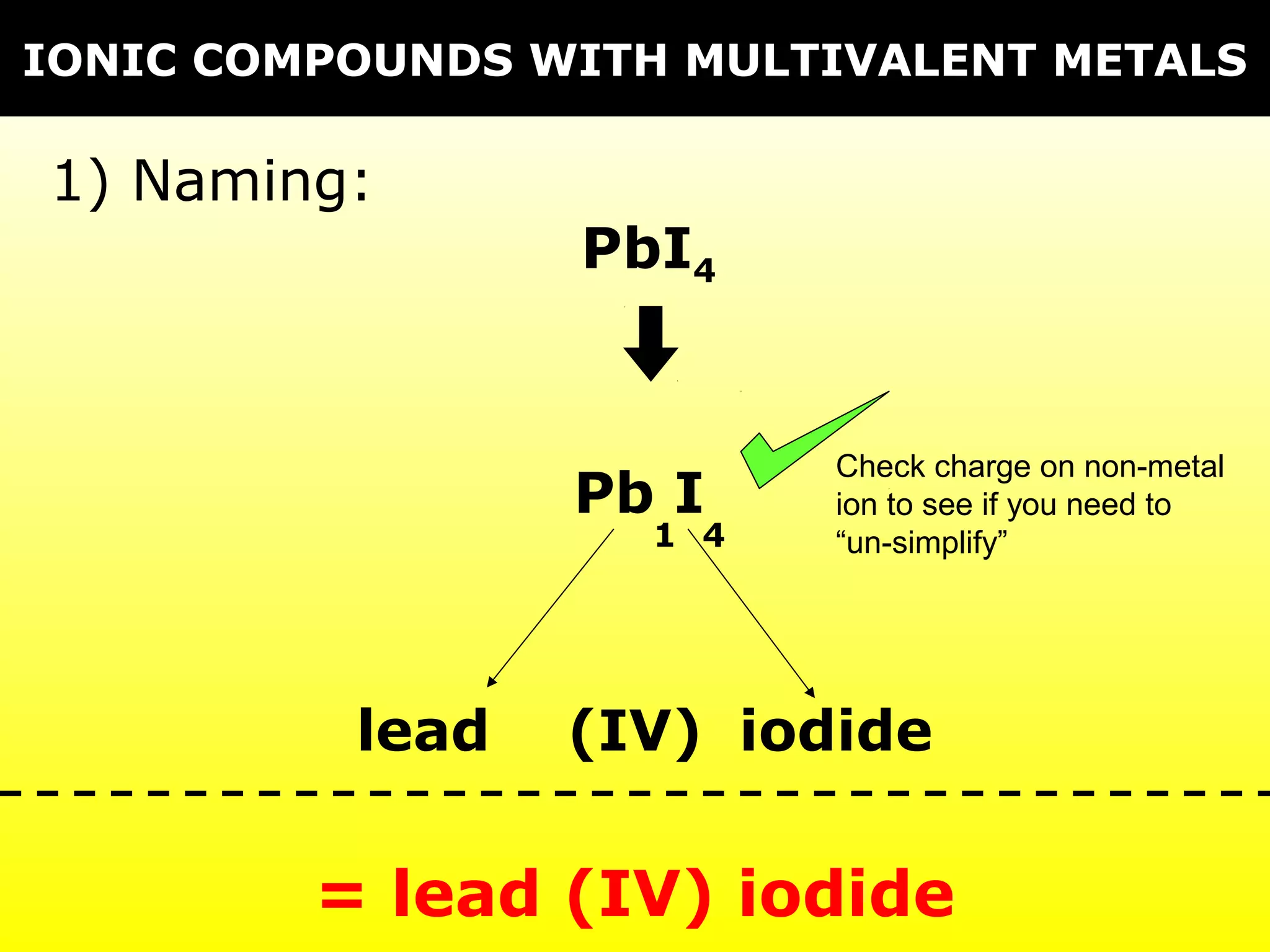
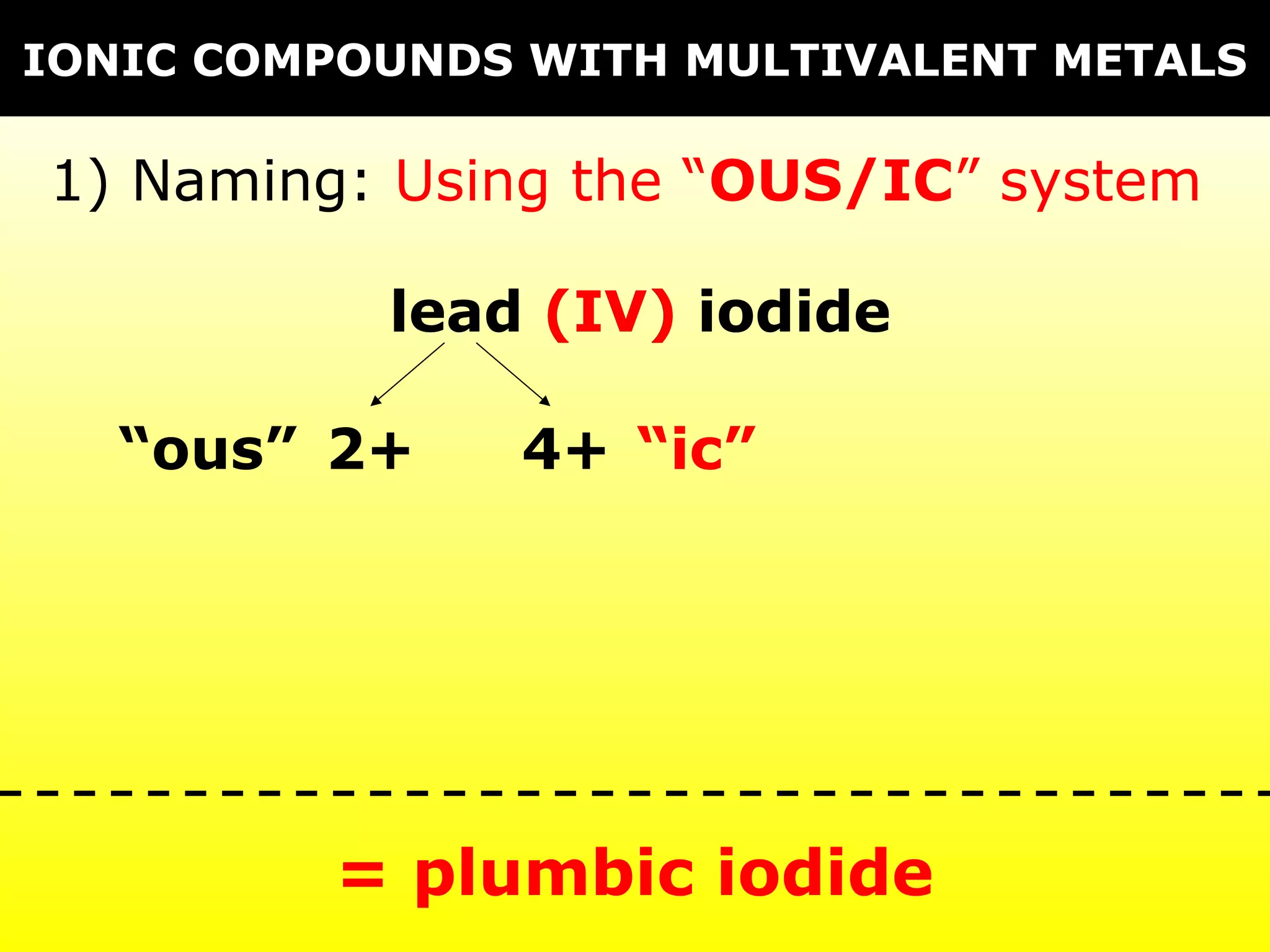
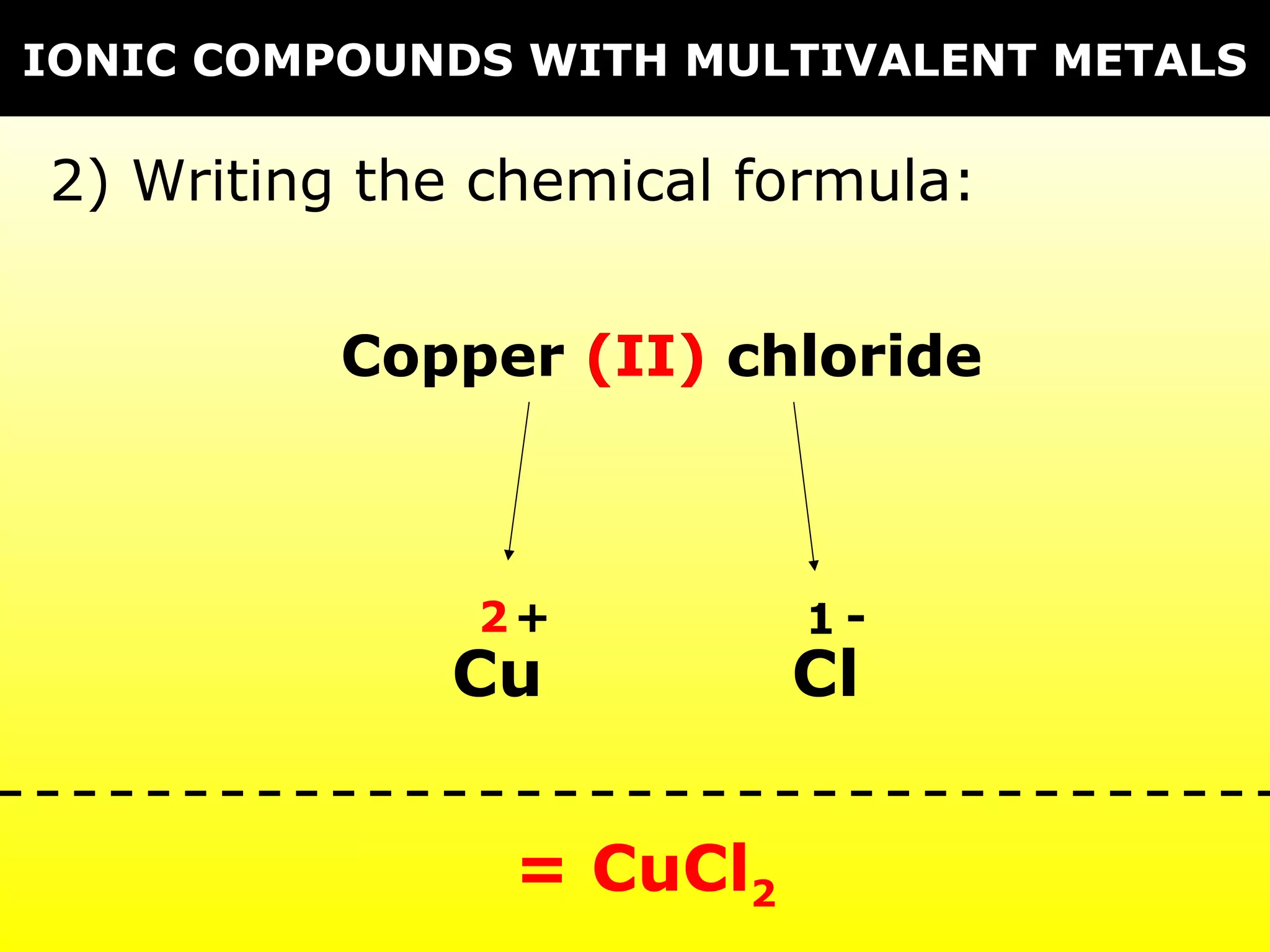
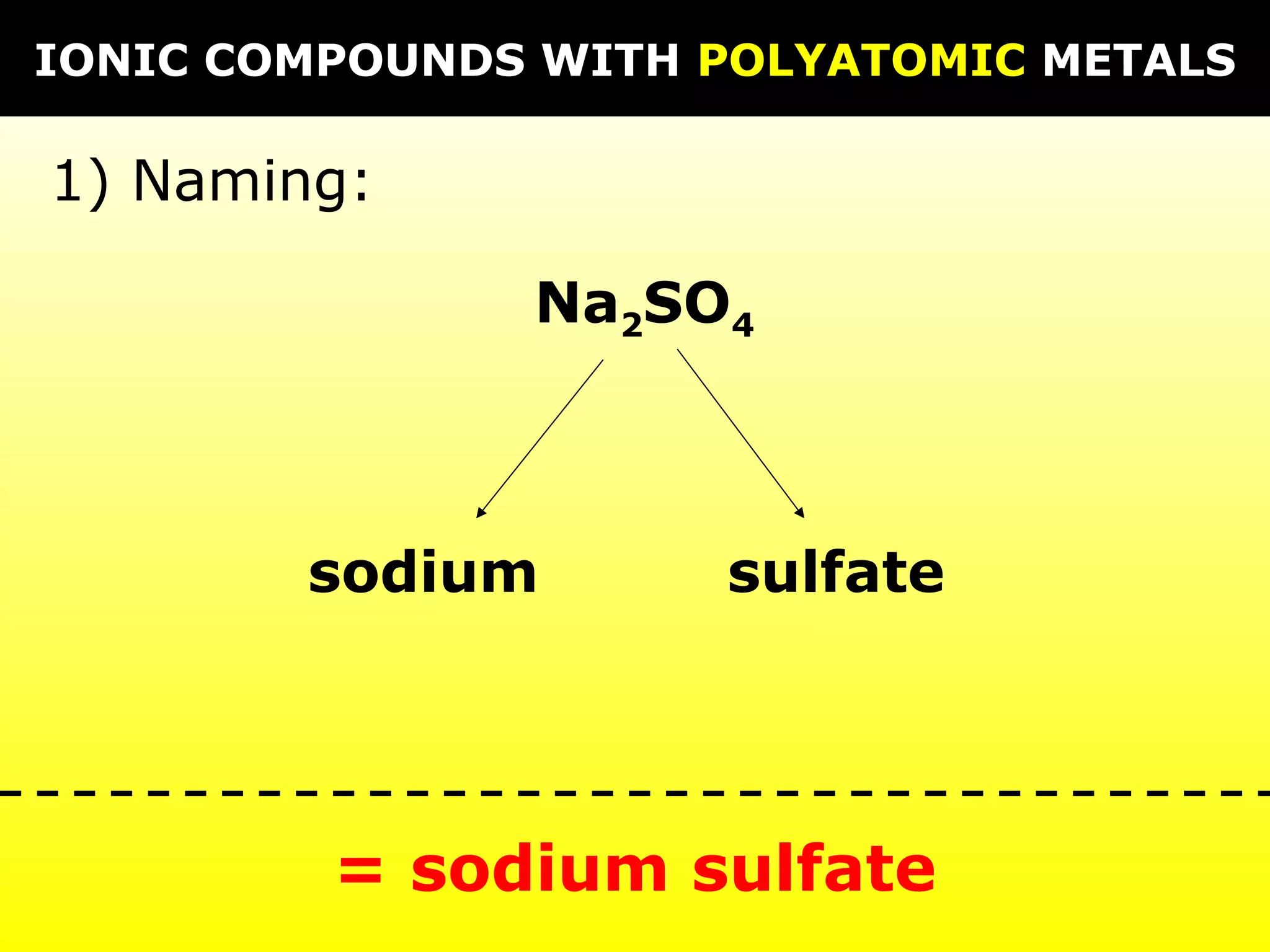
