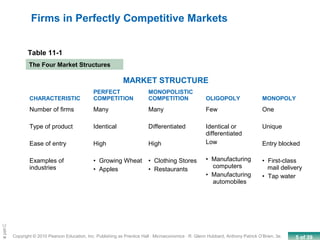
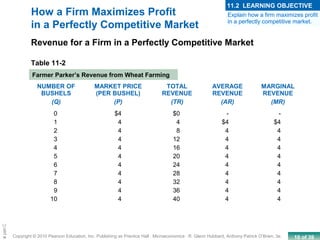
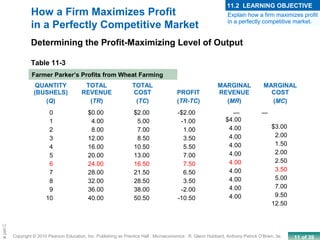
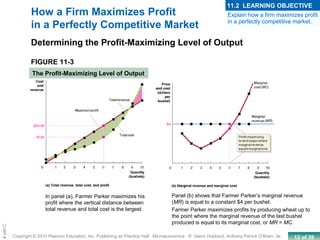
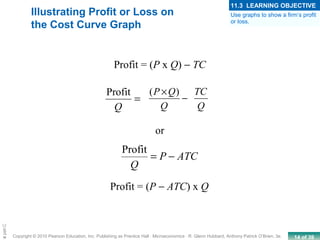
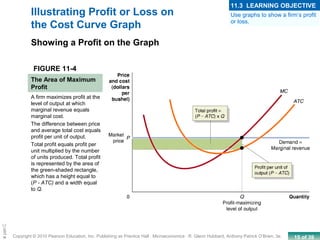
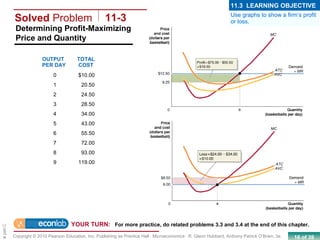
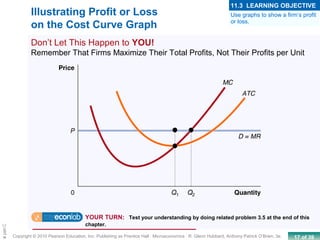
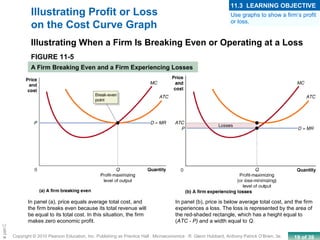
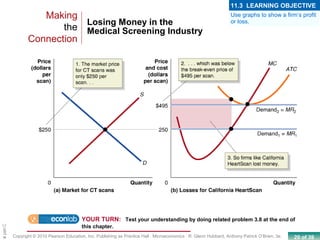
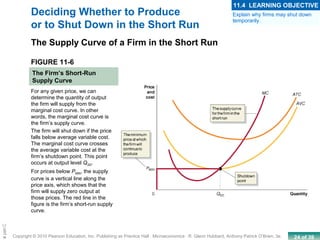
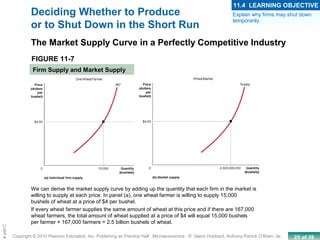
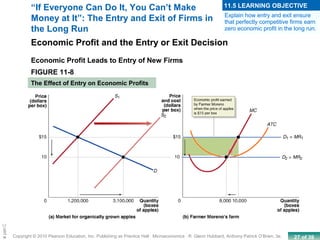
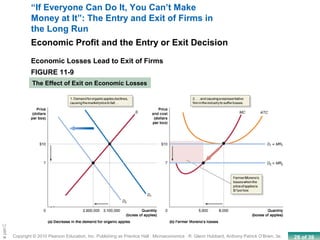
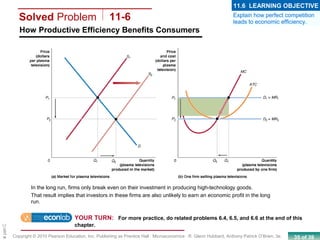
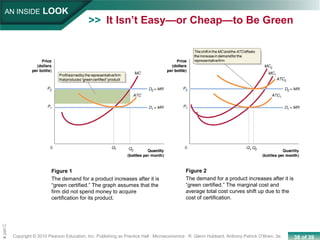
This chapter discusses the characteristics of perfect competition. A perfectly competitive market is defined as having many small firms, identical products, and free entry and exit. The document outlines the key features of perfect competition and how firms operate in this market structure. It explains that in perfect competition, each firm is a price taker and faces a horizontal demand curve. This means the firm can sell all it wants at the going market price but cannot affect the price. The chapter also discusses how a perfectly competitive firm determines its profit-maximizing level of output by producing where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.