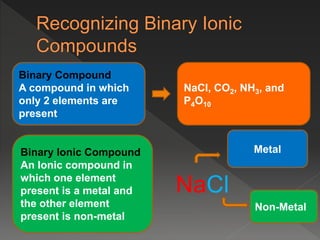
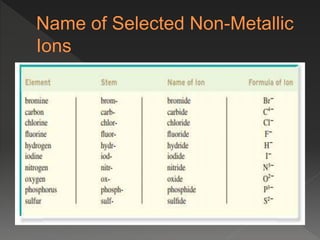
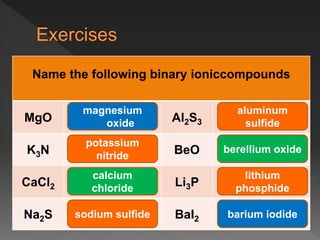
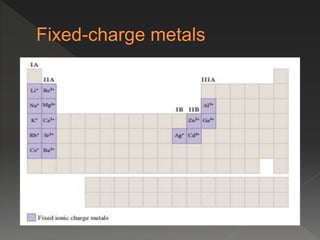
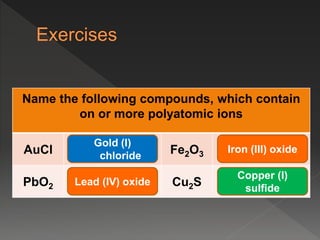
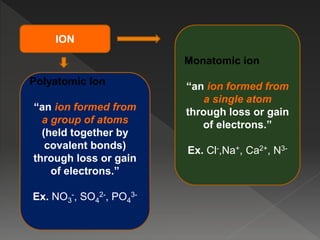
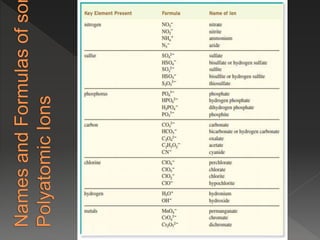
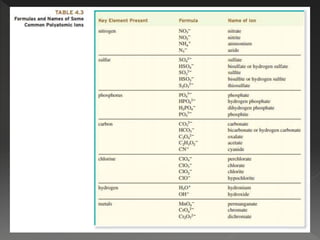
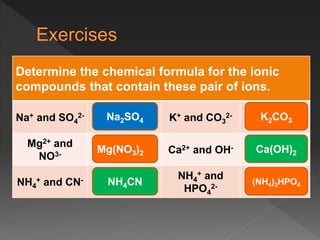
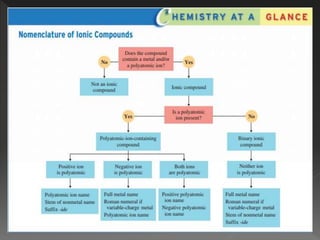
This document provides information on binary compounds and ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions. It defines binary compounds as those containing only two elements and ionic binary compounds as those where one element is a metal and the other is a non-metal. Rules are provided for naming ionic compounds containing metals and non-metals or polyatomic ions. Key points include that polyatomic ions are charged groups that don't occur alone and ionic compounds contain positive and negative ions to be neutral overall. Formulas show how to write names and formulas for ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions.