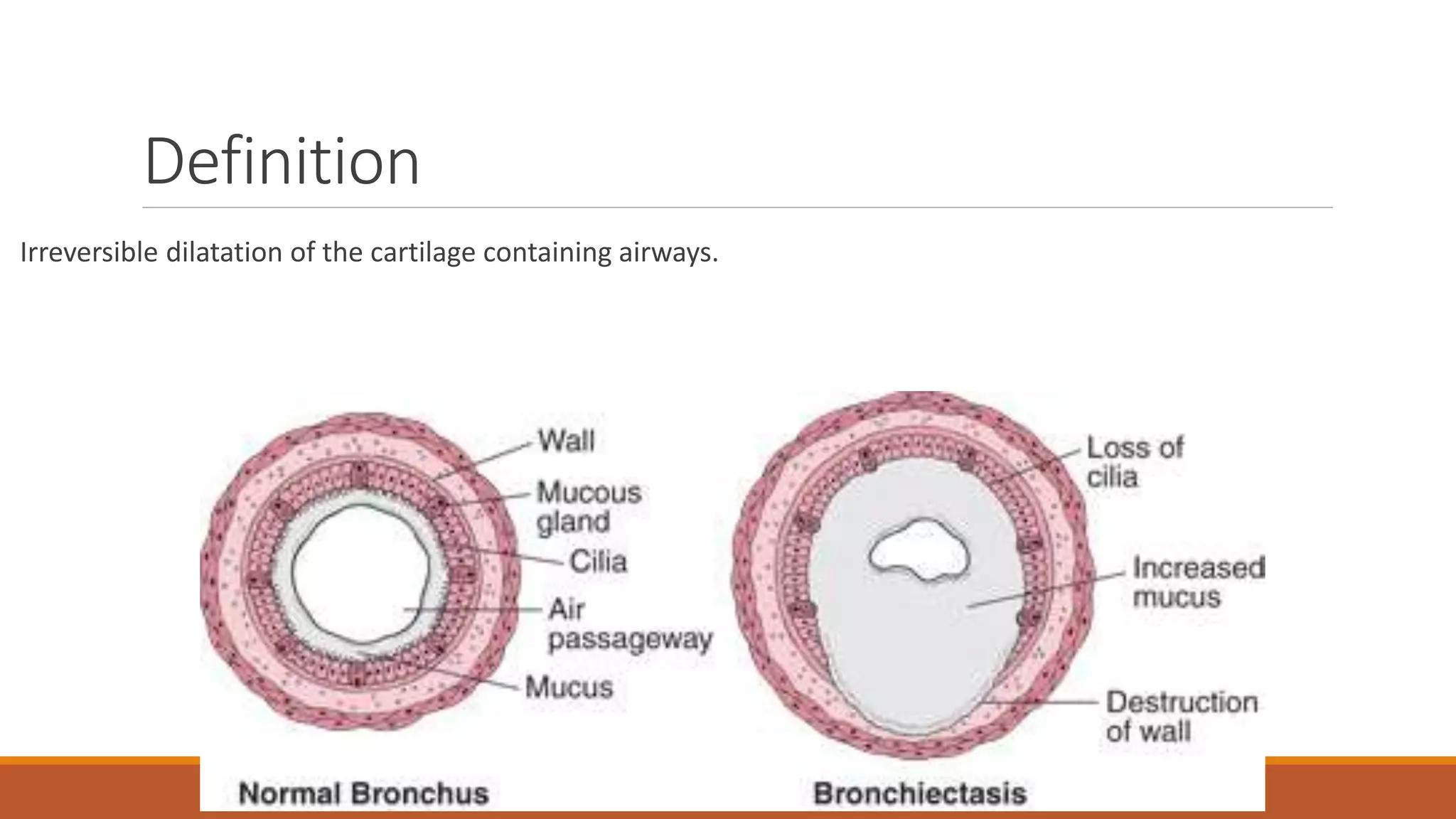
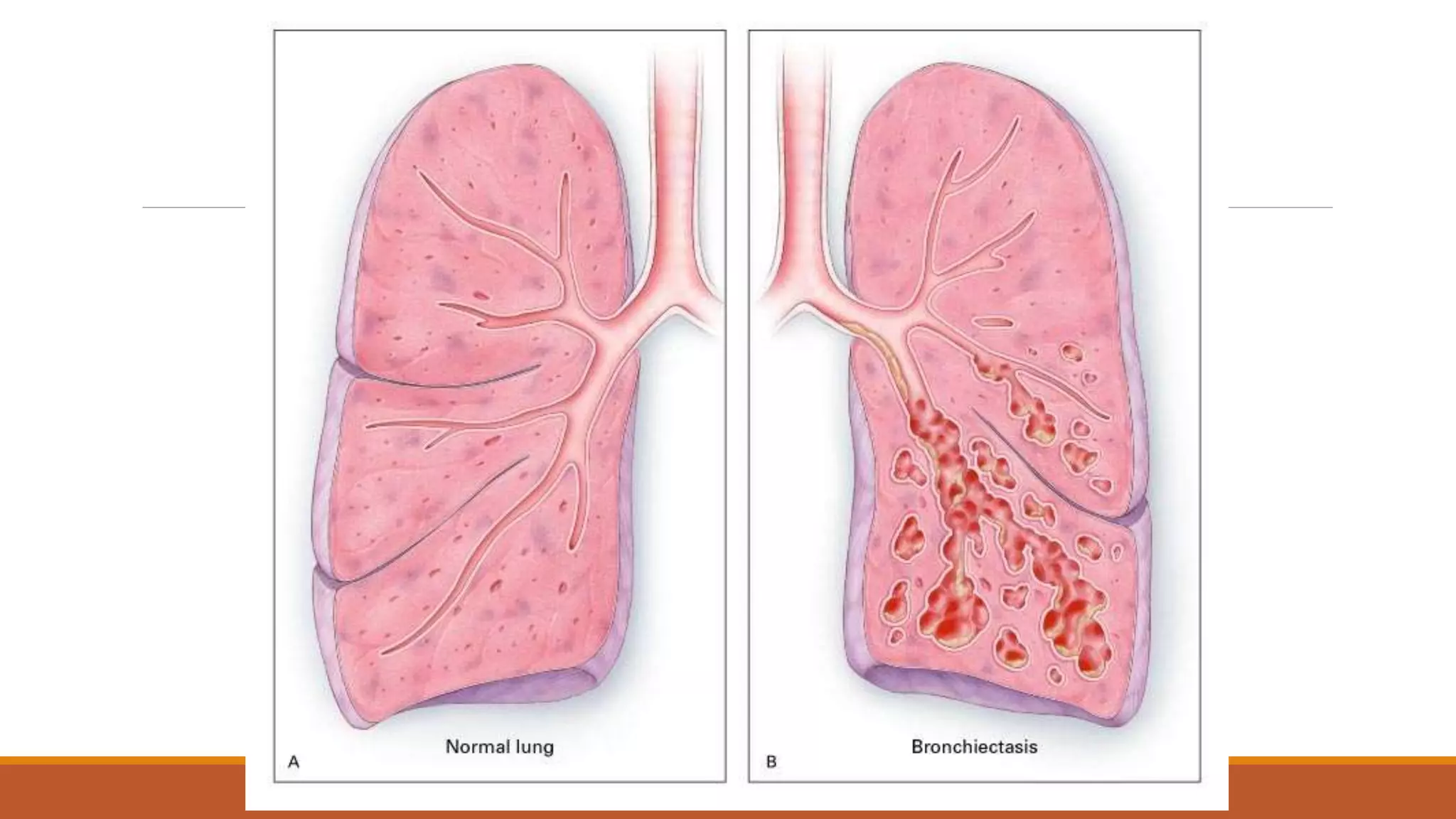
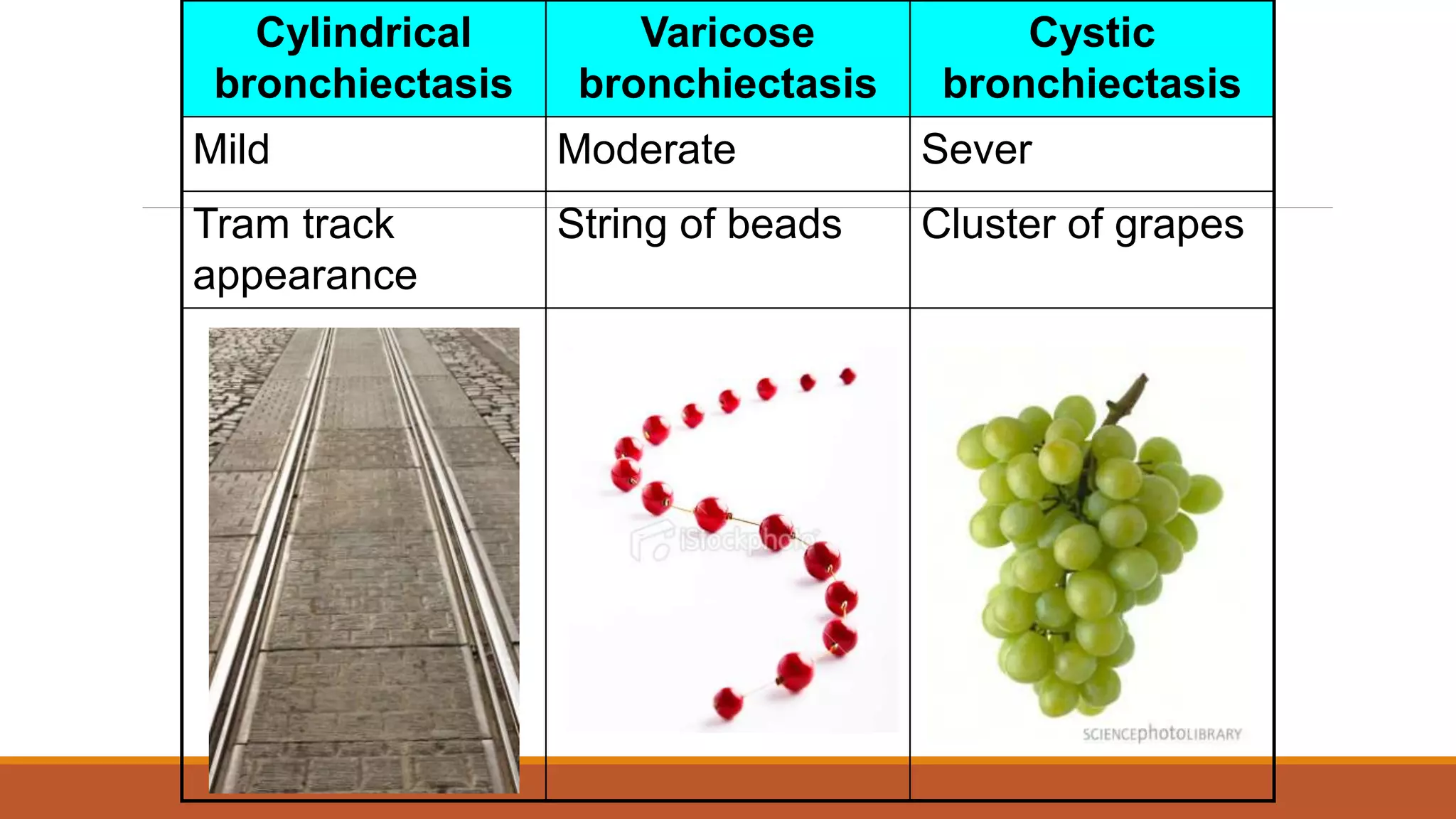
