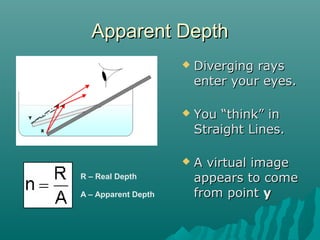
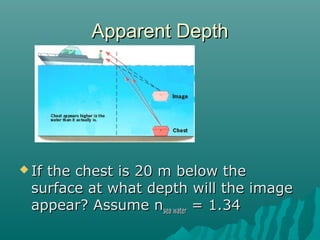
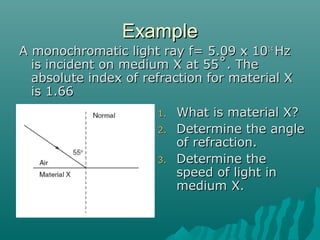
This document discusses various topics relating to waves and reflection and refraction of light, including:
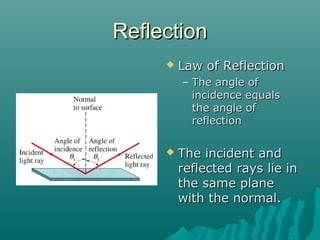
- The law of reflection, which states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
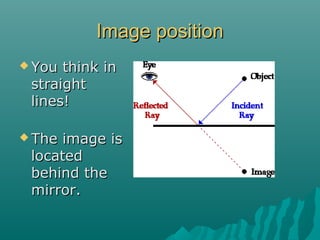
- Reflection can be specular (mirror-like) or diffuse (scattered), depending on whether the surface is smooth or rough.
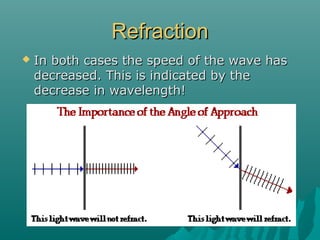
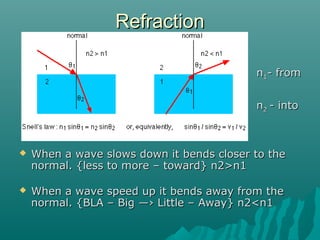
- Refraction occurs when a wave changes speed as it passes from one medium to another, causing it to change direction. The direction of bending depends on whether the wave speeds up or slows down.
- Snell's law relates the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction to the refractive indices of the two media. The refractive index depends on the frequency