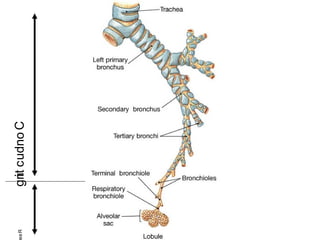
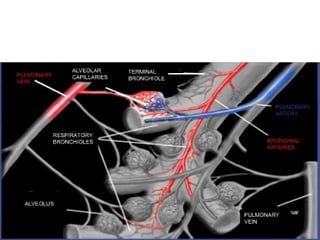
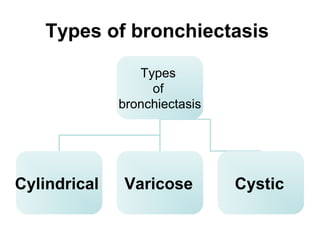
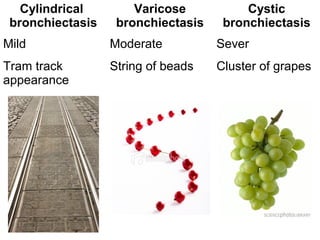
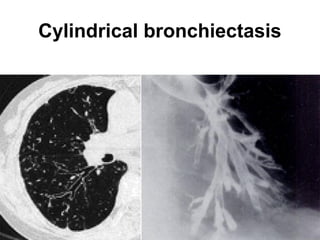
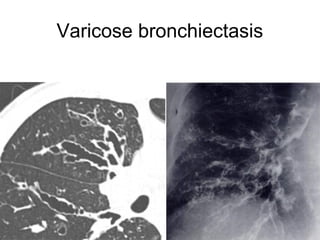
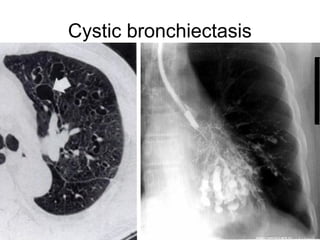
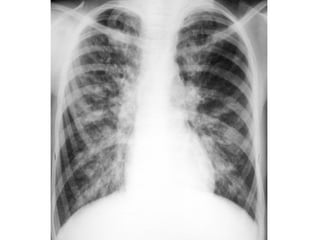
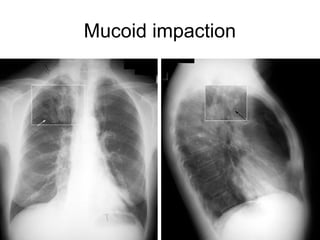
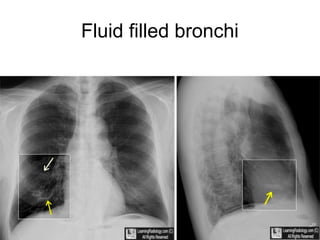
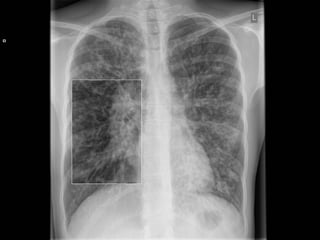
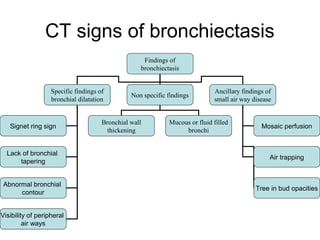
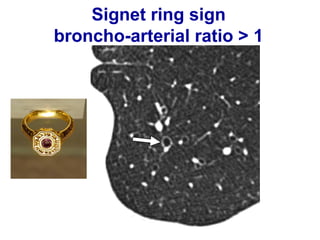
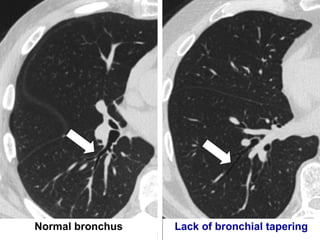
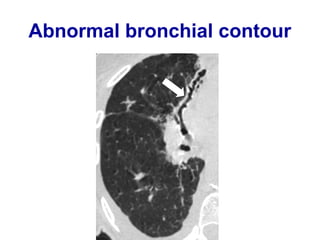
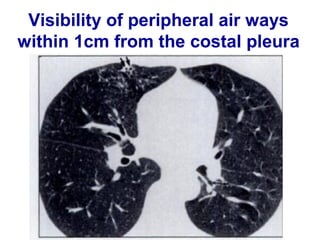
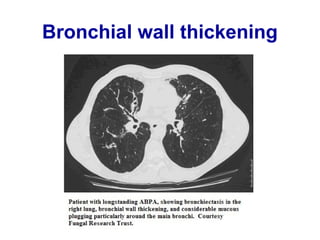
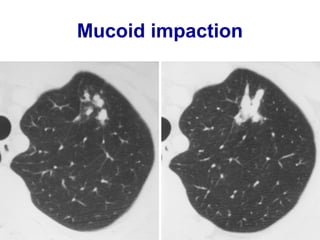
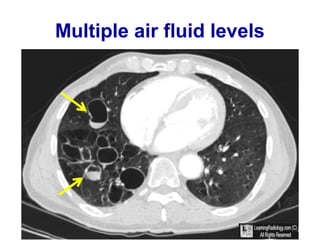
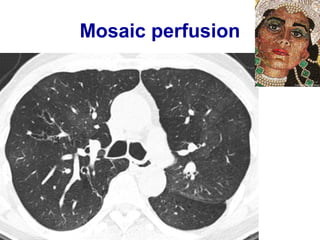
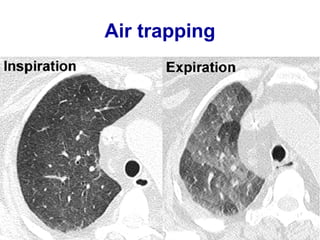
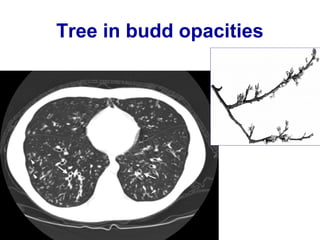
