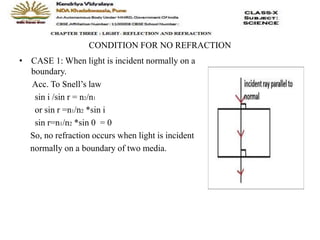
The document discusses the refraction of light, including concepts such as absolute and relative refractive indices, the cause and laws of refraction, and the behavior of light when transitioning between different media. It explains the angles involved in refraction, conditions for no refraction, and specifics of refraction through a glass slab, including lateral displacement. The key principles highlight how light bends at the boundary of two media based on their respective optical densities.