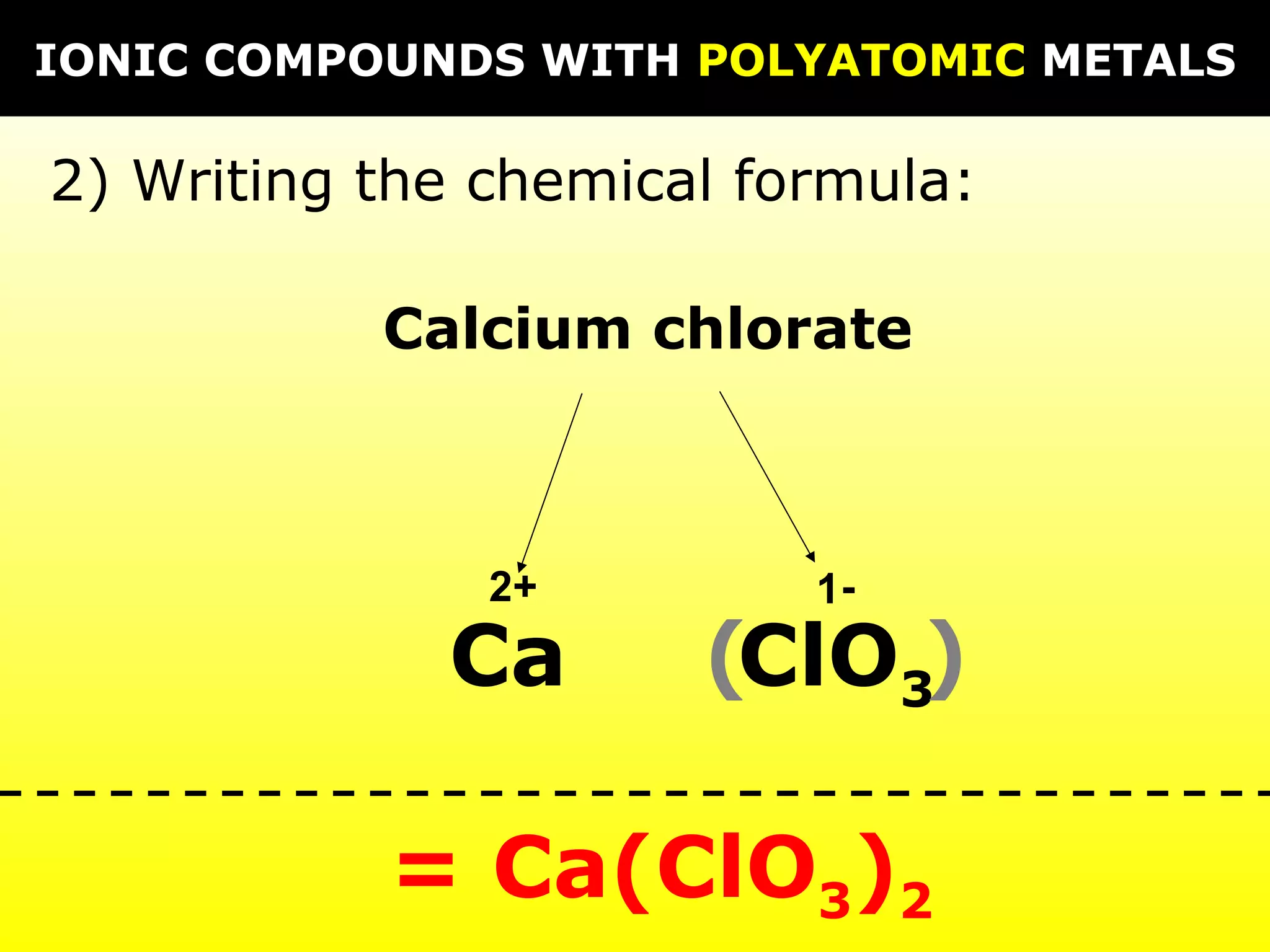
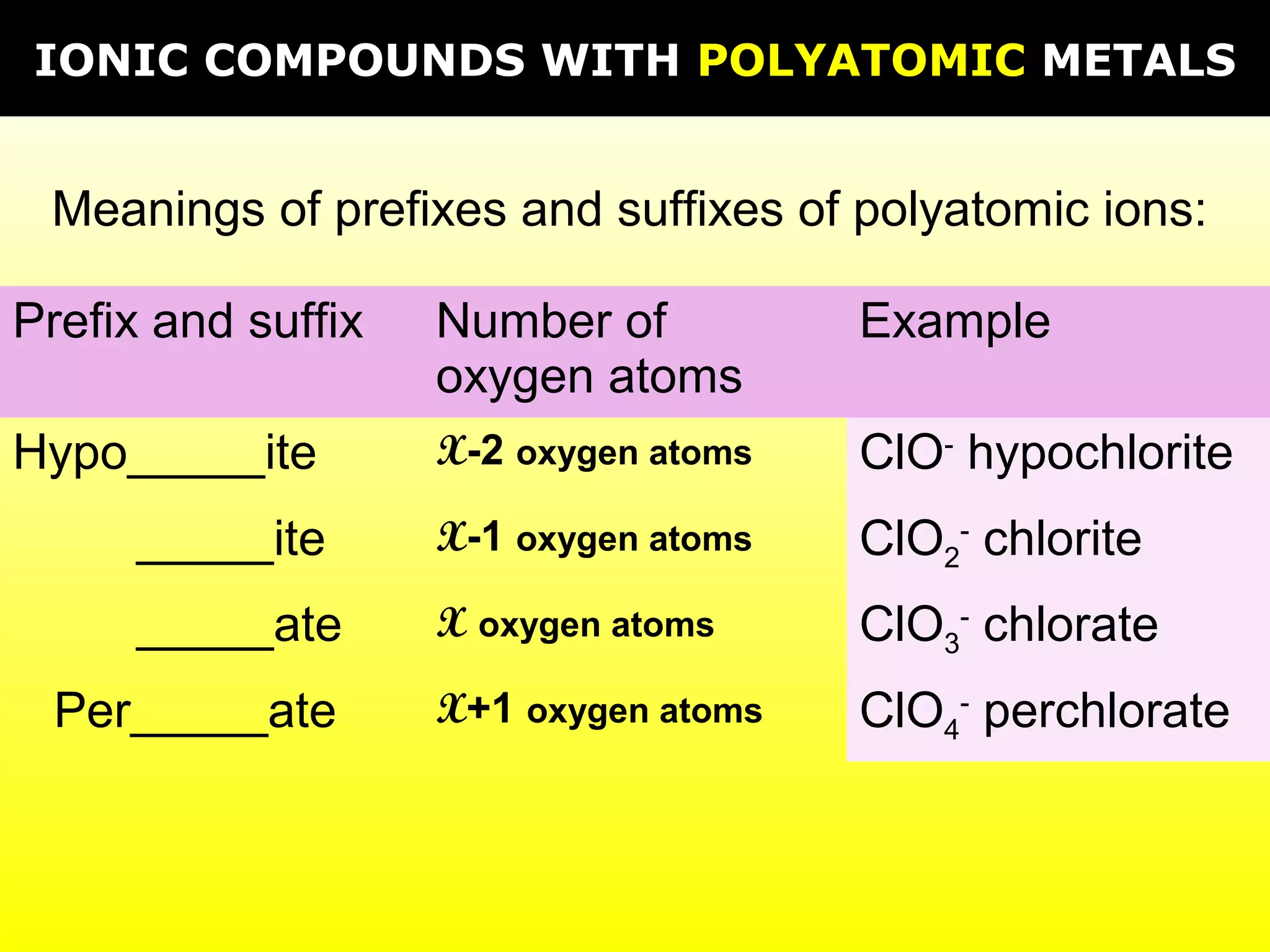
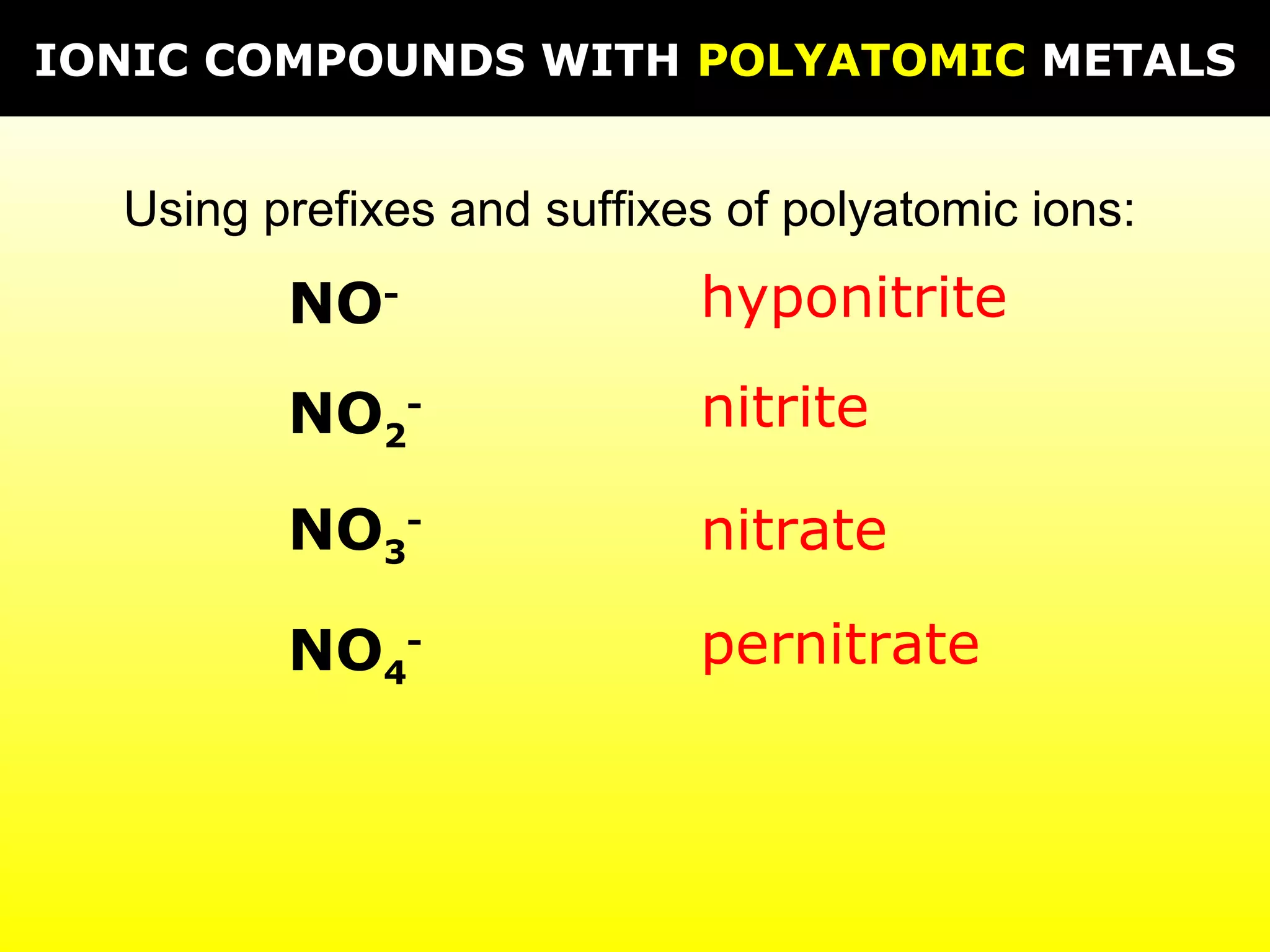