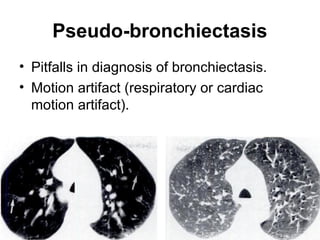
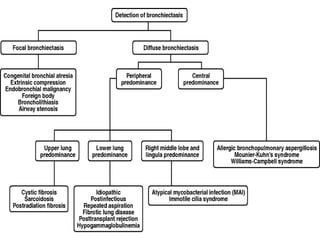
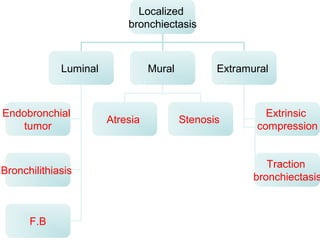
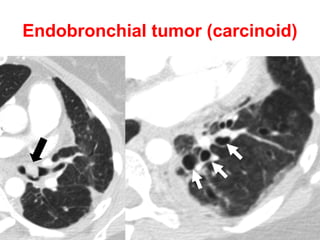
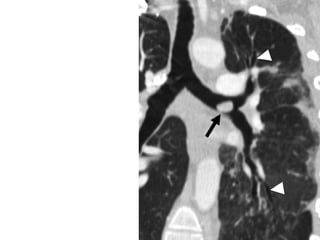
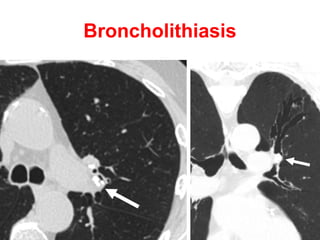
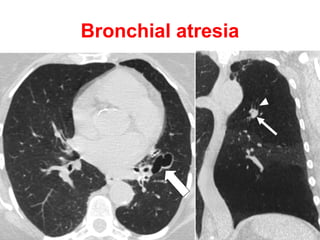
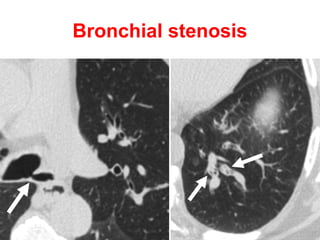
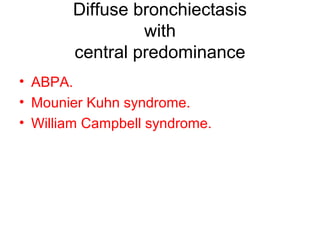
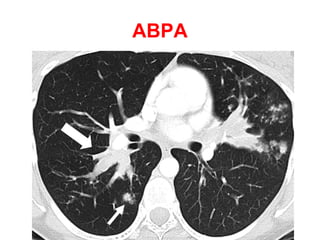
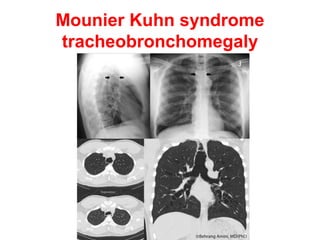
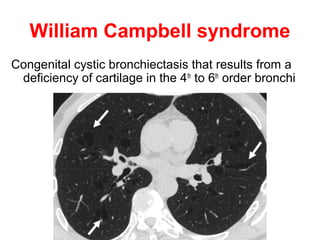
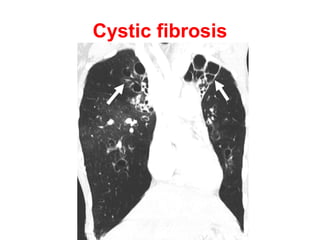
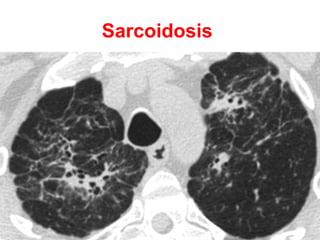
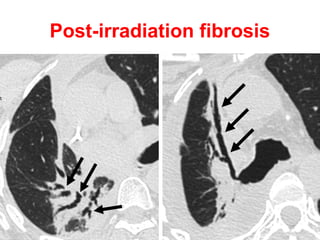
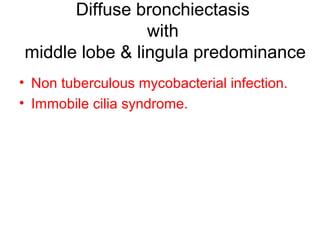
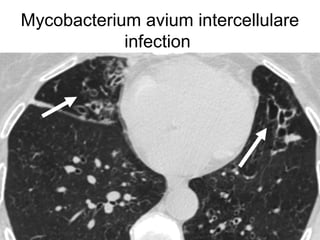
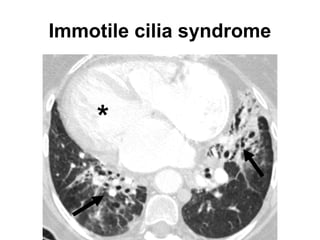
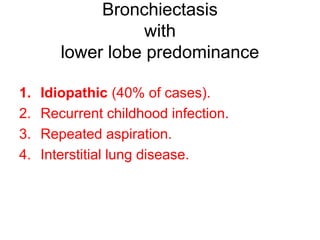
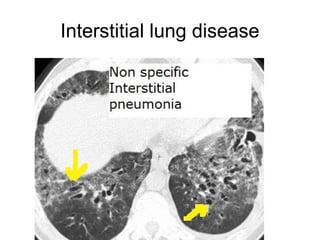
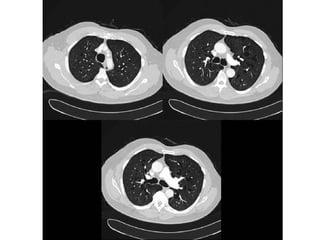
