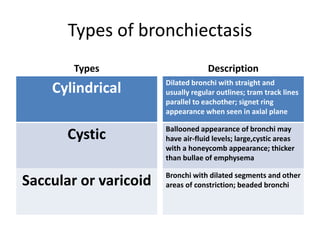
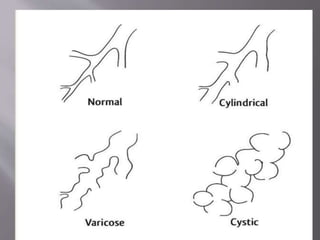
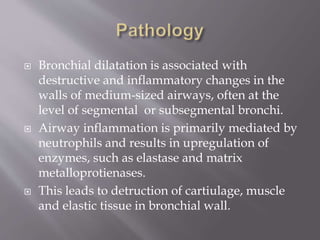
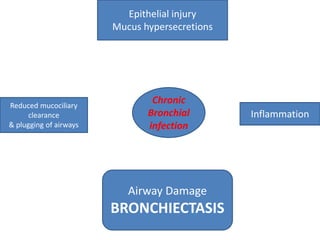
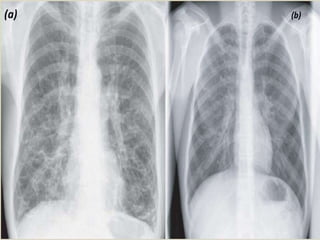
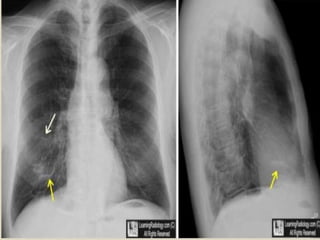
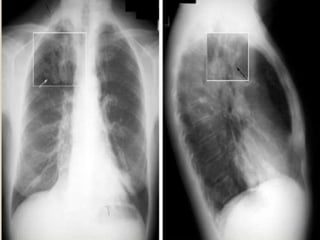
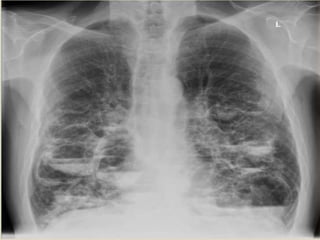
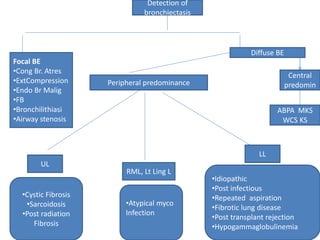
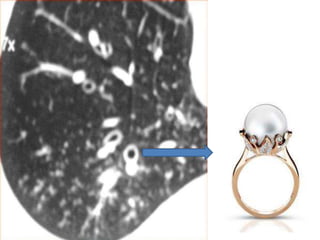
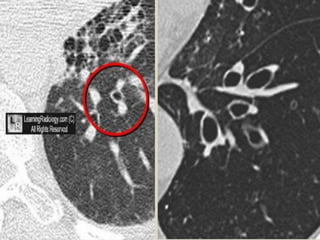
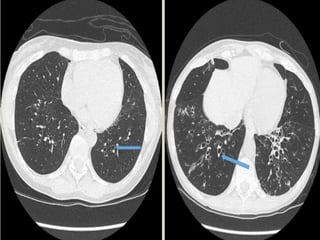
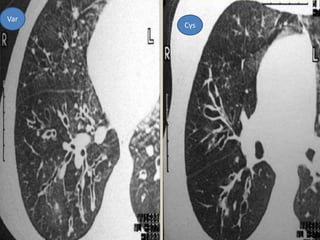
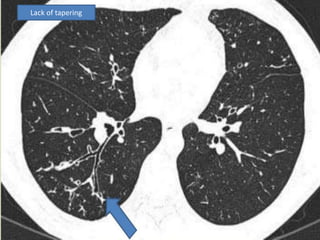
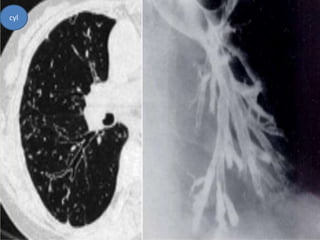
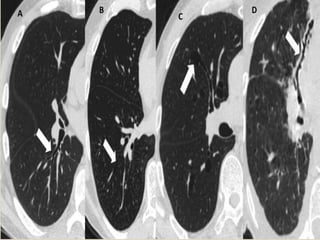
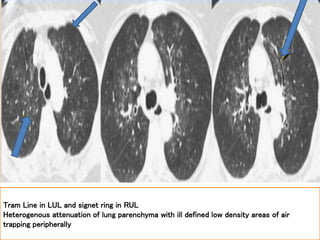
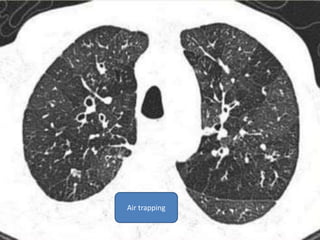