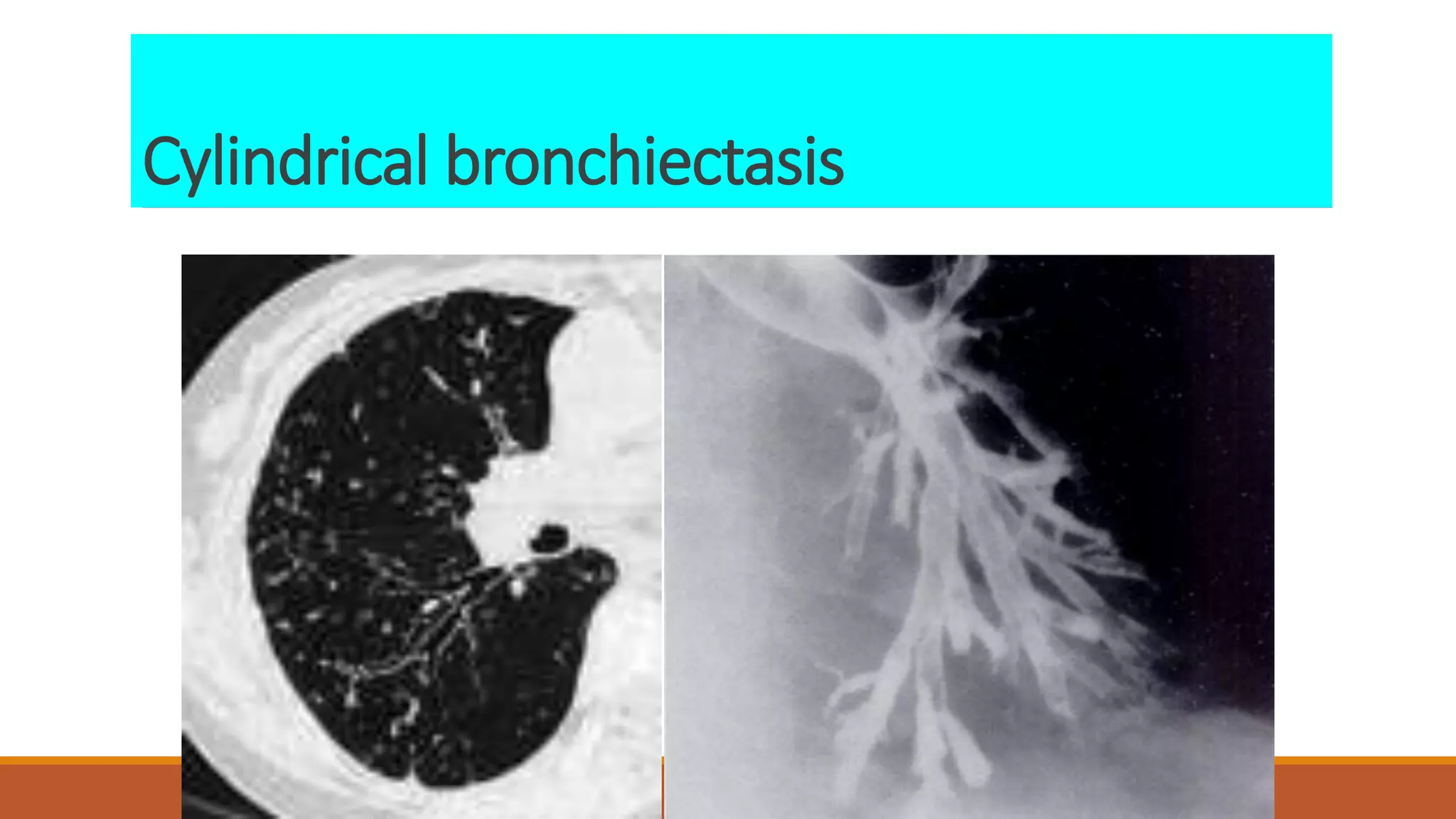
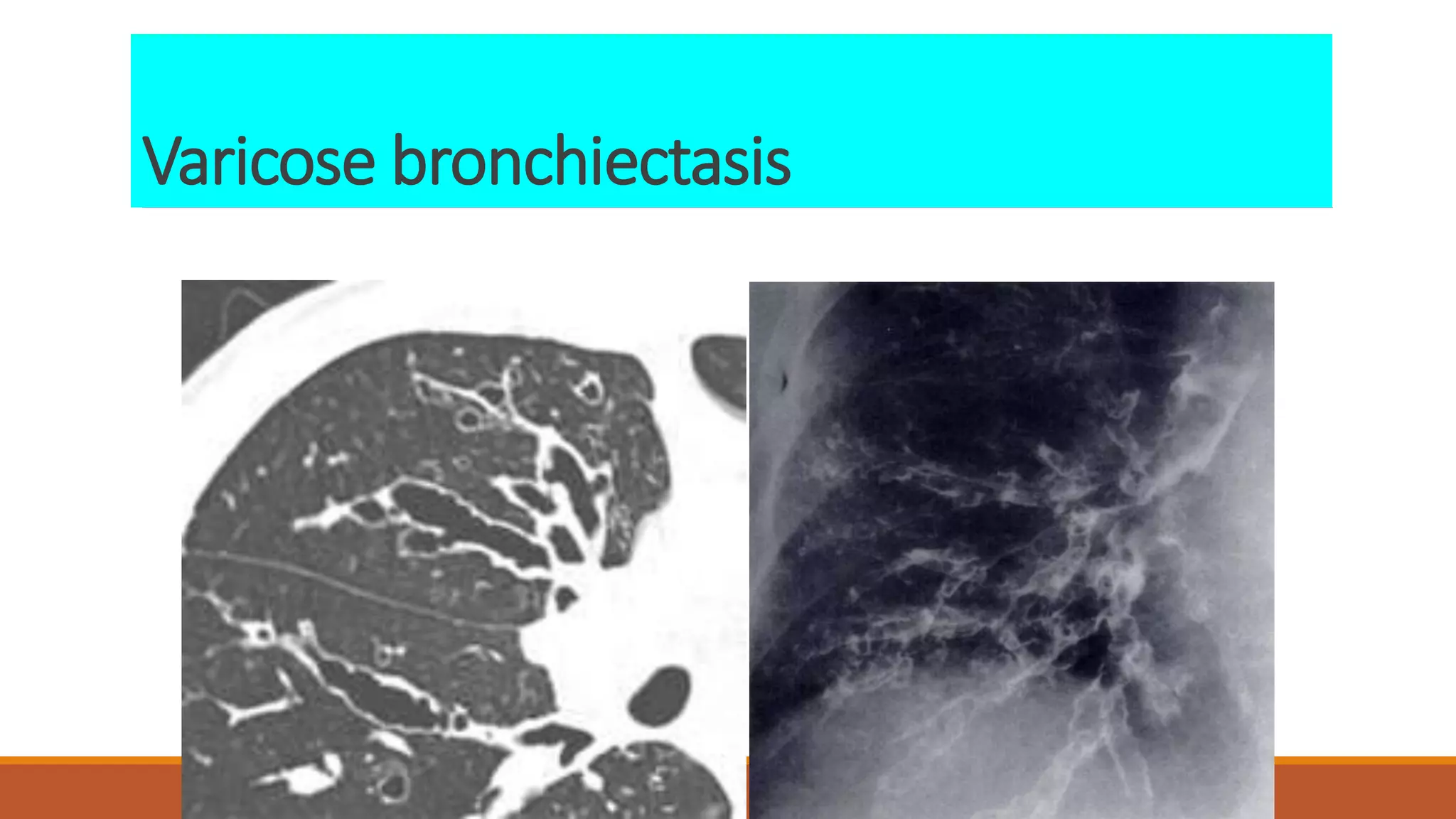
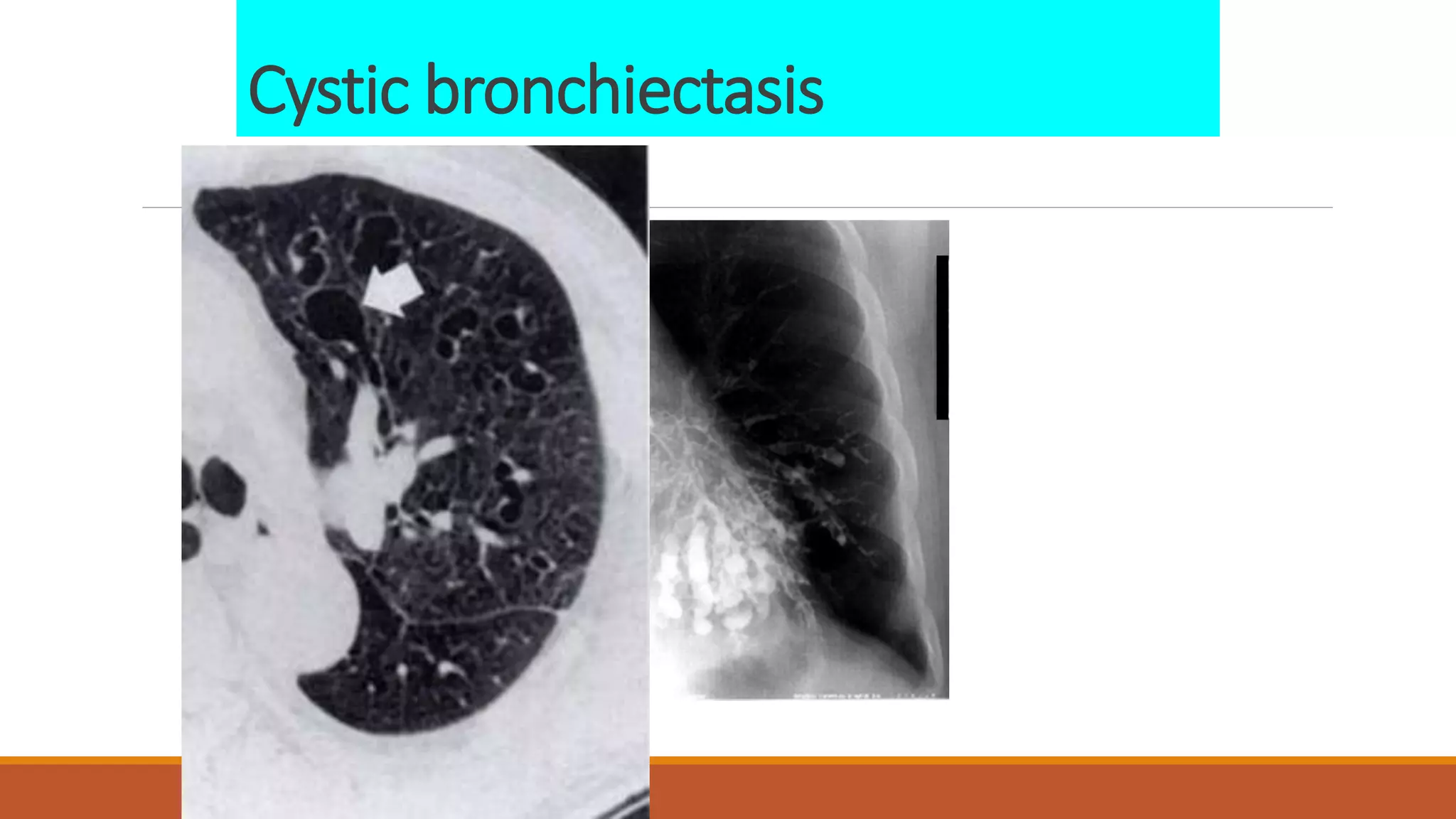