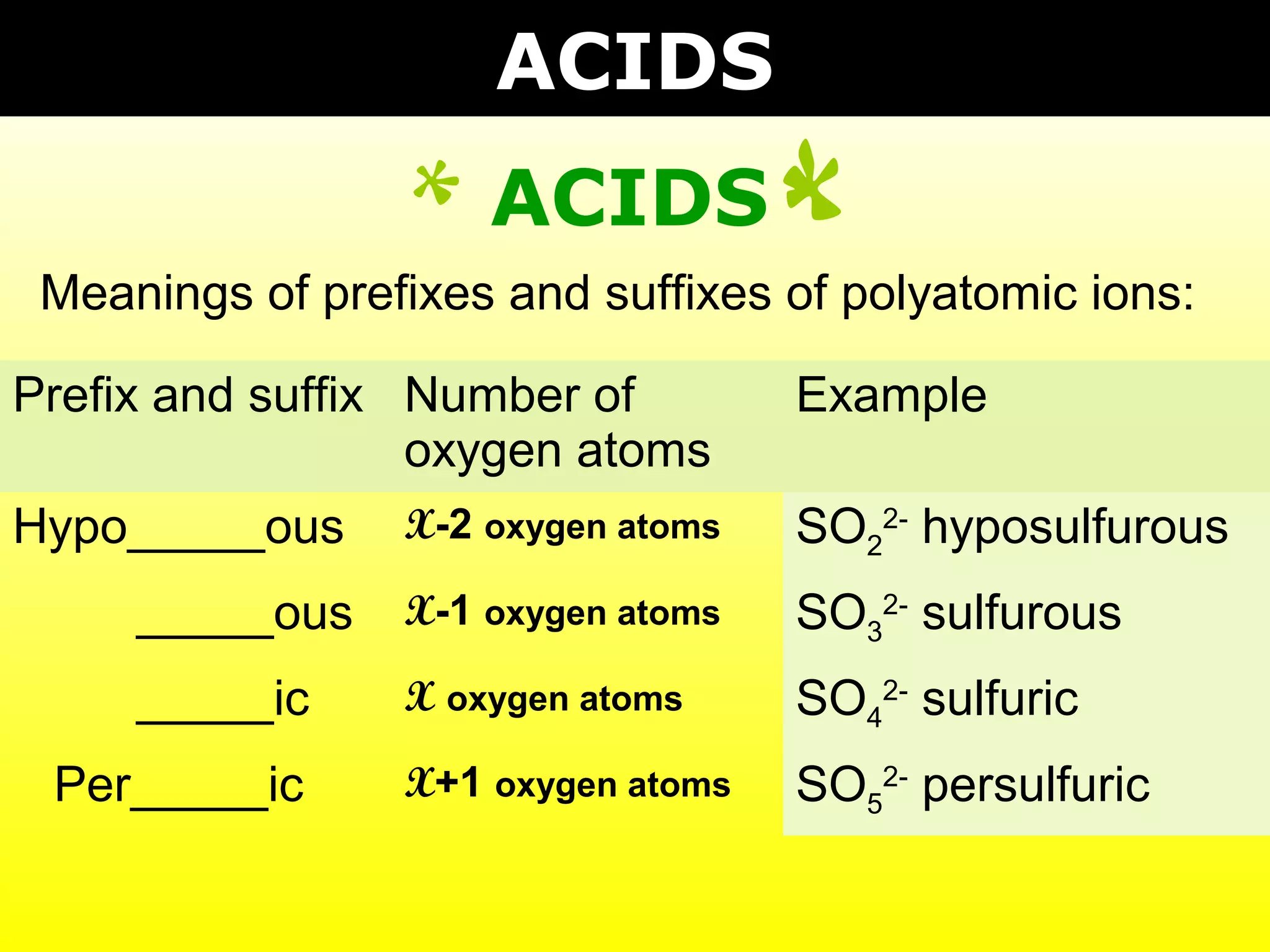
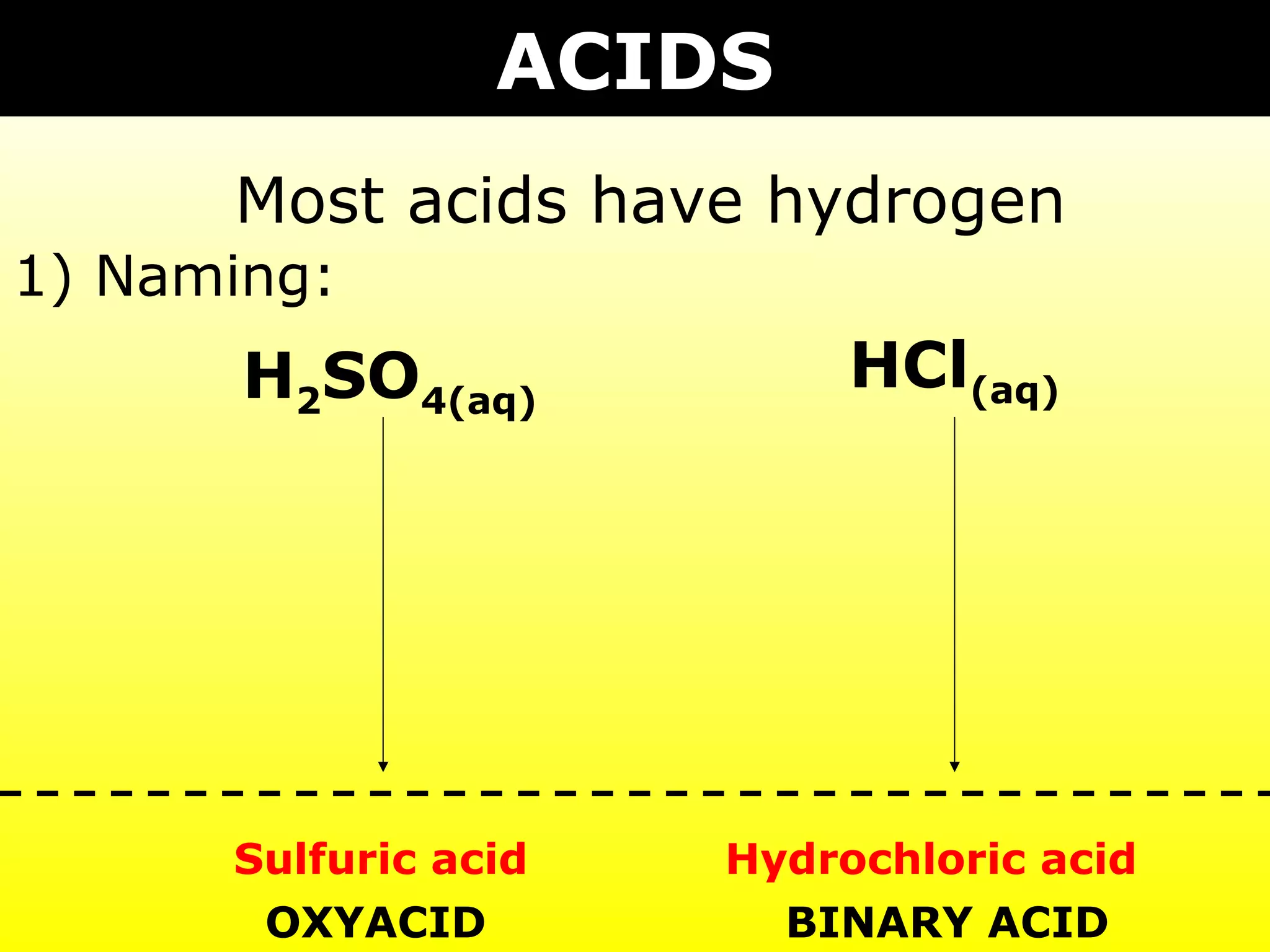
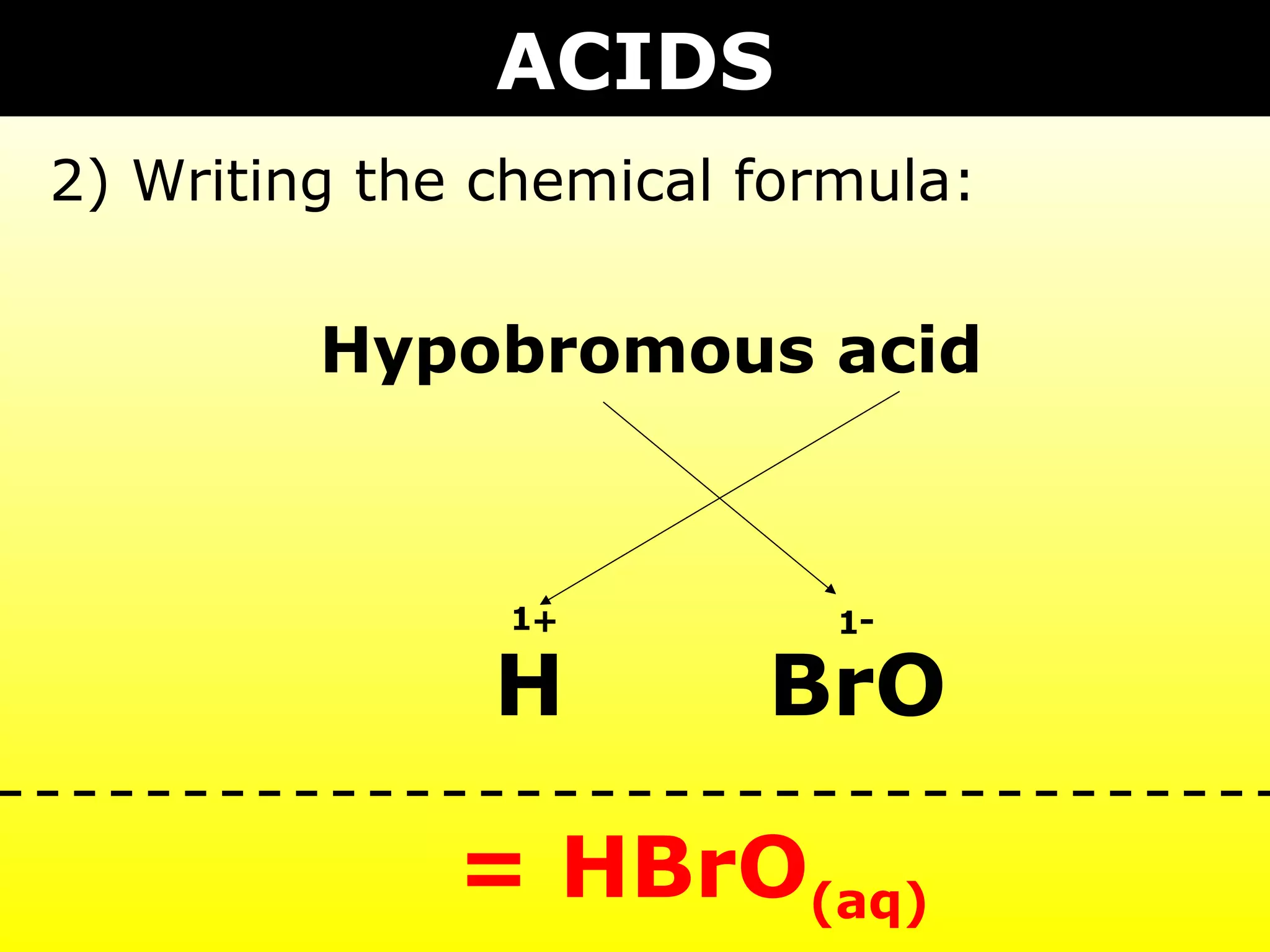
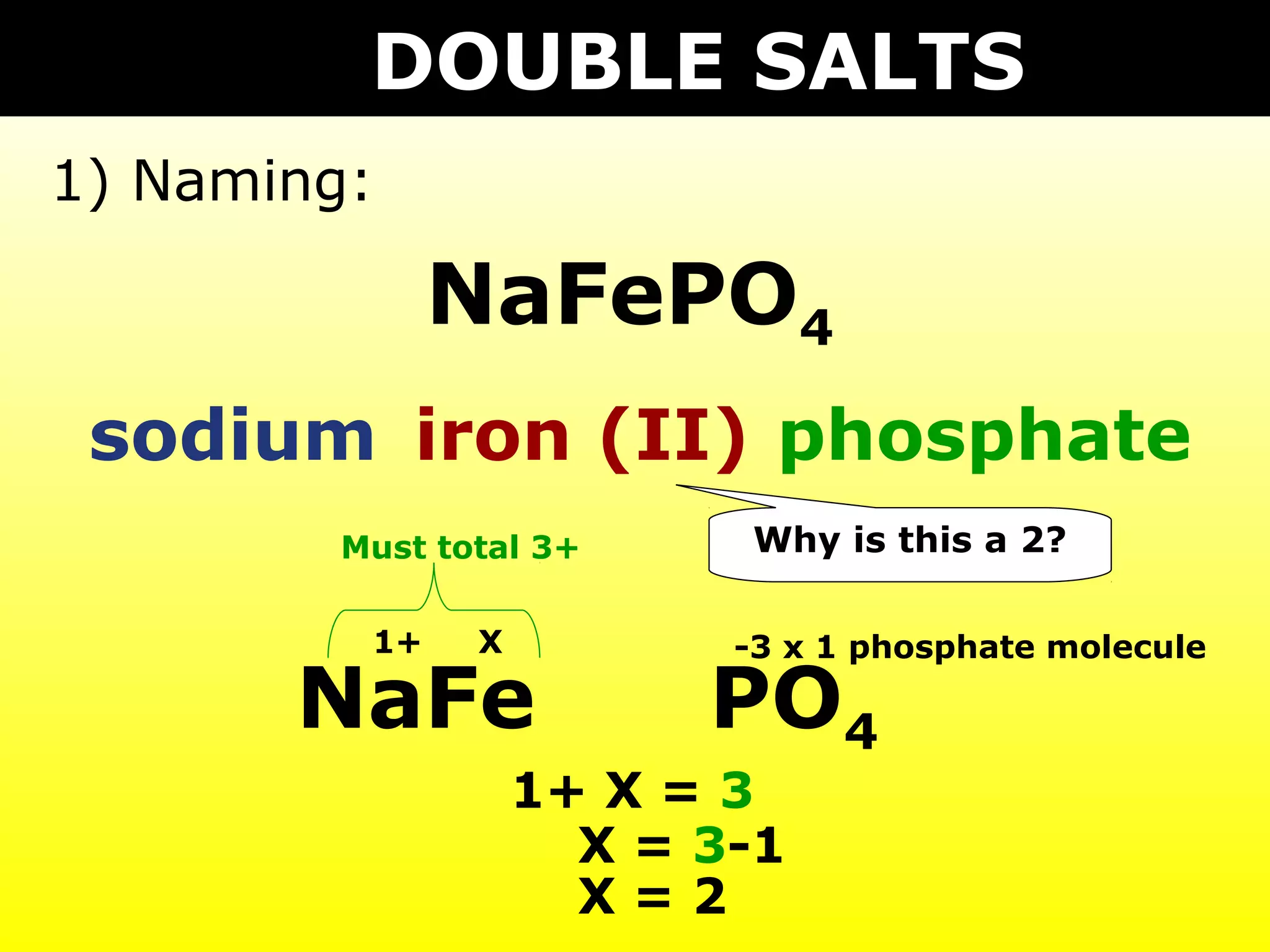