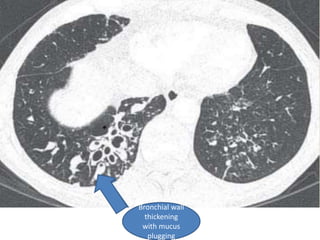
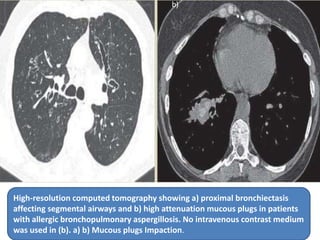
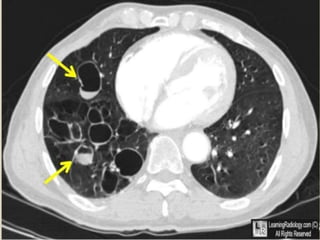
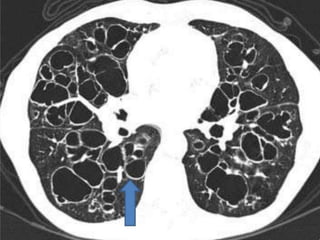
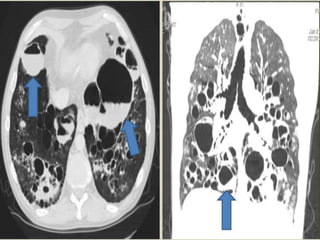
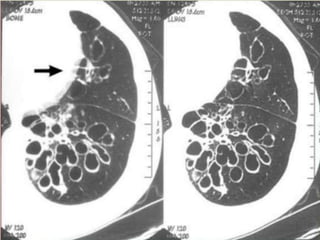
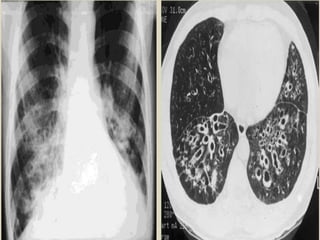
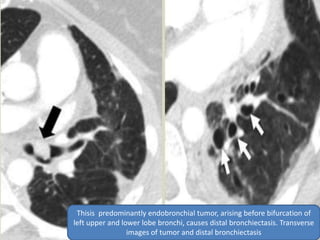
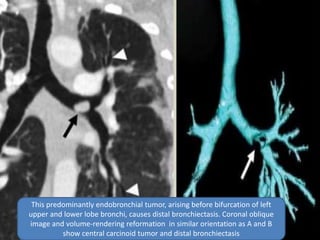
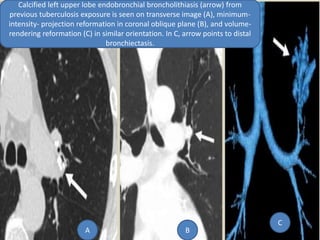
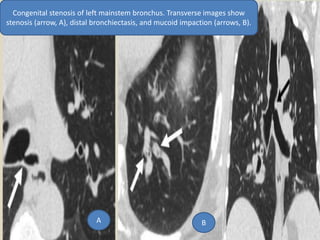
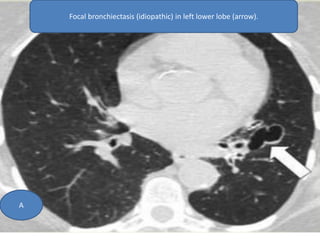
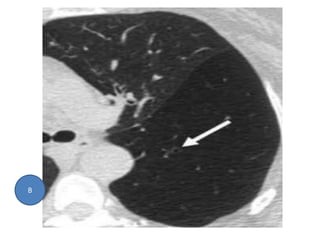
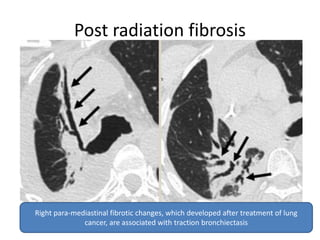
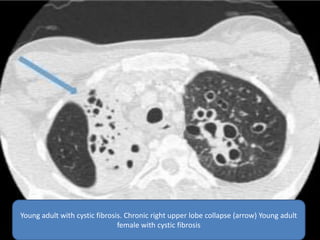
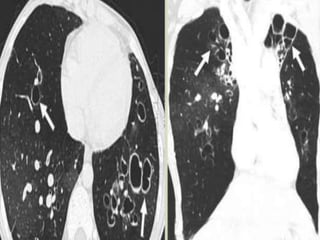
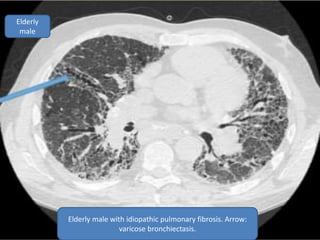
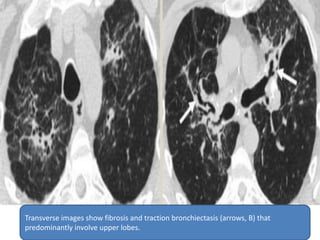
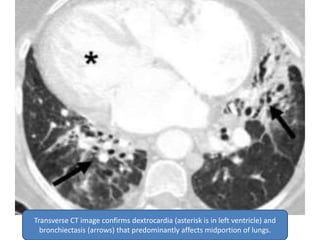