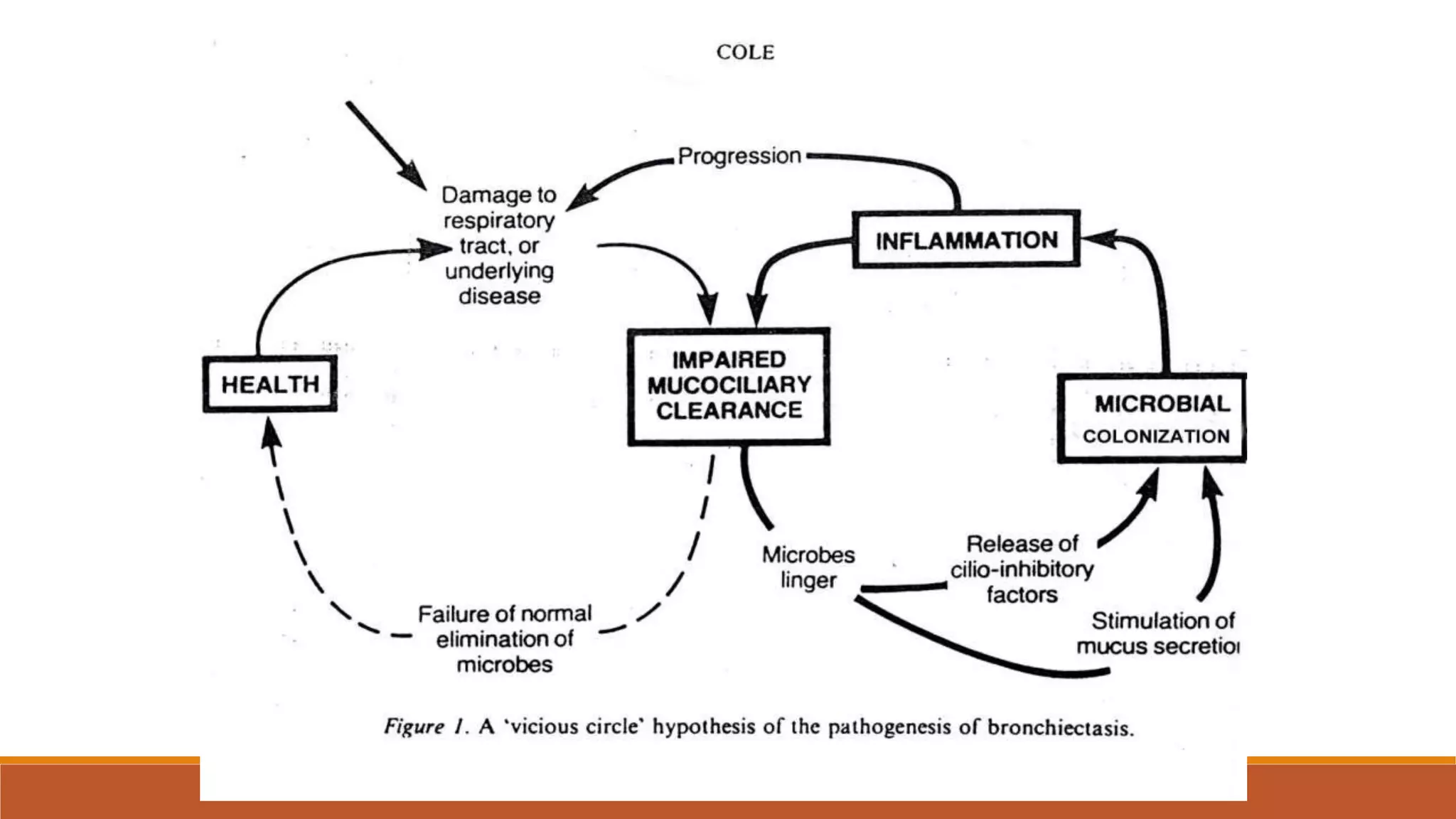
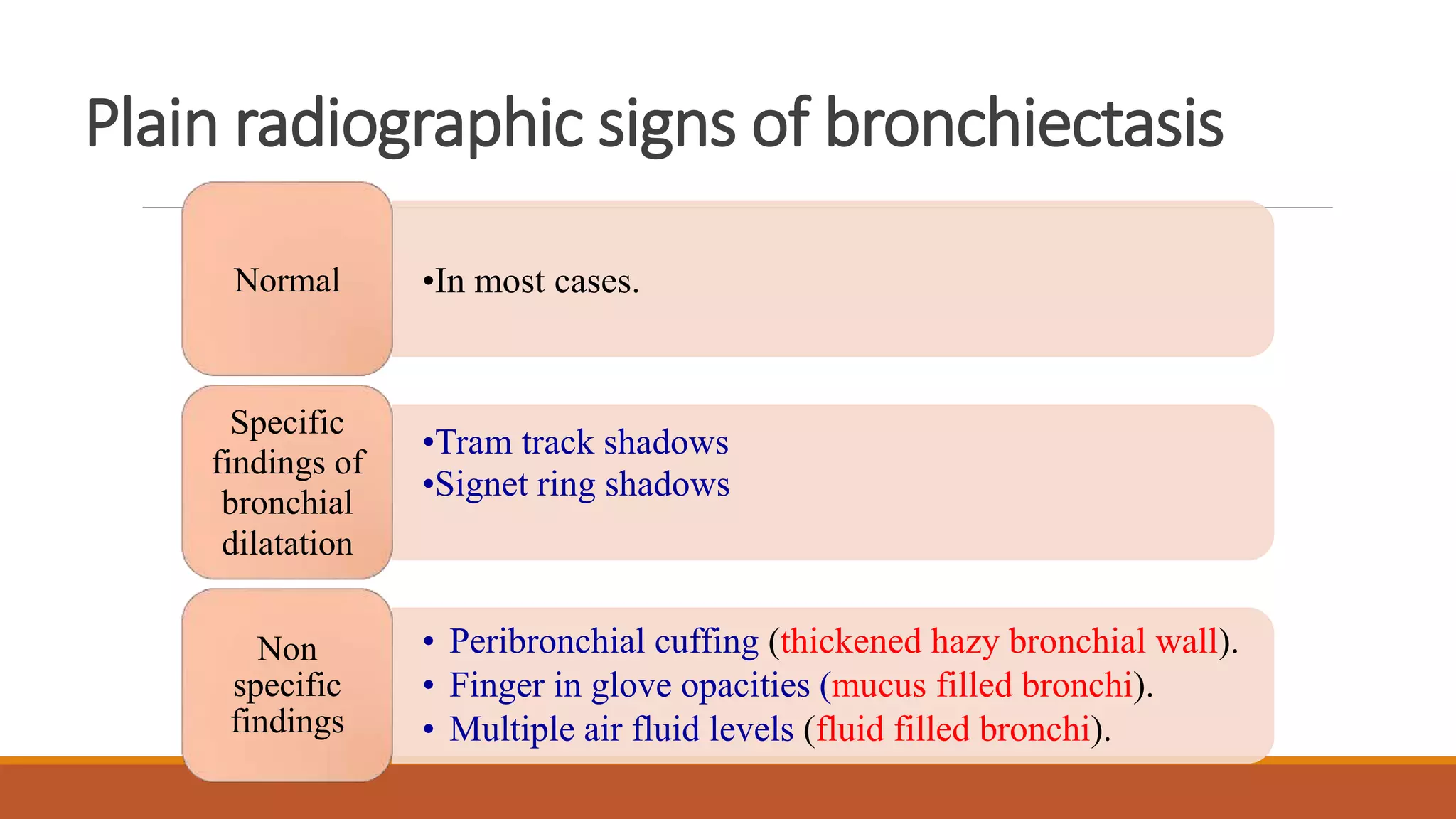
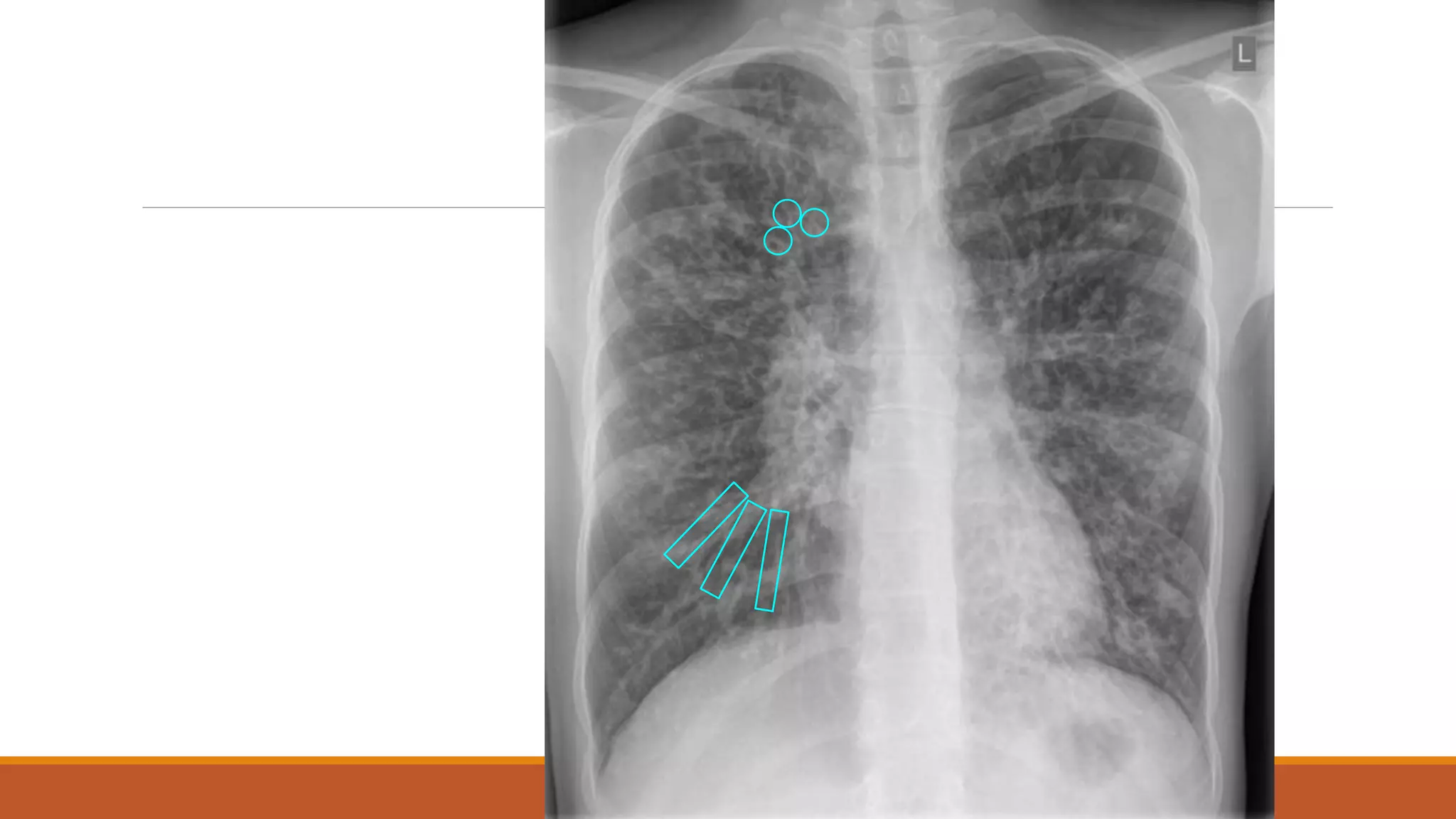
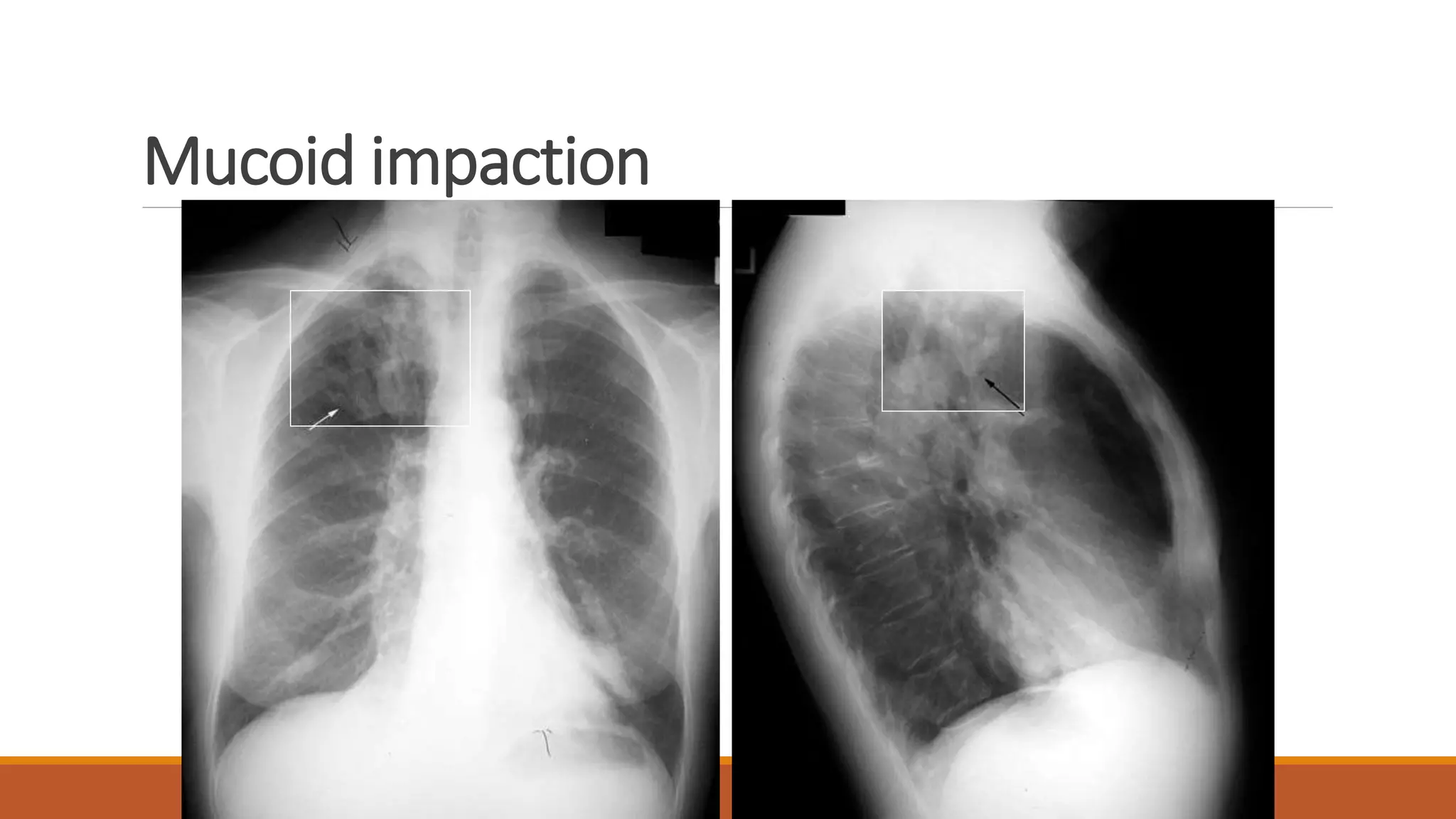
