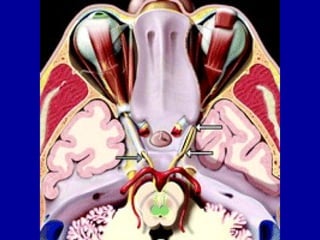
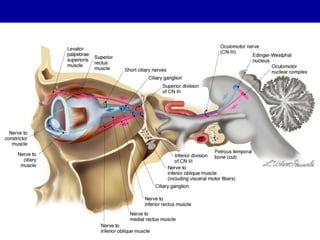
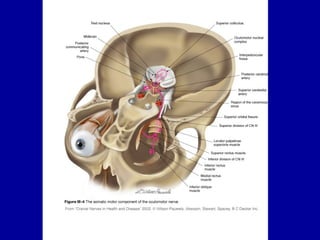
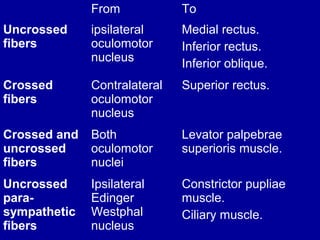
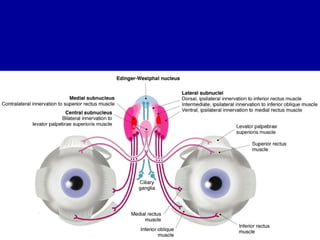
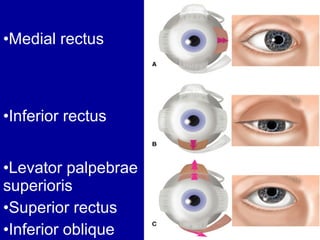
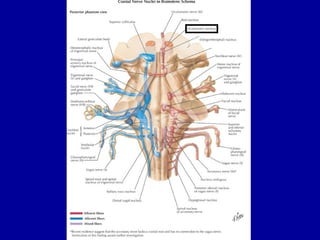
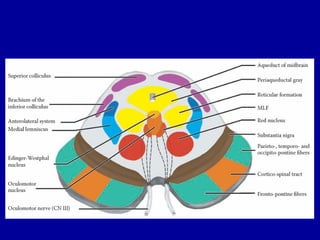
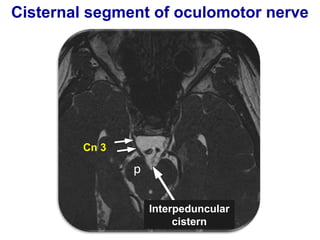
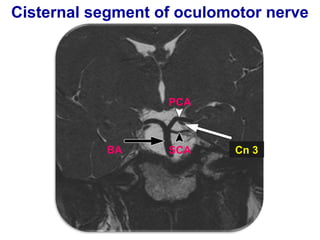
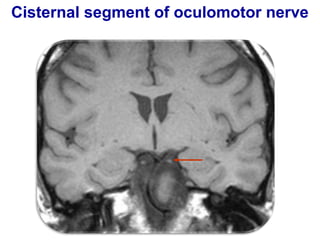
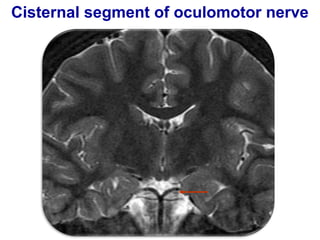
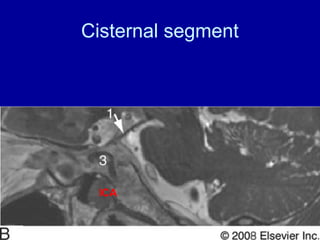
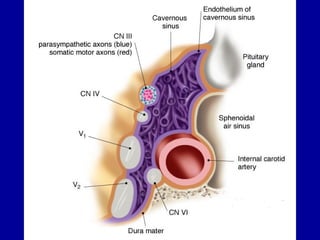
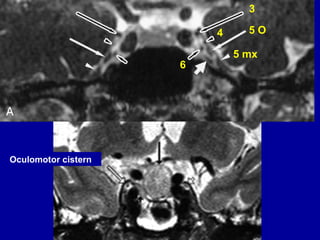
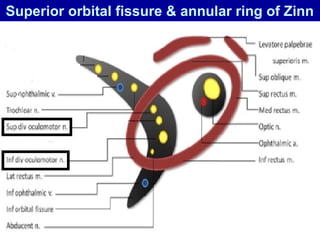
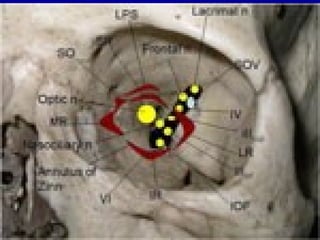
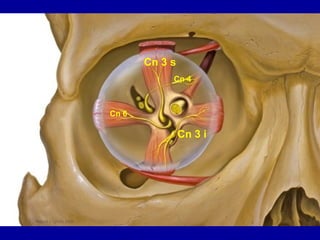
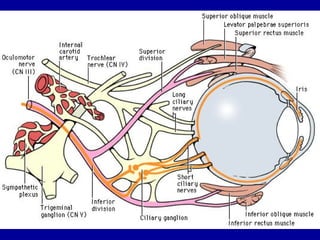
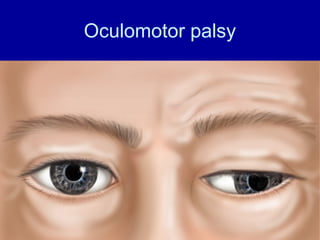
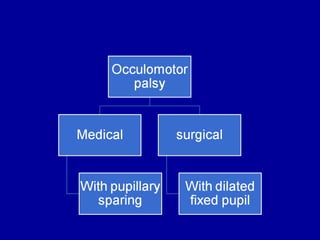
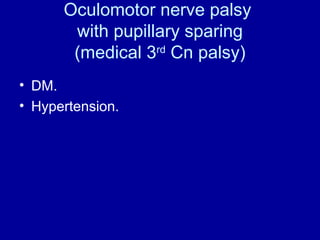
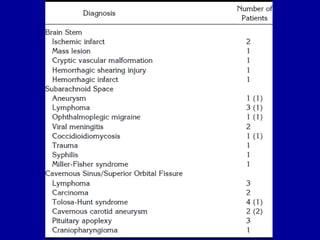
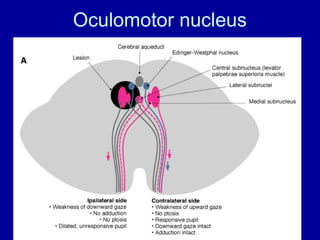
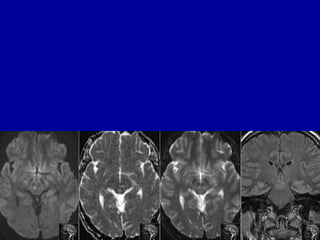
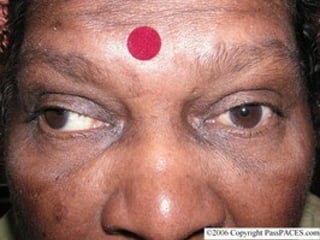
