This document discusses key concepts related to the refraction of light, including:
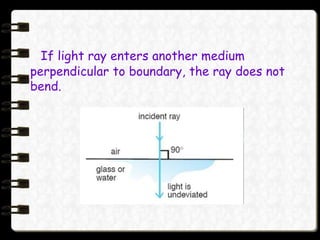
- Refraction occurs when light passes from one medium to another, changing direction as it enters the new medium. The degree of bending depends on the optical density of the materials.
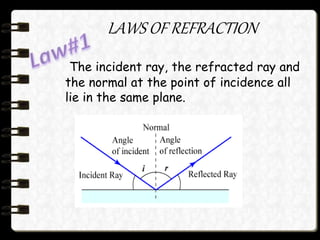
- Two laws govern refraction: Snell's law states that the ratio of sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is a constant; and the law of refraction states that the incident ray, refracted ray, and normal all lie in the same plane.
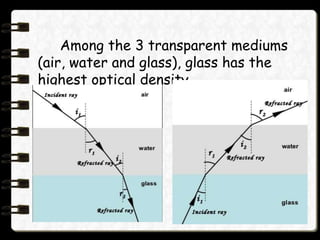
- The refractive index is a measure of how much light bends when entering a material, and depends on the material's optical density - the higher the density, the greater the refractive index