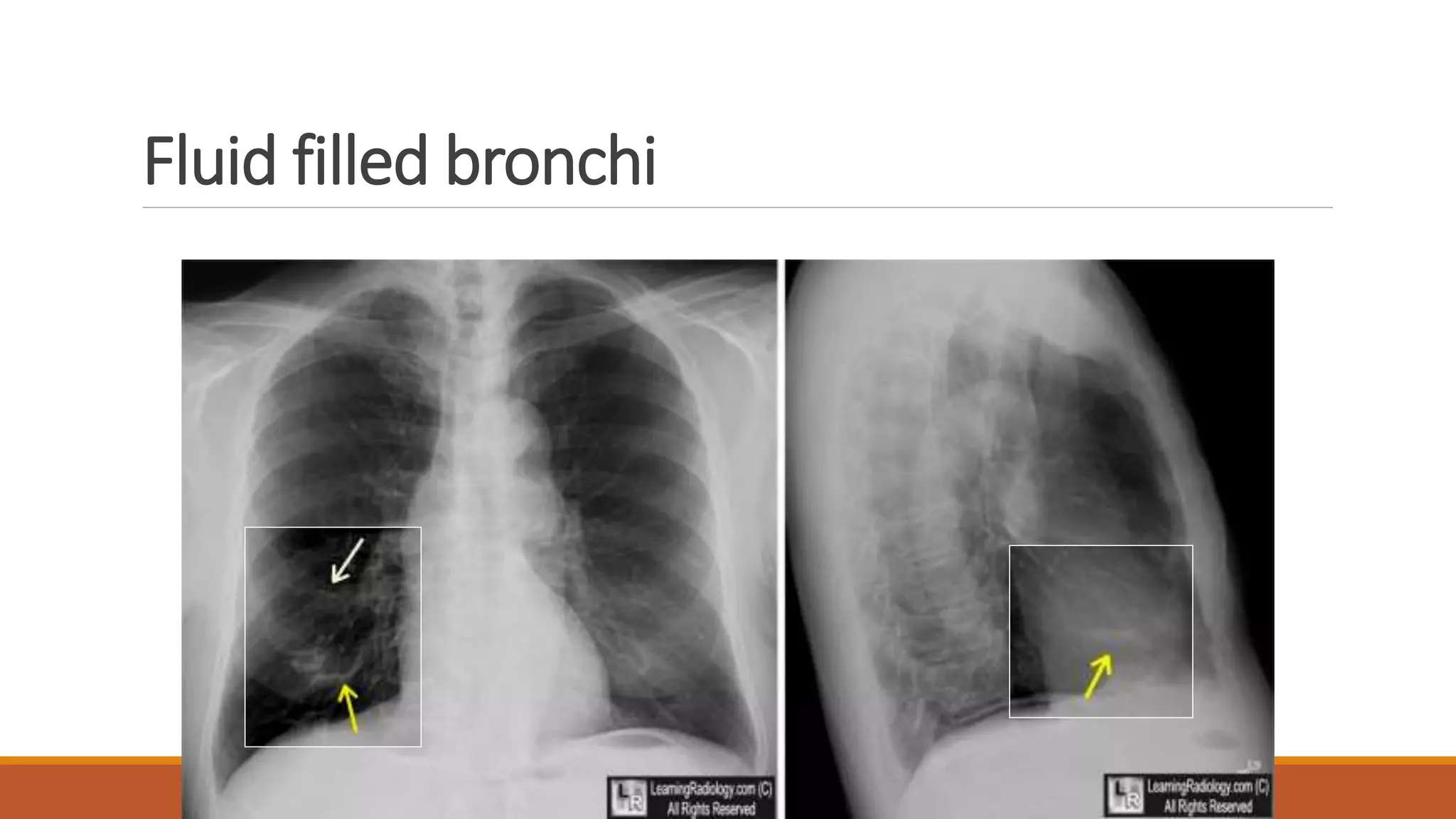
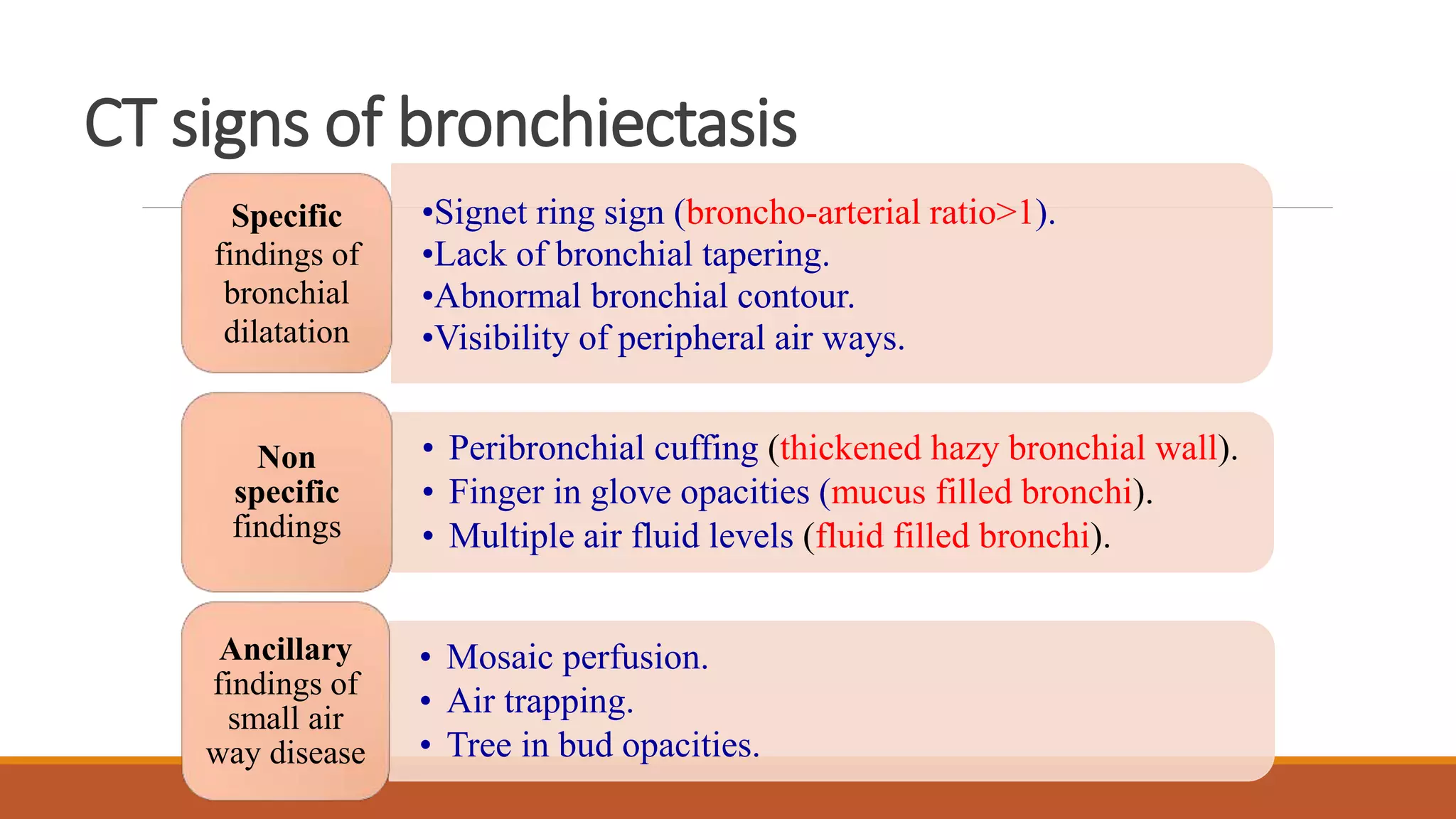
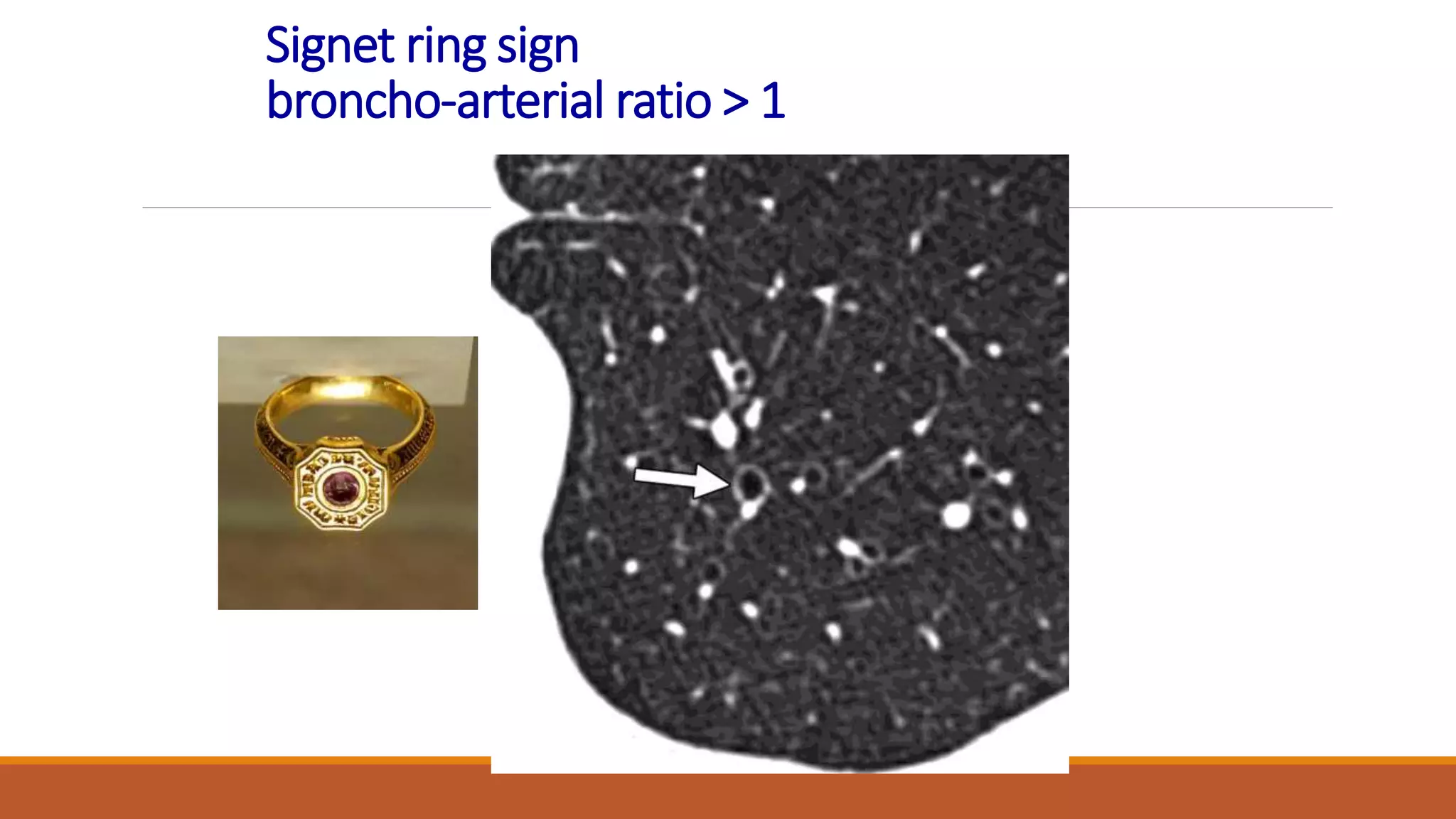