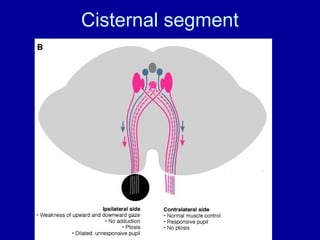
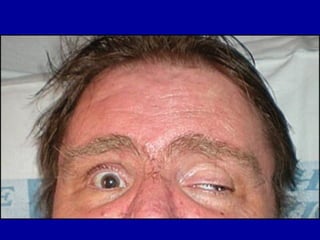
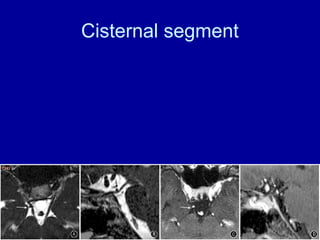
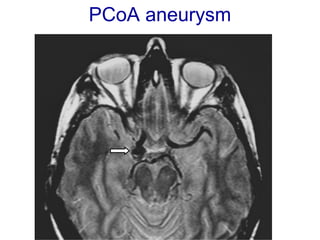
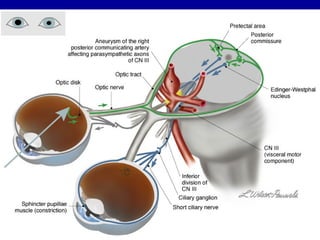
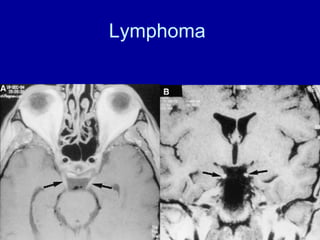
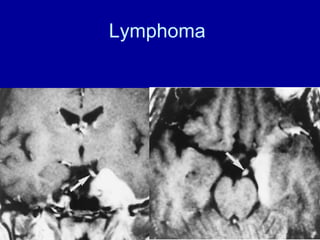
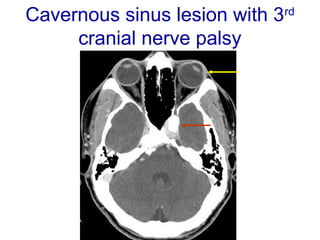
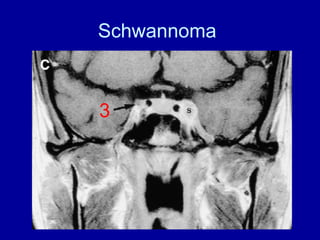
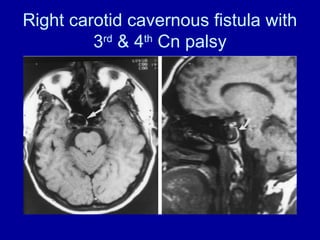
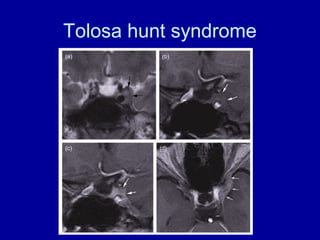
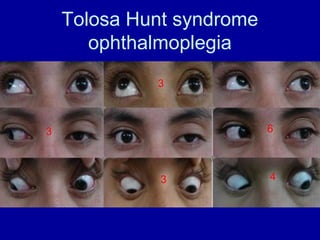
The oculomotor nerve has somatic and visceral motor components. The somatic component supplies four extraocular muscles and the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. The visceral component provides parasympathetic innervation to the constrictor pupillae and ciliary muscles. The oculomotor nerve originates in the midbrain, passes through the cavernous sinus, and enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure to innervate the extraocular muscles. Damage to the oculomotor nerve can cause an oculomotor nerve palsy and result in drooping of the eyelid and eye muscle weakness.