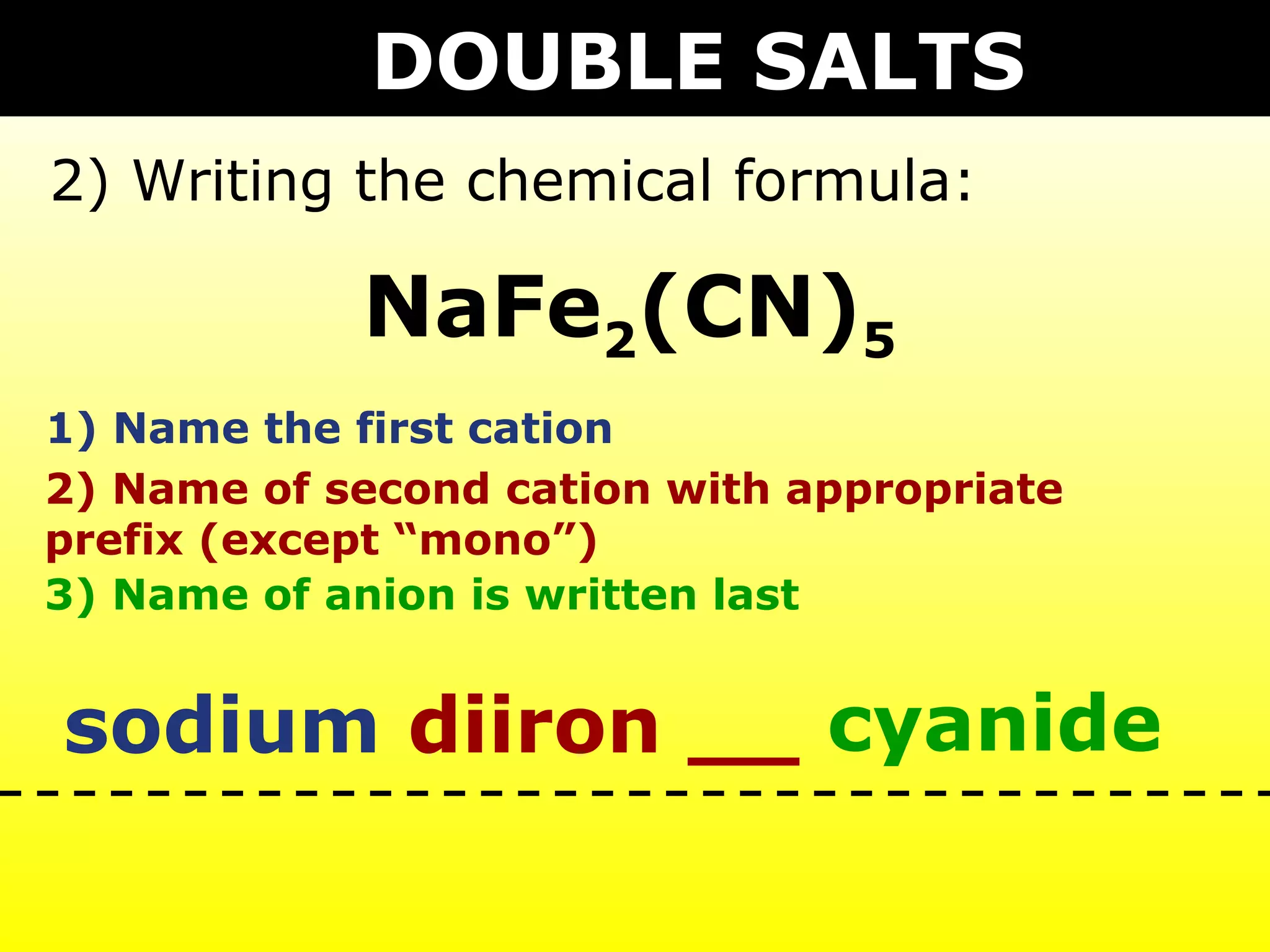
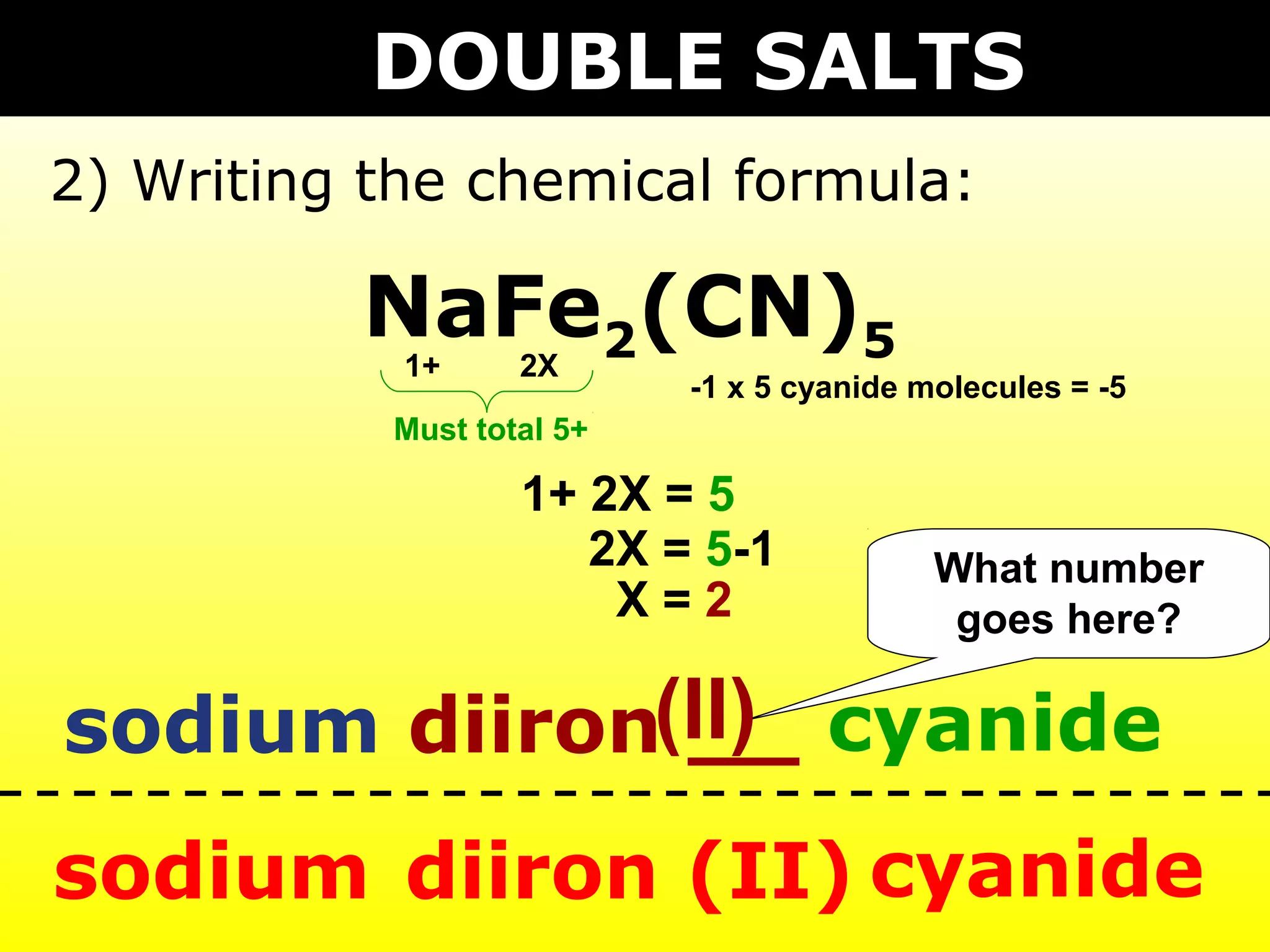
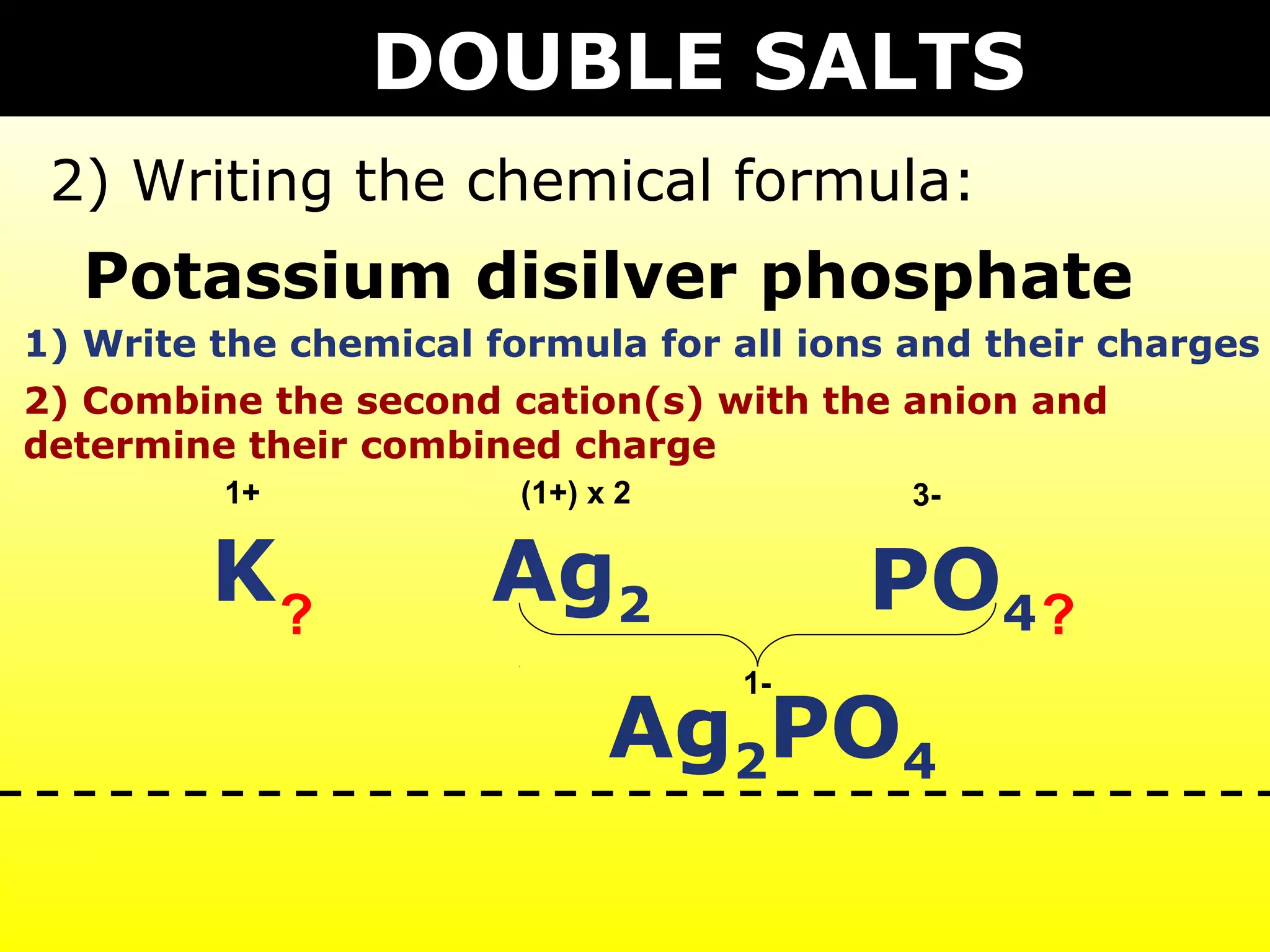
The document provides information on