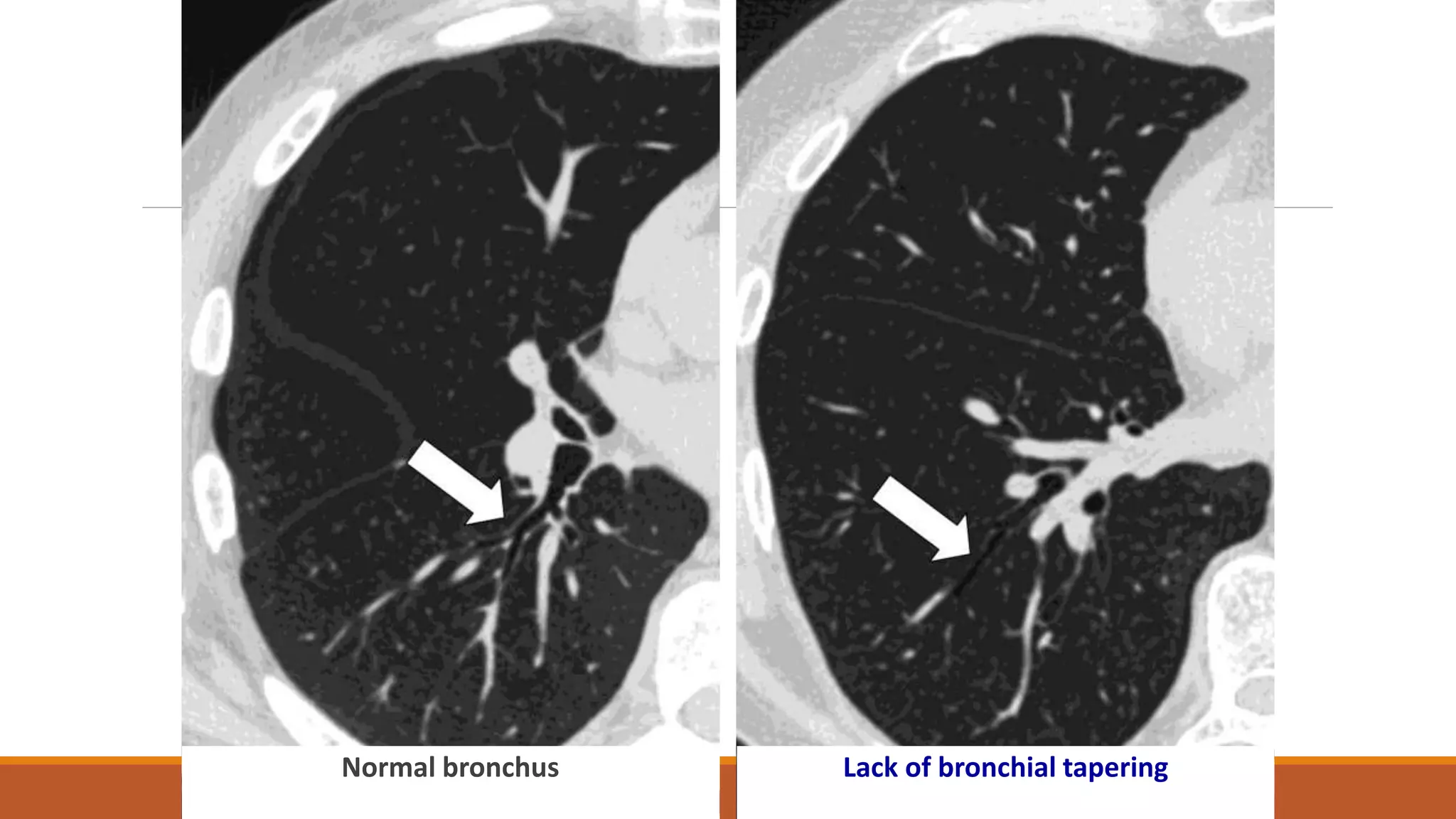
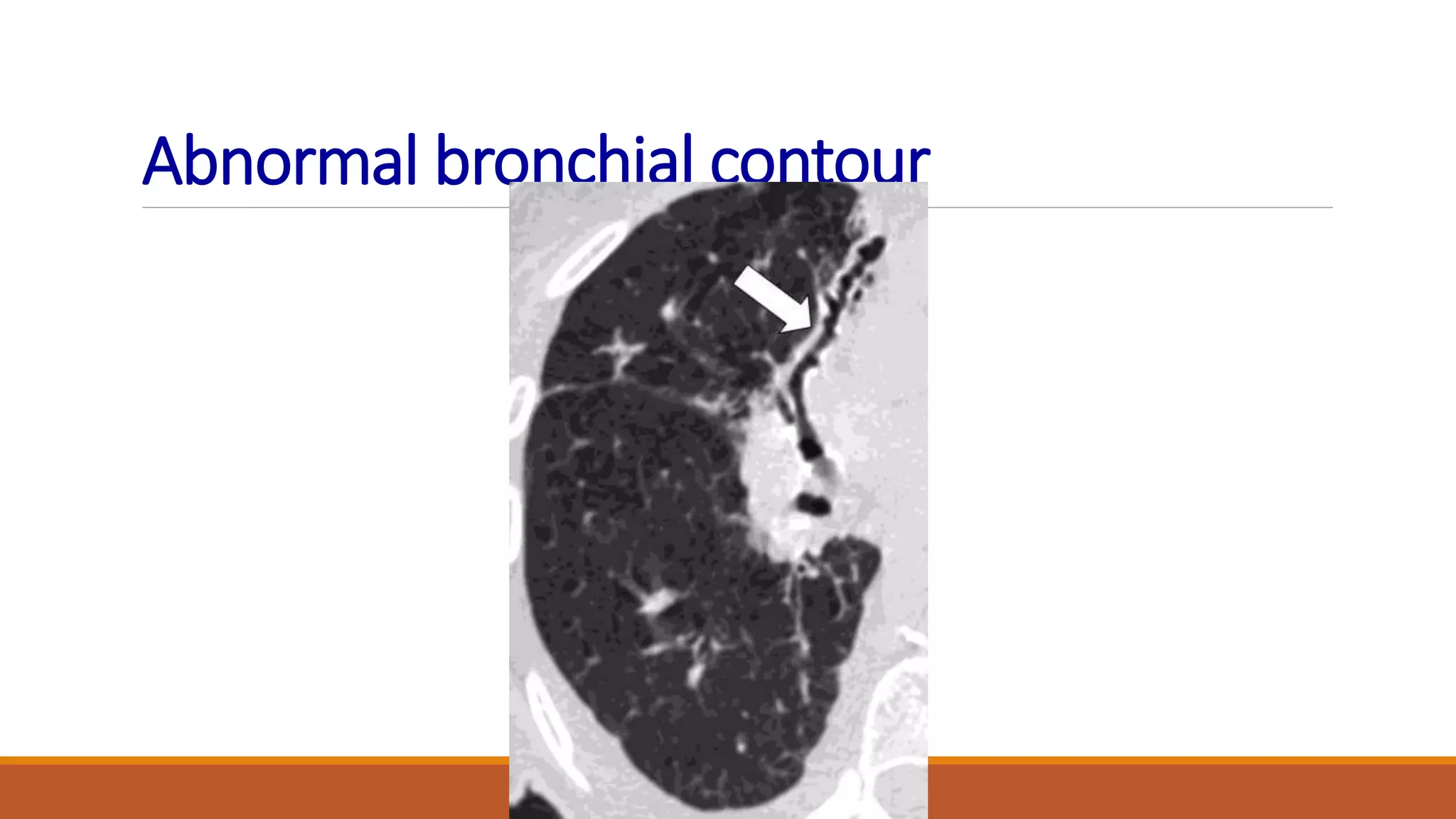
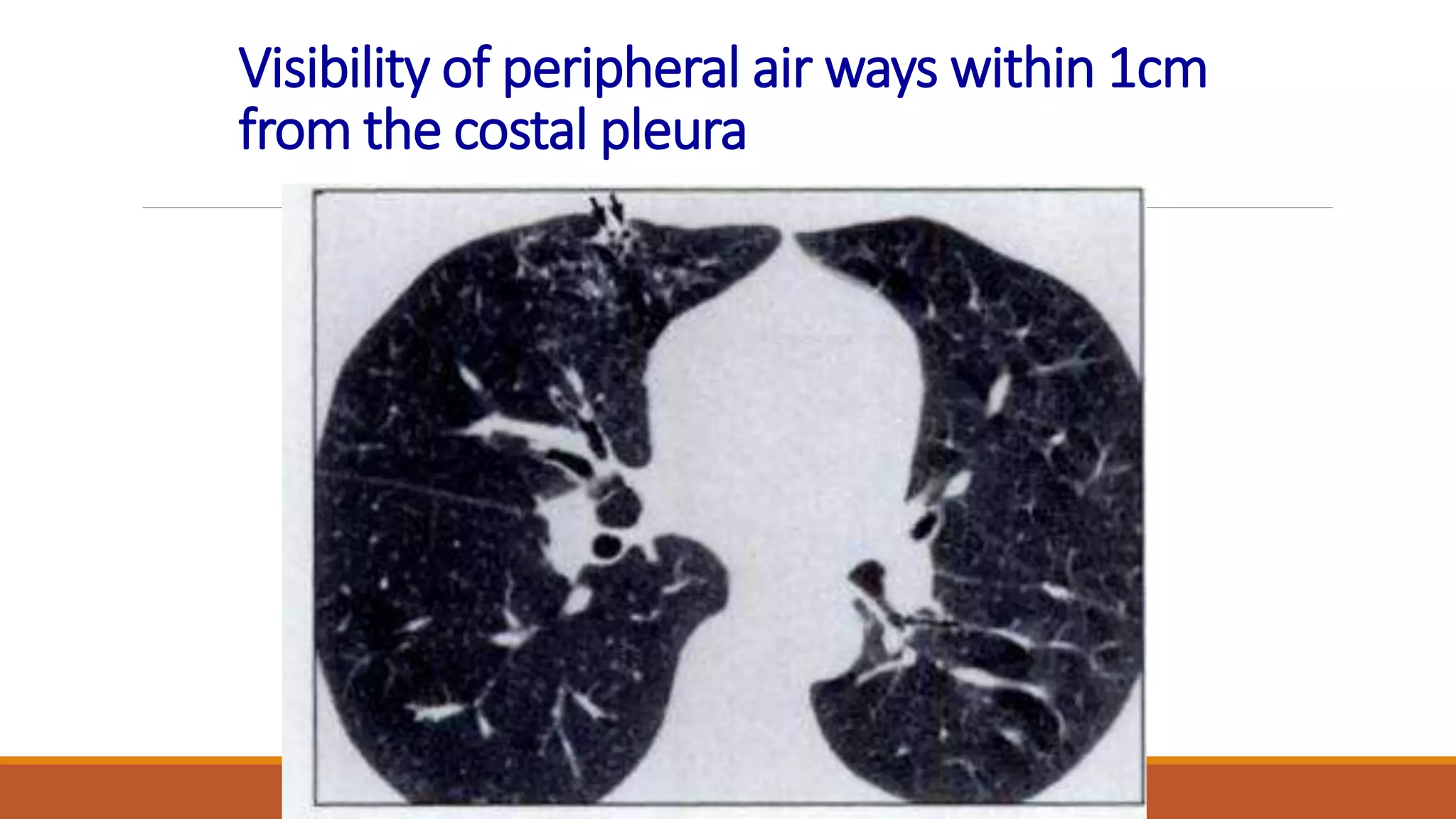
