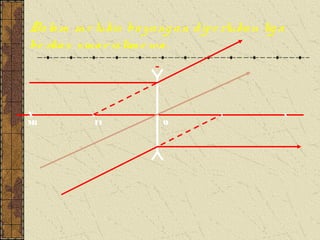
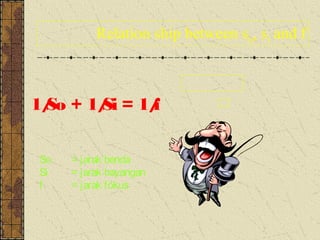
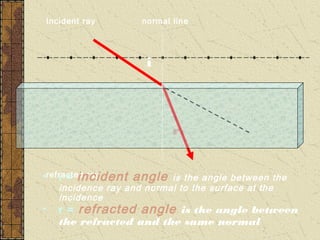
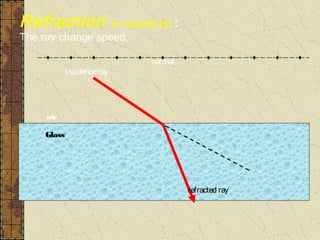
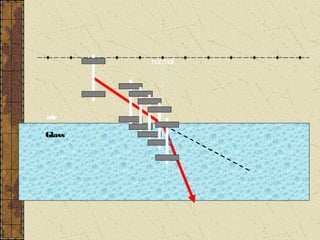
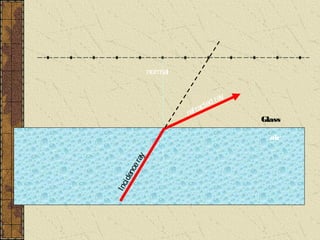
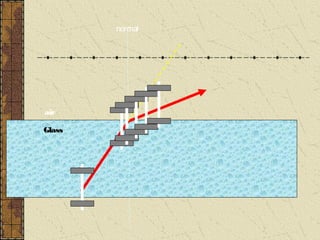
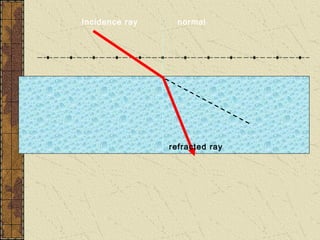
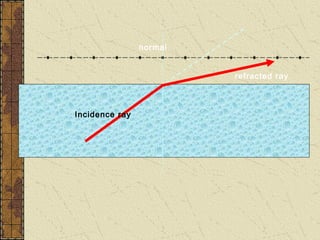
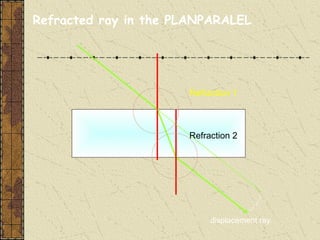
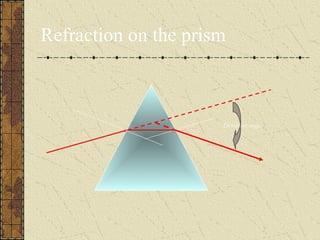
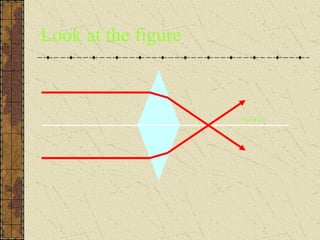
1. Refraction is the bending of light when passing from one medium to another. It occurs because the speed of light changes depending on the medium.