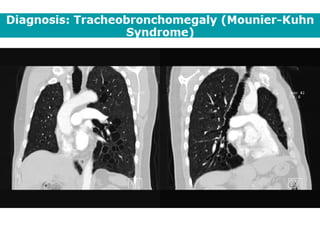
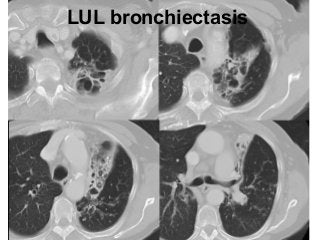
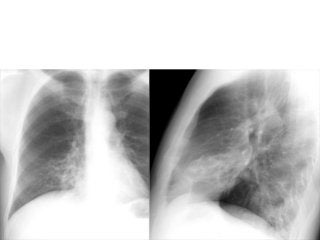
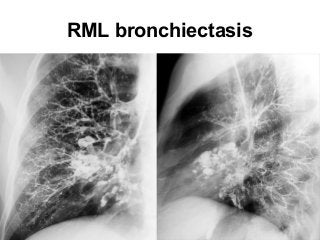
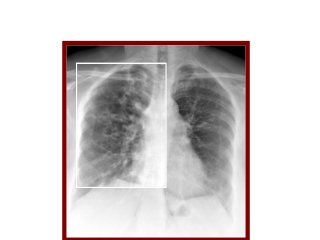
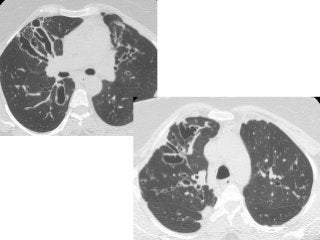
Bronchiectasis is the irreversible dilatation of the airways. There are different types including cylindrical, varicose, and cystic bronchiectasis. CT scans are useful for diagnosis and can show signs like the signet ring sign, lack of bronchial tapering, and visibility of peripheral airways. Pseudo-bronchiectasis can occur due to artifacts or conditions like tumors, broncholithiasis, or post-irradiation fibrosis. Common causes of diffuse bronchiectasis include cystic fibrosis, sarcoidosis, nontuberculous mycobacterial infections, and immotile cilia syndrome. Idiopathic bronchiectasis and recurrent childhood infections are common