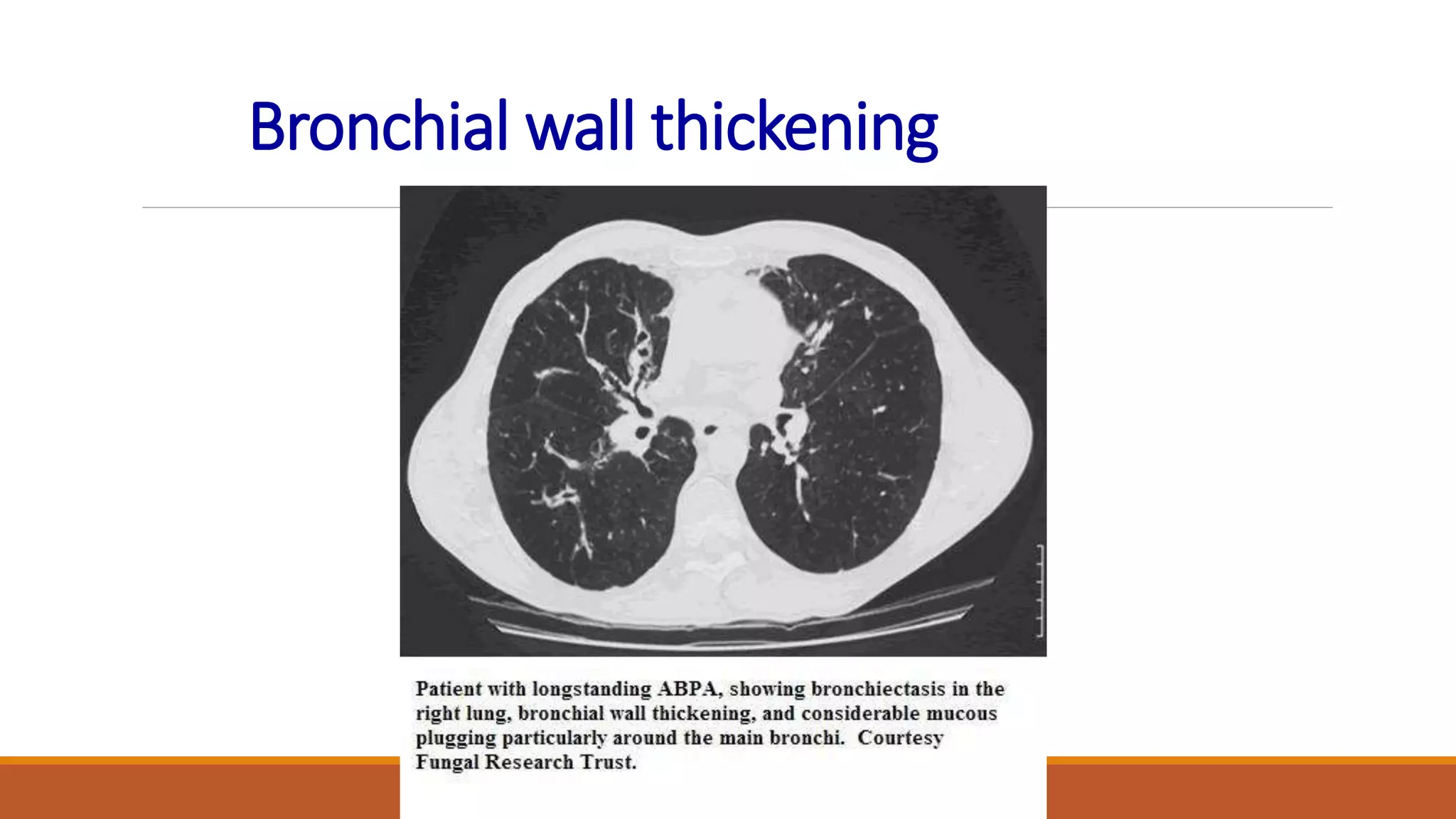
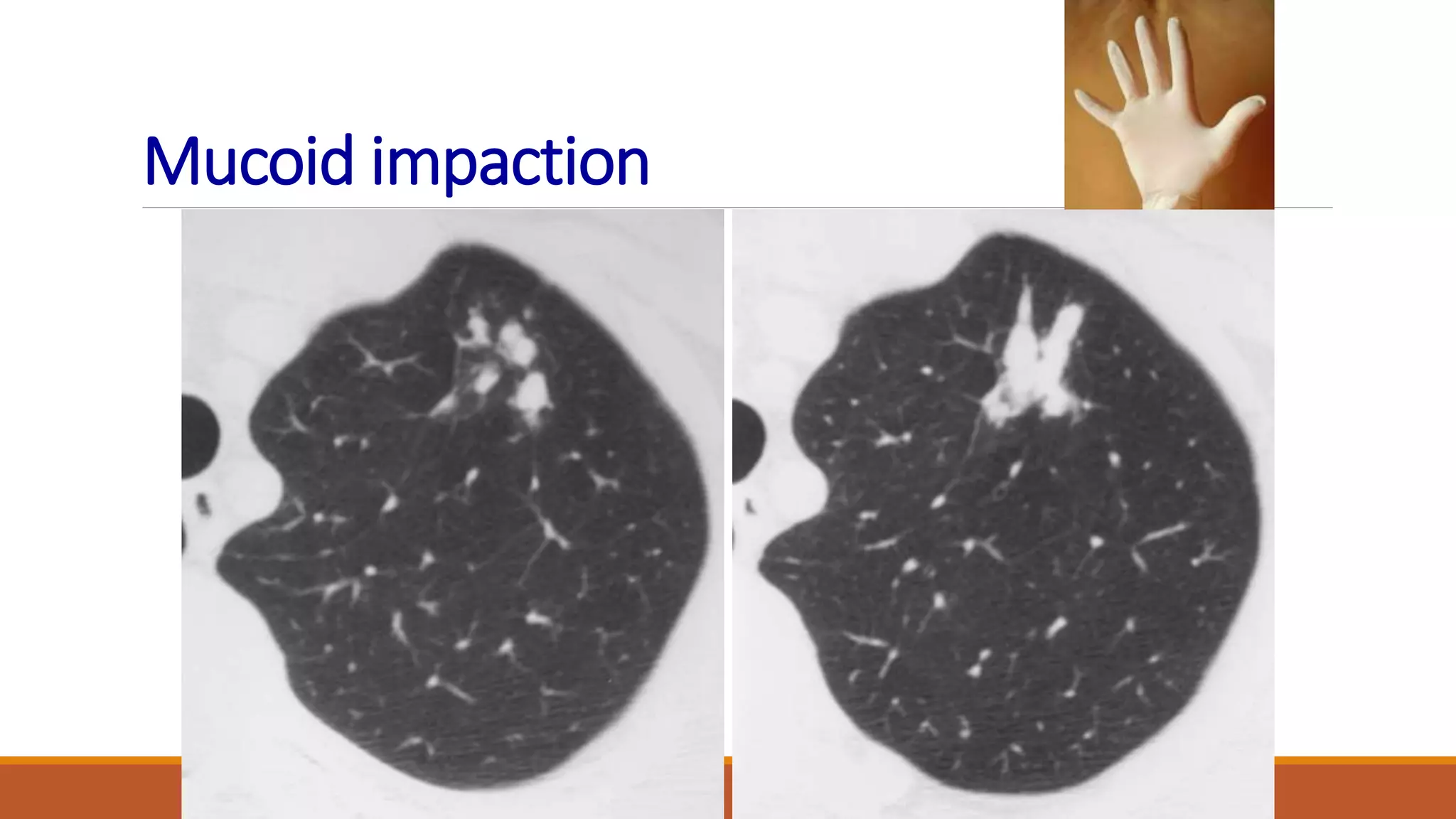
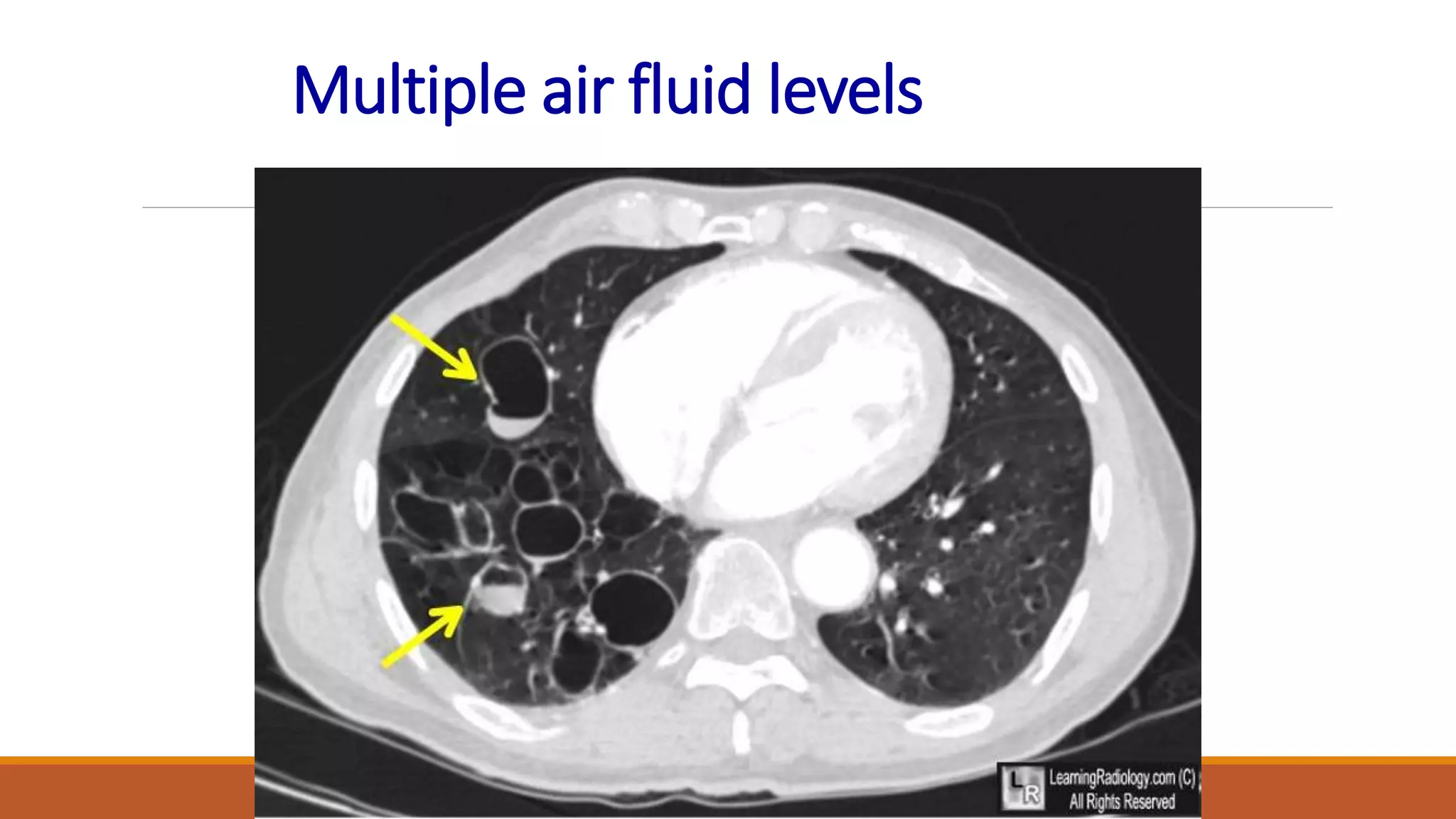
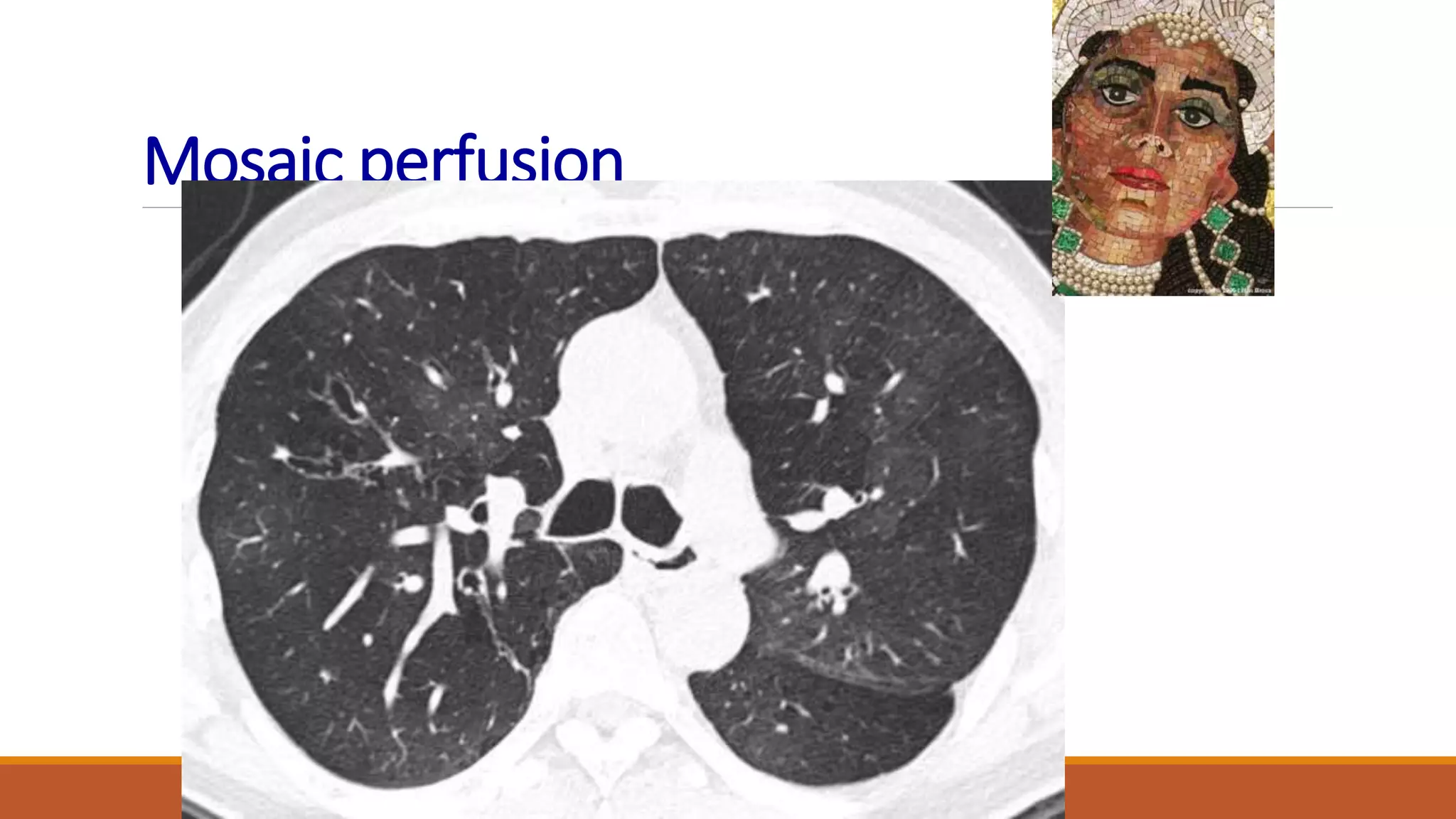