naming and writing formulas for different types of compounds including:
1) Binary ionic compounds, ionic compounds with multivalent metals, ionic compounds with polyatomic ions, acids, hydrated salts, acid salts, and double salts.
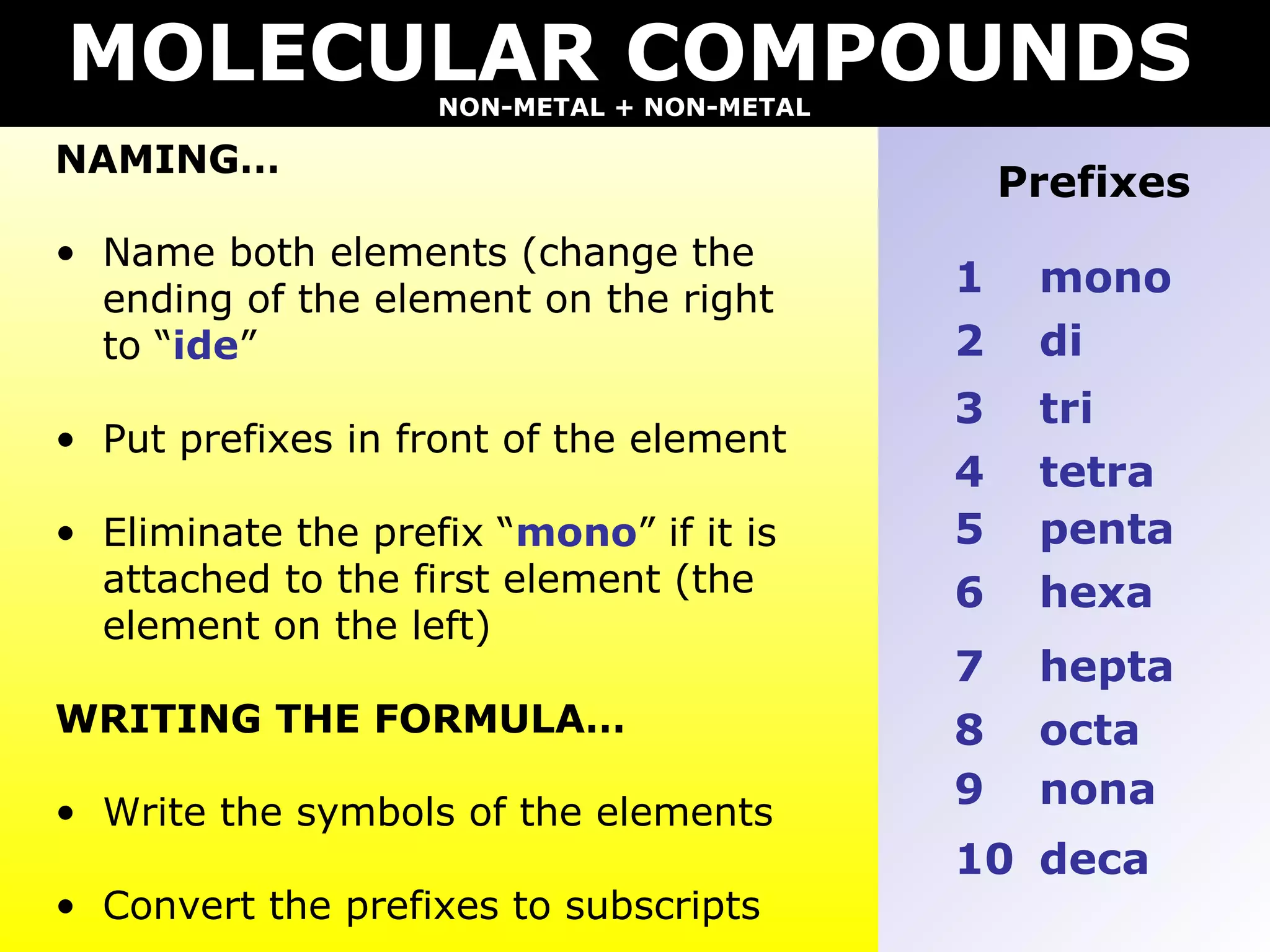
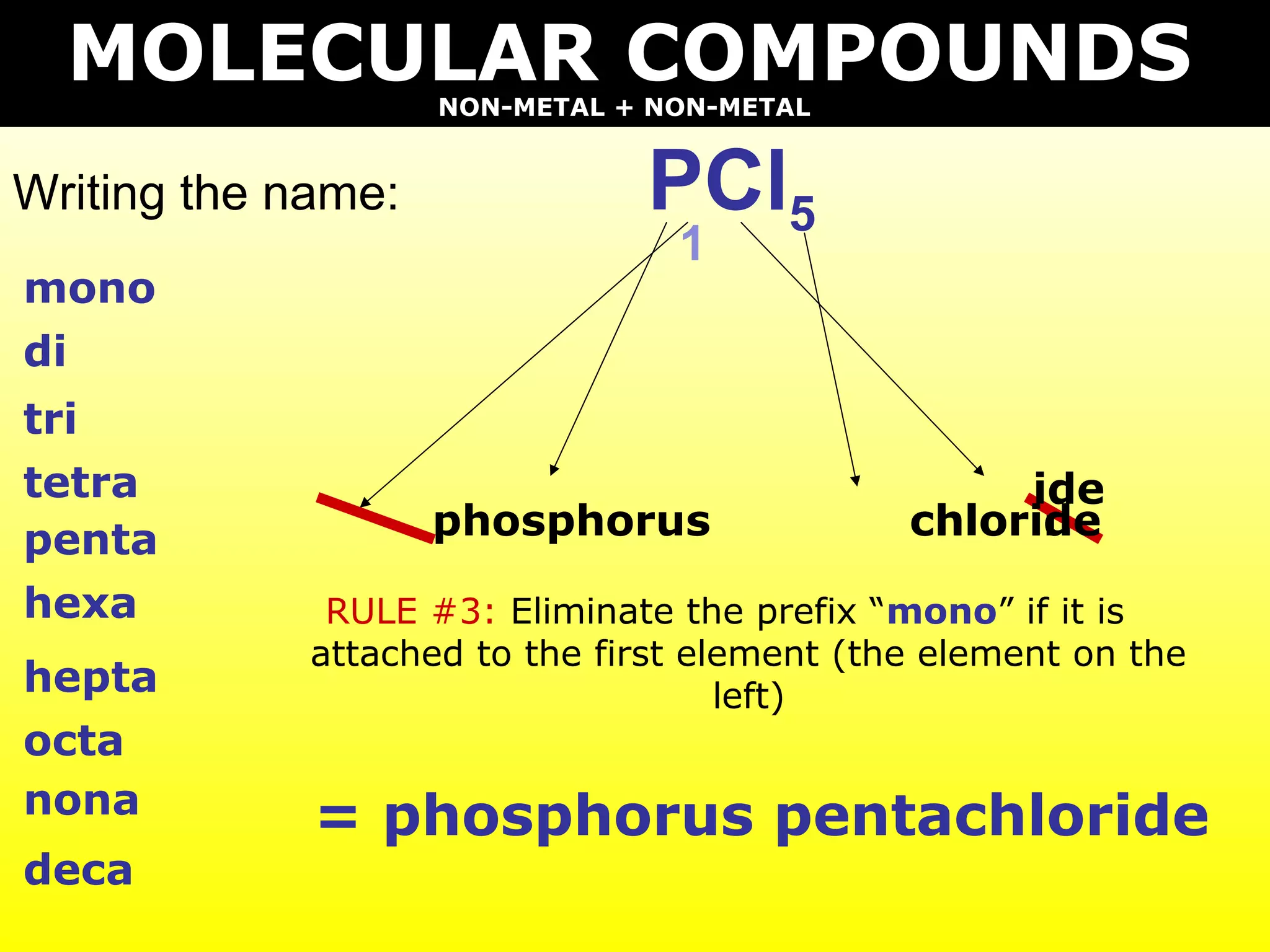
