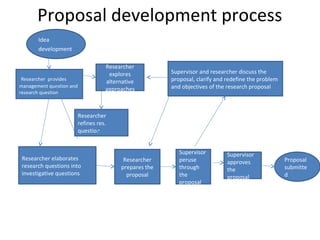
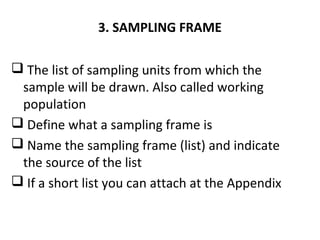
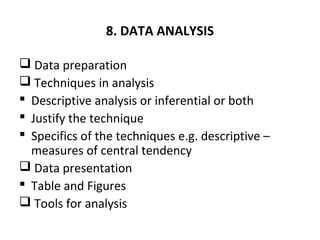
This document provides an overview of research methods and the research proposal process. It discusses key components of a research proposal including selecting a topic, developing research questions and objectives, reviewing relevant literature, and describing the proposed methodology. The methodology section should address the research design, population, sampling technique, data collection instruments, and data analysis plan. Developing a strong proposal is important to obtain approval for the study and guide the research process.
















































![REFERENCES cont.
• Corporate authors – The name of corporate authors are usually spelled out each
time they appear in the text citation or abbreviated thereafter.
• e.g ….[National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), 2011], or [Kenya Commercial
Bank, (KCB), 2008], subsequent appearance, use (NIMH, 2000); KCB (1999)
• Reference List
- Reference cited in the text – It must appear in the reference list, conversely, each
entry in the reference list must be cited in the text. The author must make certain
that each source referenced appears in both places and that the citation and
references list entry are identical. Failure to do so can result in an expensive
change after the research project report has been bound.
- Reference List Format and order – The reference list format should provide the
author’s last name and initials, the year of publication, the title, the city, and
publisher in the sequence for a text book. For a Journal article; the author’s last
name and initials, the year of publication, the title of article, the Journal name,
Volume No., the first and last page No.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2ndlecturesresearch-150201020331-conversion-gate02/85/RESEARCH-METHODS-LESSON-2-52-320.jpg)