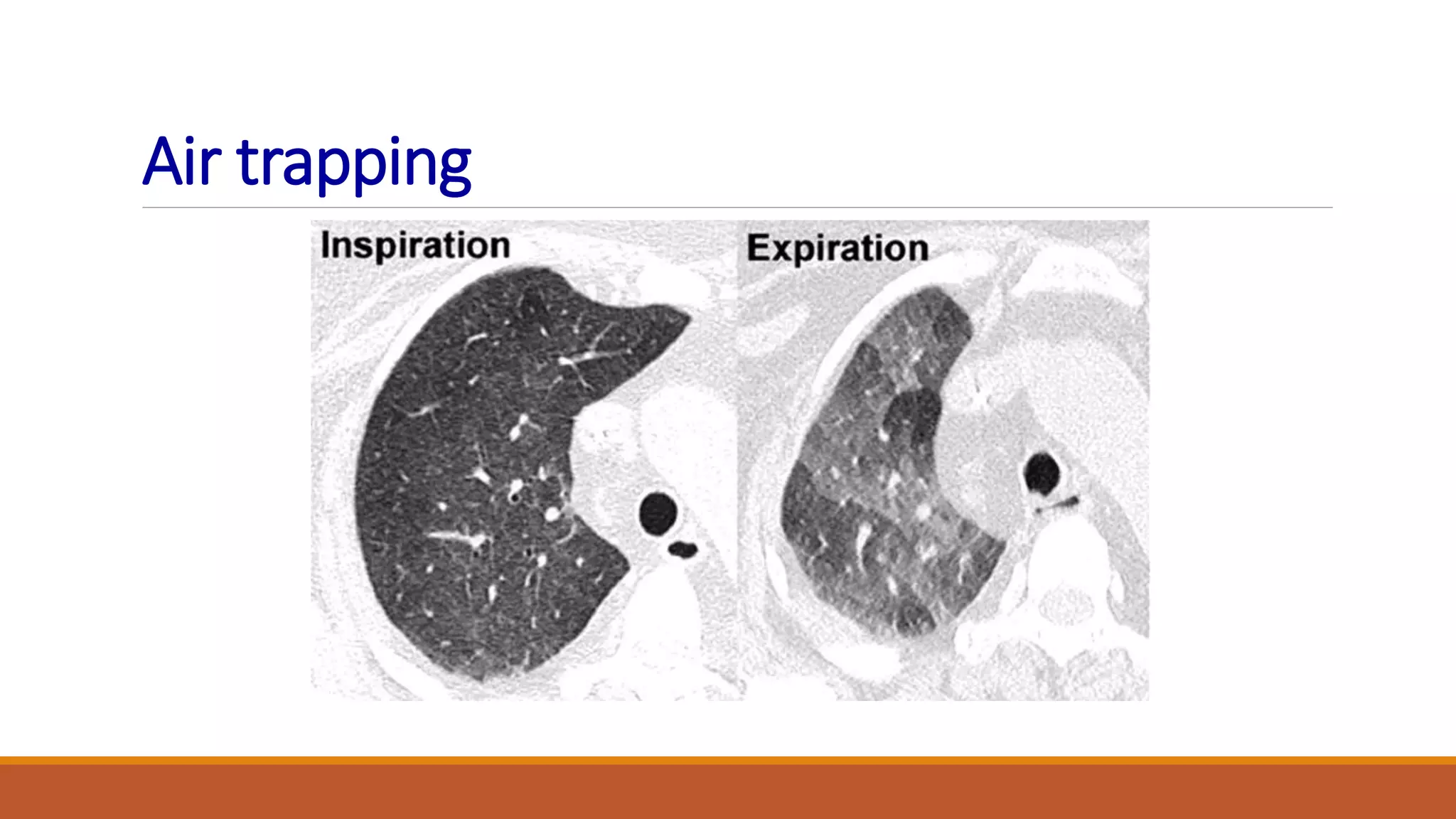
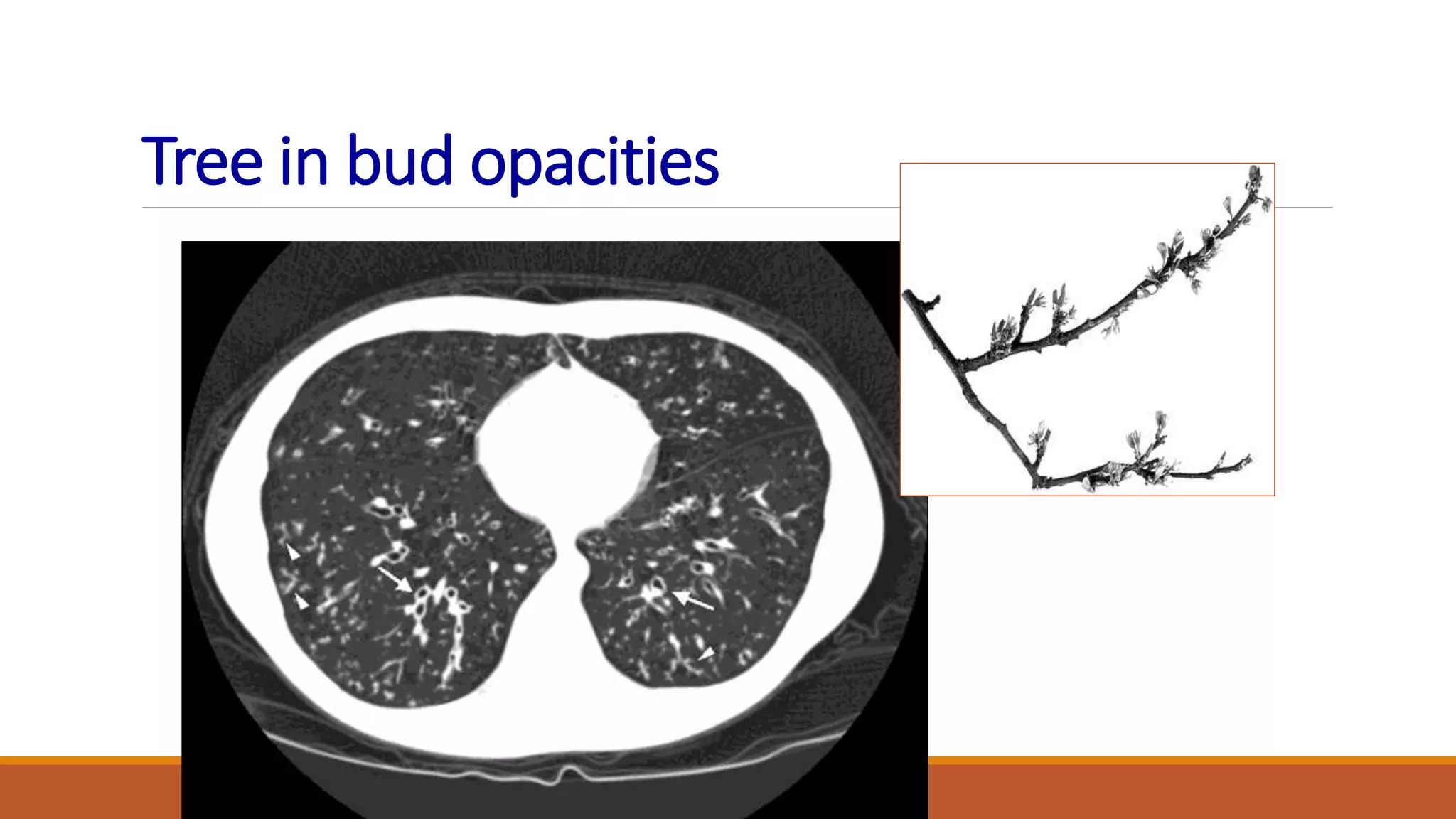
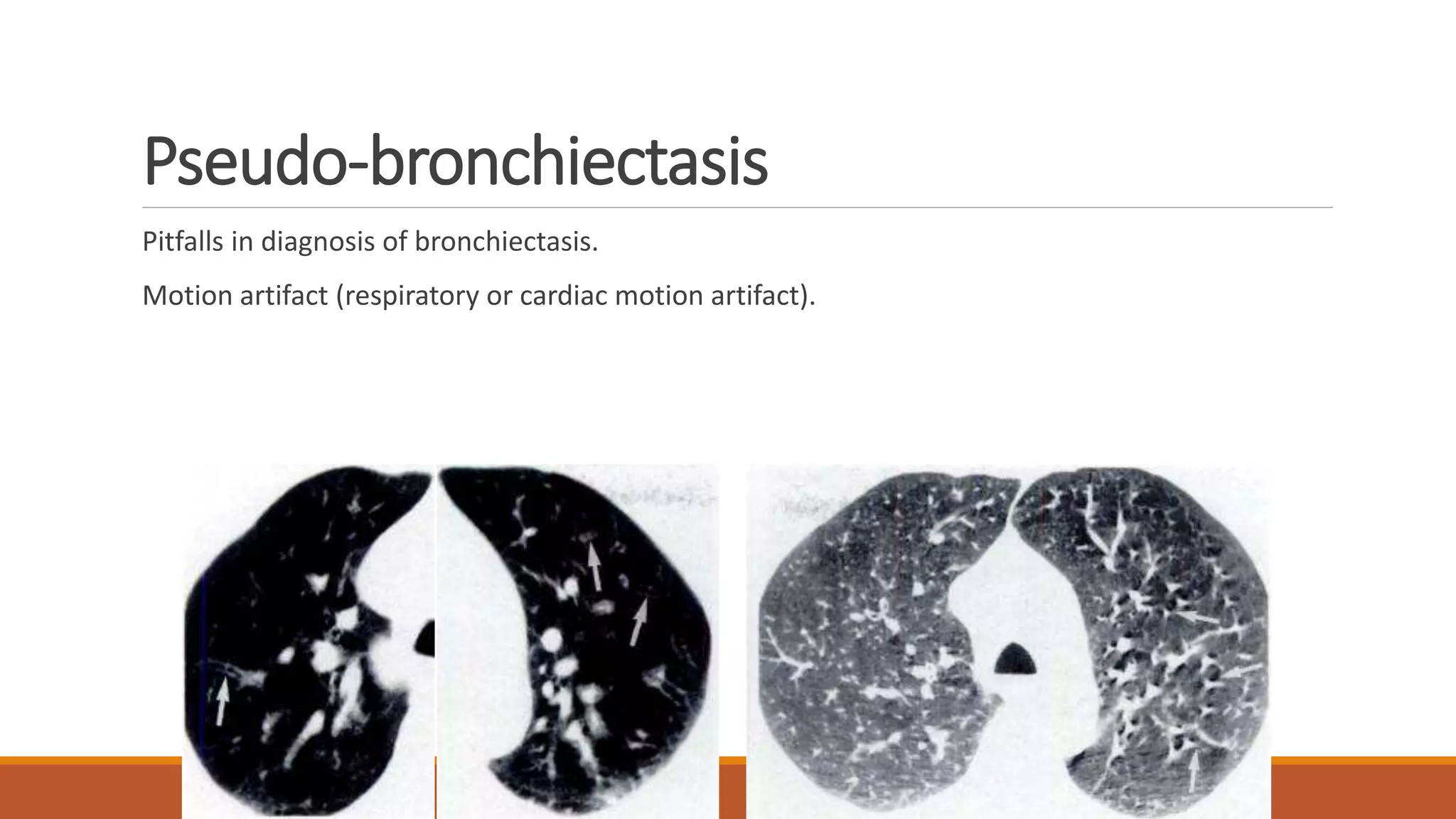
