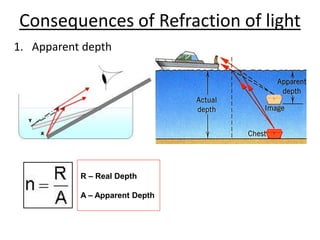
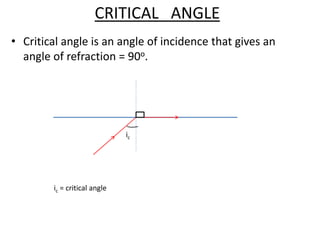
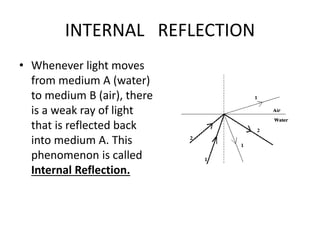
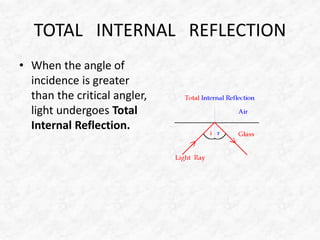
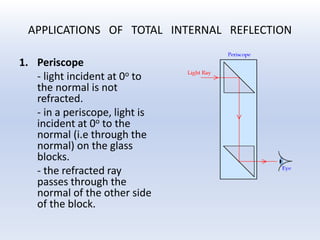
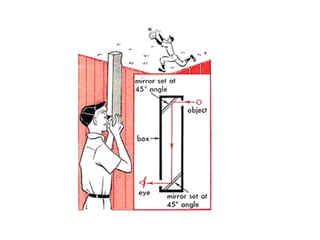
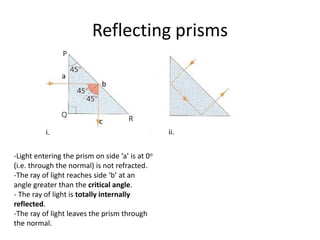
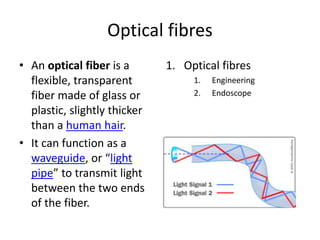
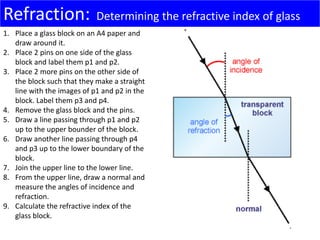
Light travels as waves and can undergo various phenomena including reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference. Reflection occurs when light hits a surface, causing it to bounce off at the same angle. Refraction happens when light passes from one medium to another of different density, causing it to change speed and bend. This bending is described by Snell's law. Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from a denser to less dense medium at an angle greater than the critical angle, causing it to reflect back inside the denser medium. This principle is applied in devices like optical fibers.


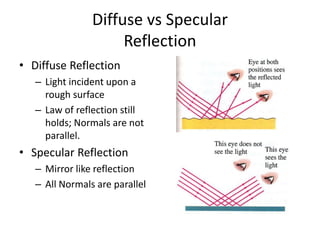
![Reflection
• Law of Reflection
– The angle of incidence
equals the angle of
reflection [ <i = < r ]
- The incident and
reflected rays and the
normal lie in the same
plane.
Reflection: the bouncing back of light as it strikes a barrier (mirror).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150109064903-conversion-gate01/85/3-2-form-4-light-4-320.jpg)




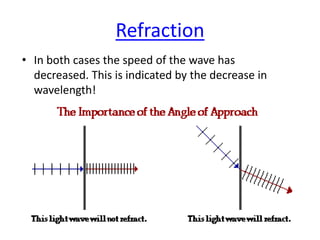
![Refraction : Bending light
The speed of light waves depends on the material they are travelling
through.
If the light waves enter a different material [e.g. from glass into air]
the speed changes.
This causes the light to bend [or refract].
Air = Fastest Diamond = slowestGlass = slower
Glass
Refraction: the bending of light as it moves from one medium to another due to
change in wave speed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150109064903-conversion-gate01/85/3-2-form-4-light-12-320.jpg)
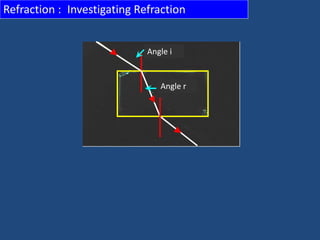



![Refraction : Summary
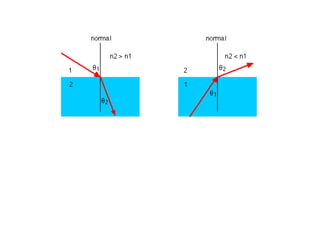
When light bends this is called refraction.
Refraction happens because the light changes speed [or
velocity].
When light enters a more dense medium [e.g. glass], it
bends towards the normal.
When light enters a less dense medium [e.g. air], it
bends away from the normal.
If the incident ray hits a surface at 0º, no
refraction occurs.
Remember that the angle of reflection [r] and angle of
refraction [r] have the same symbol.
In reflection, <I = <r
In refraction, <I <r](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-150109064903-conversion-gate01/85/3-2-form-4-light-21-320.jpg)