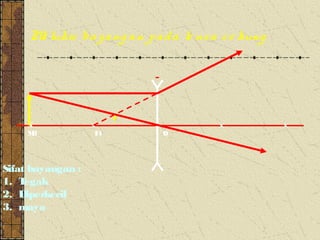
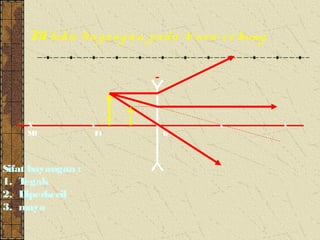
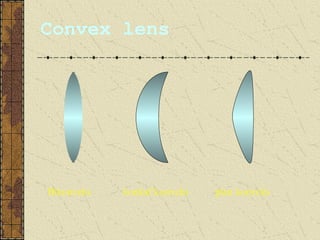
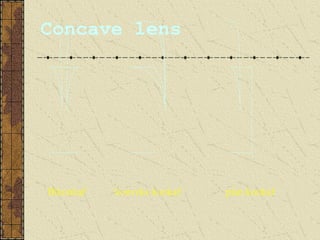
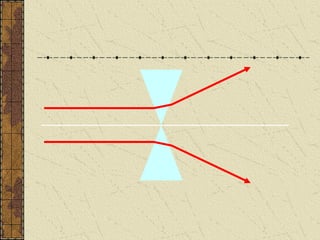
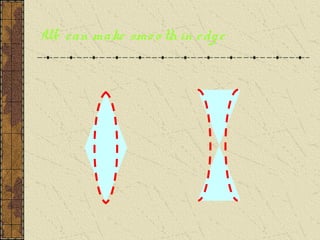
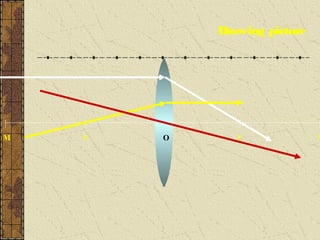
2. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle and cause light rays to converge, resulting in a real, inverted, and magnified image. Concave lenses are thinner in the middle and cause light rays to diverge, resulting in a virtual, upright, and minified image.
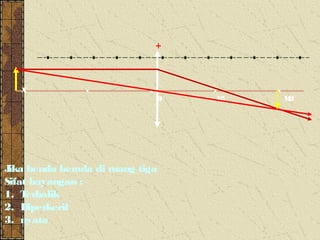
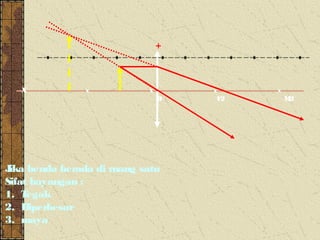
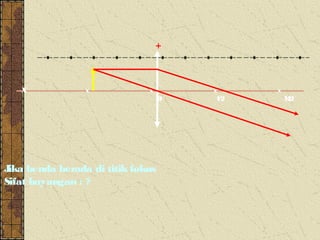
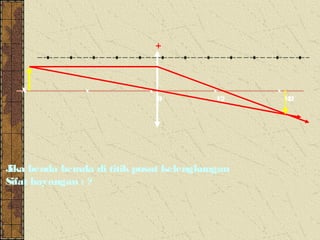
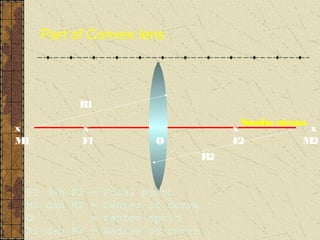
3. The focal length of a lens is the distance between the focal point and the center of the lens. Lens properties like image type, orientation, size, and position depend on the location of the object relative to the focal points and center of the lens.













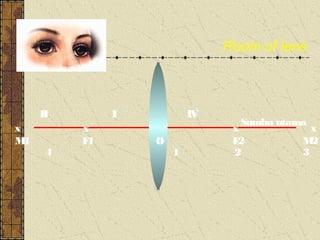
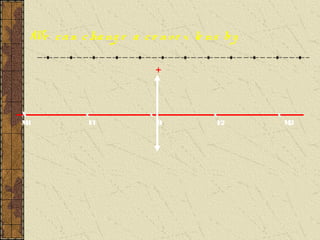
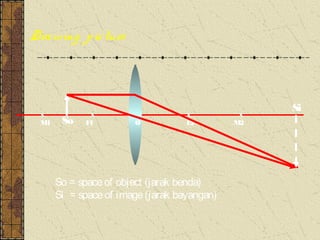
![Perbesaran bayangan (M)
Perbesarann bayangan
dapat dirumuskan
M = [Si/So] = h’/h](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lightrefractedray-120726025414-phpapp01/85/Refraction-of-Light-41-320.jpg)