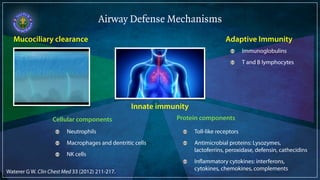
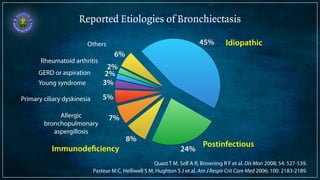
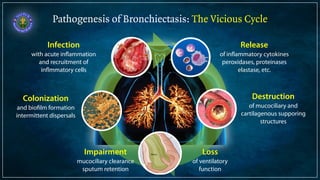
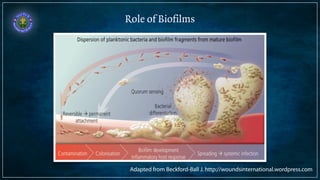
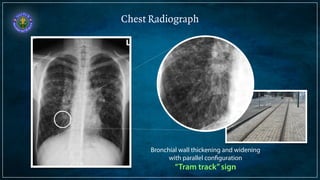
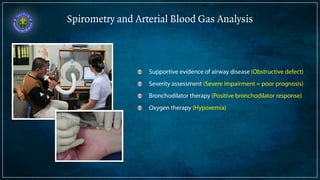
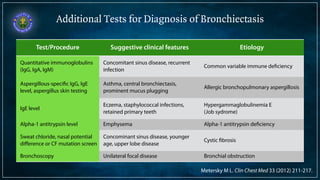
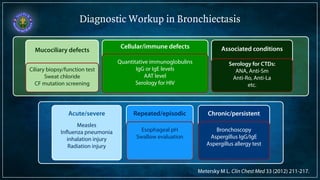
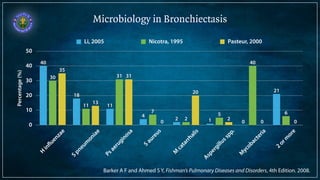
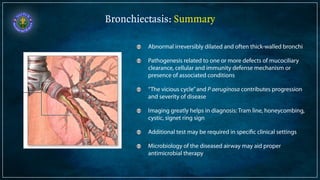
Bronchiectasis is defined as abnormal irreversibly dilated and thick-walled bronchi resulting from destruction of the bronchial wall. Its pathogenesis involves defects in mucociliary clearance, cellular immunity, or associated conditions. High-resolution CT is helpful for diagnosis by showing features like tram lines or honeycombing. Additional tests may be needed to identify underlying causes. Microbiology of infected airways guides antimicrobial therapy for managing the vicious cycle of infection and inflammation that can progress the disease.