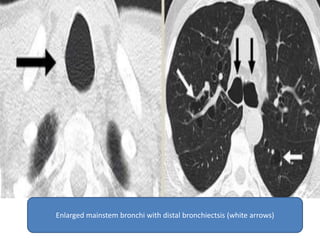
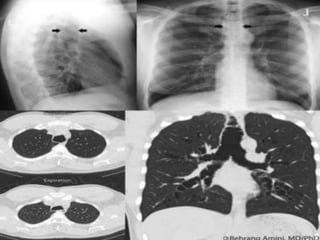
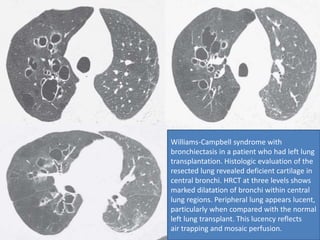
This document summarizes bronchiectasis, including its definition, causes, clinical presentation, imaging appearance and features on CT scan. Bronchiectasis is abnormal permanent dilatation of the bronchi. It results from destruction of the bronchial wall and surrounding tissues due to various pathological processes. On CT scan, it appears as bronchial dilation, lack of tapering, tram-tracking and thickened bronchial walls. The causes discussed include post-infectious, cystic fibrosis, immune deficiencies and congenital disorders. The clinical features are chronic cough, sputum production and recurrent infections.