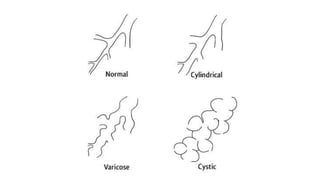
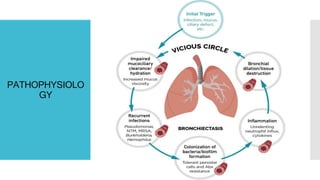
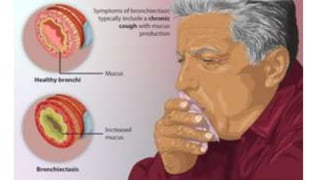
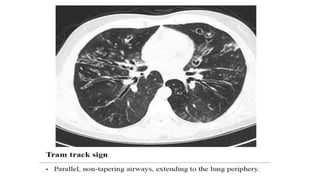
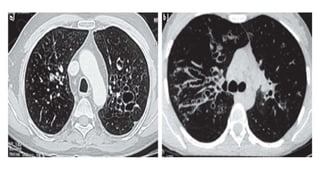
Bronchiectasis is the irreversible dilatation of the airways that can involve parts of the lung in a focal or diffuse manner. It is commonly categorized as cylindrical, varicose, or cystic. Focal bronchiectasis occurs in a localized area due to obstruction of an airway from external factors like tumors or internal factors like aspirated objects. Diffuse bronchiectasis is widespread throughout the lungs and often arises from underlying systemic or infectious diseases. Clinical manifestations include a persistent productive cough with thick sputum, clubbing of the fingers, and crackles heard on examination. Diagnosis is usually based on presentation and radiographic findings, with CT scans being more specific than chest X-rays. Treatment