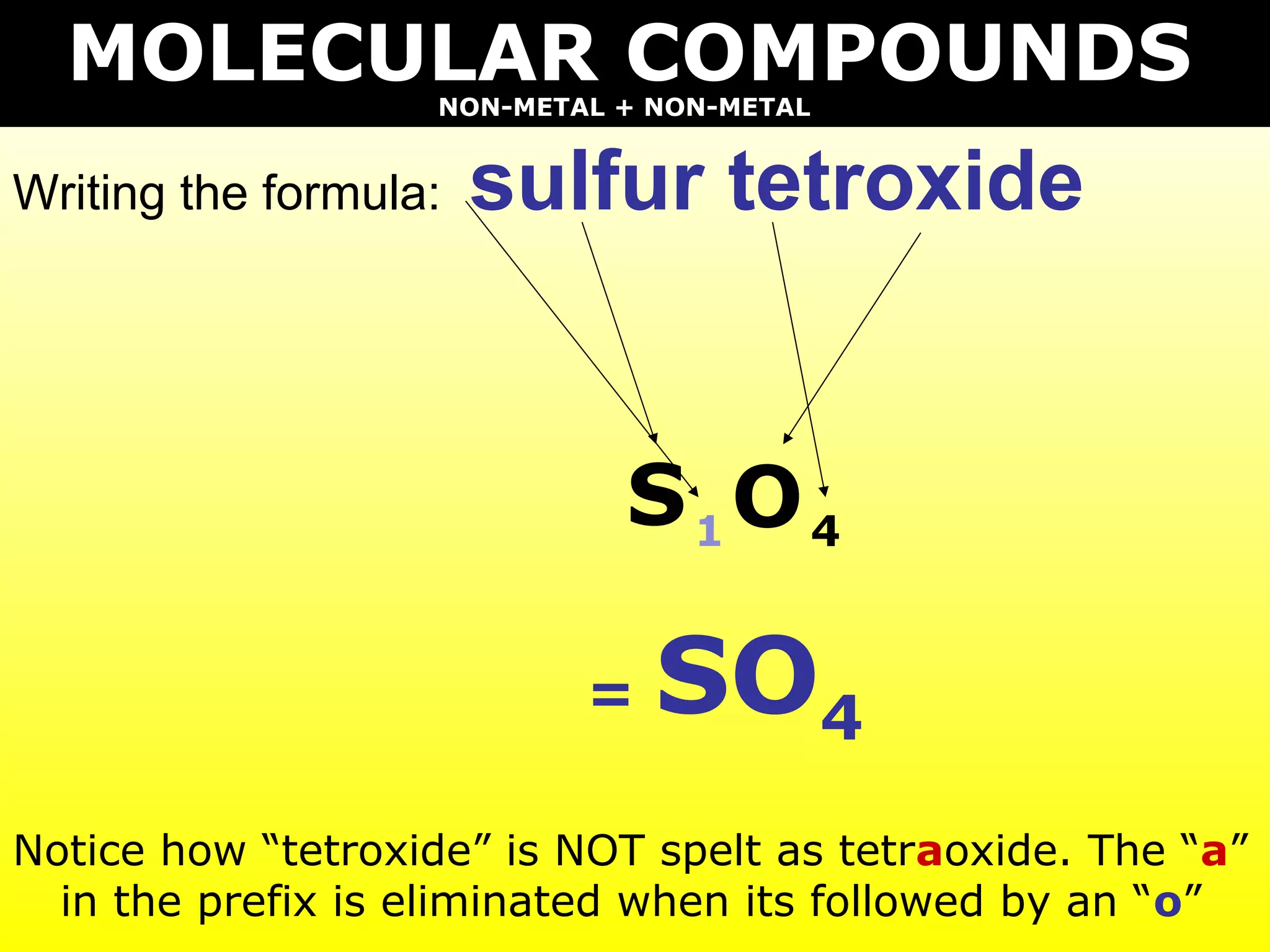
2) Molecular compounds consisting of non-metals are also covered, with prefixes converted to subscripts in formulas.
3) Key concepts include identifying cation/anion charges, recognizing polyatomic ions, and applying naming conventions based on compound type.