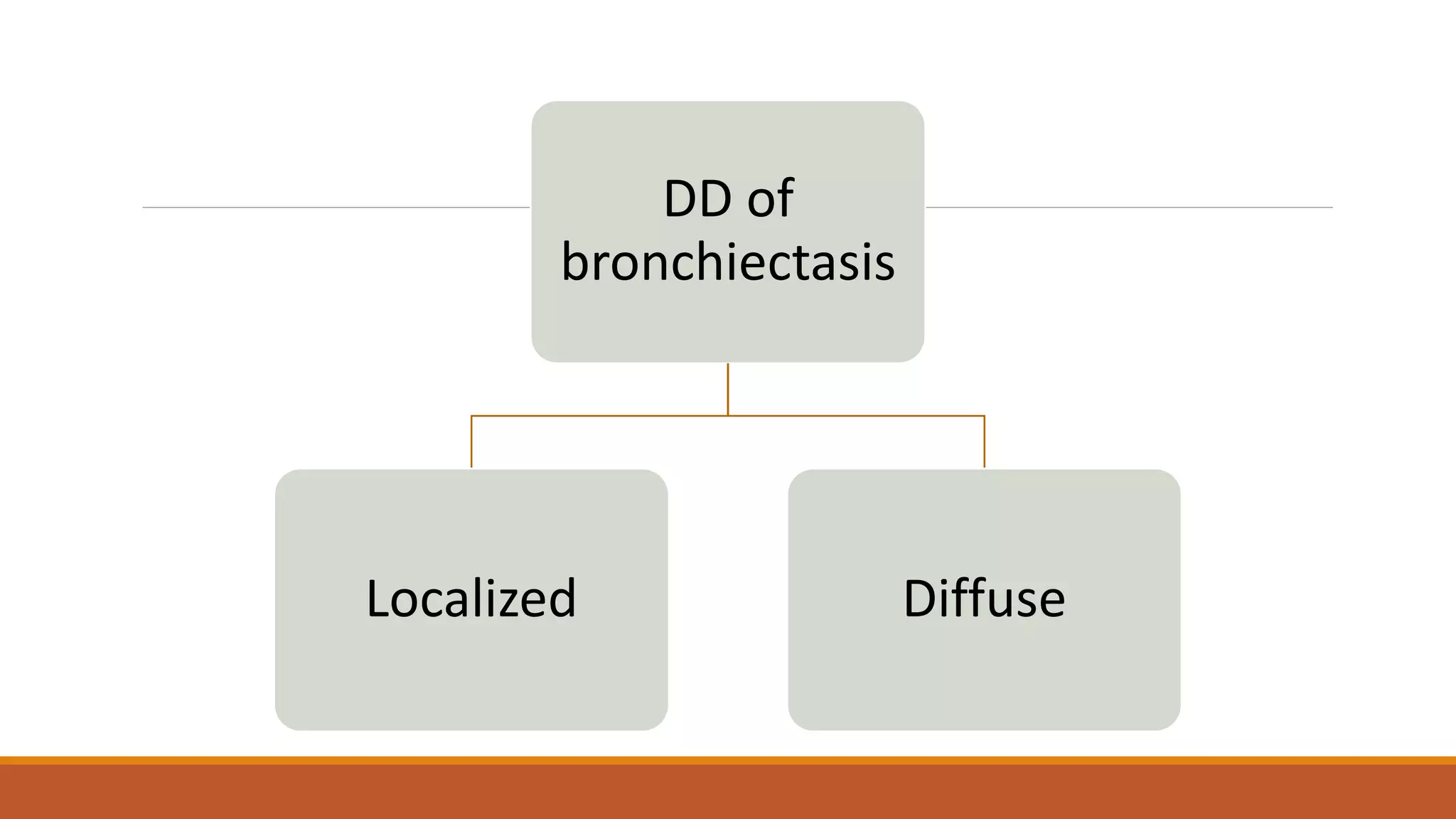
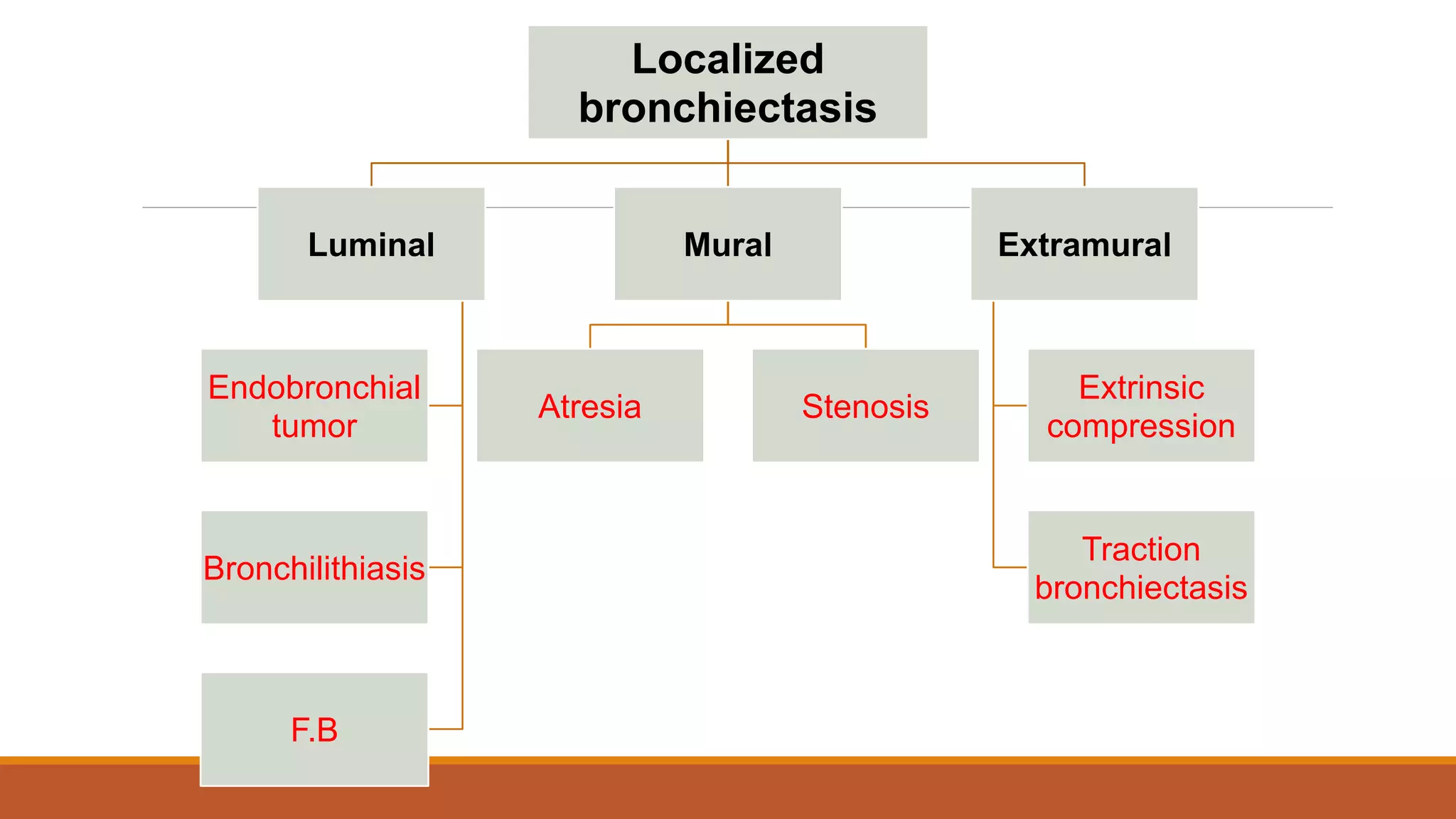
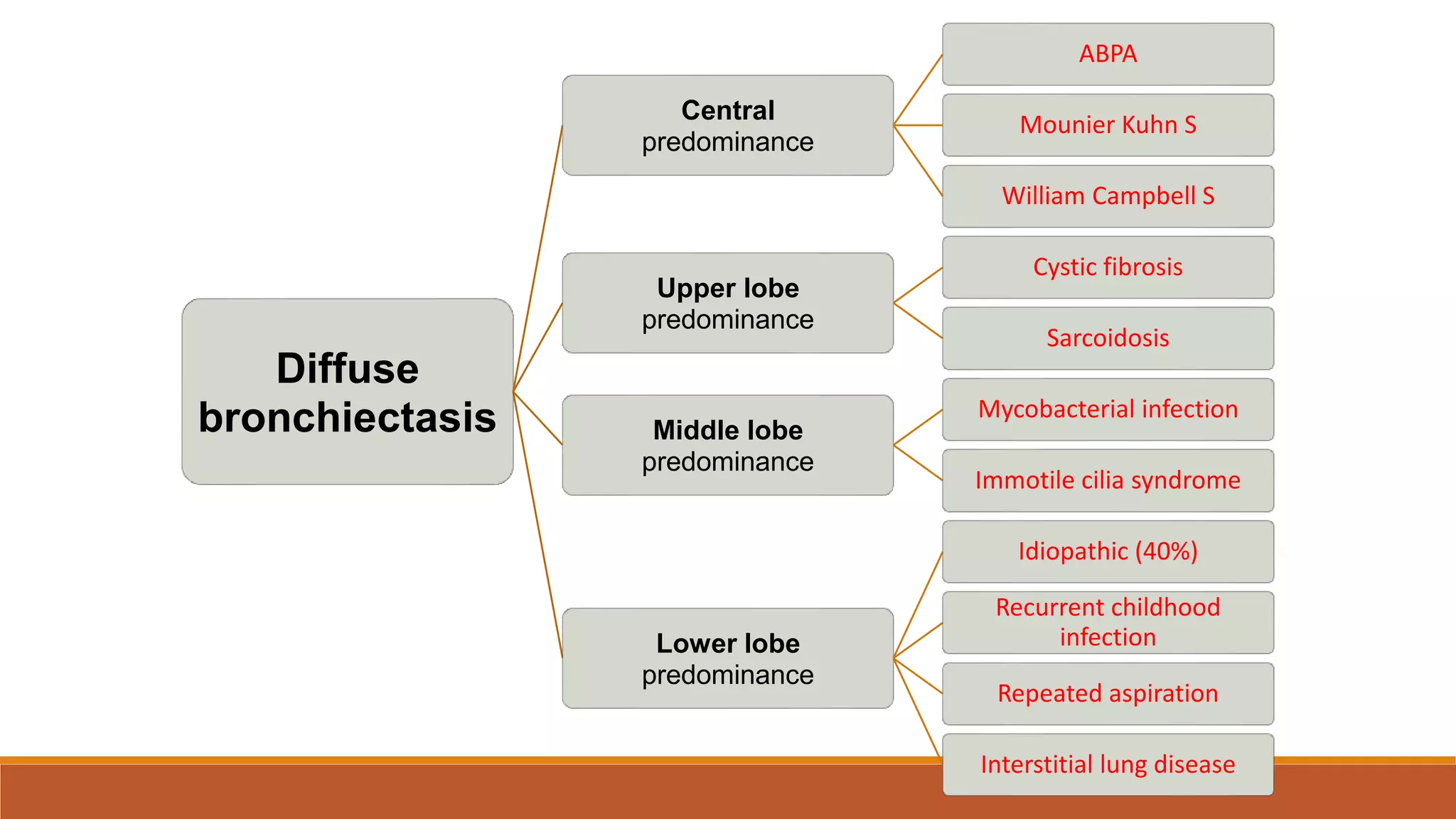
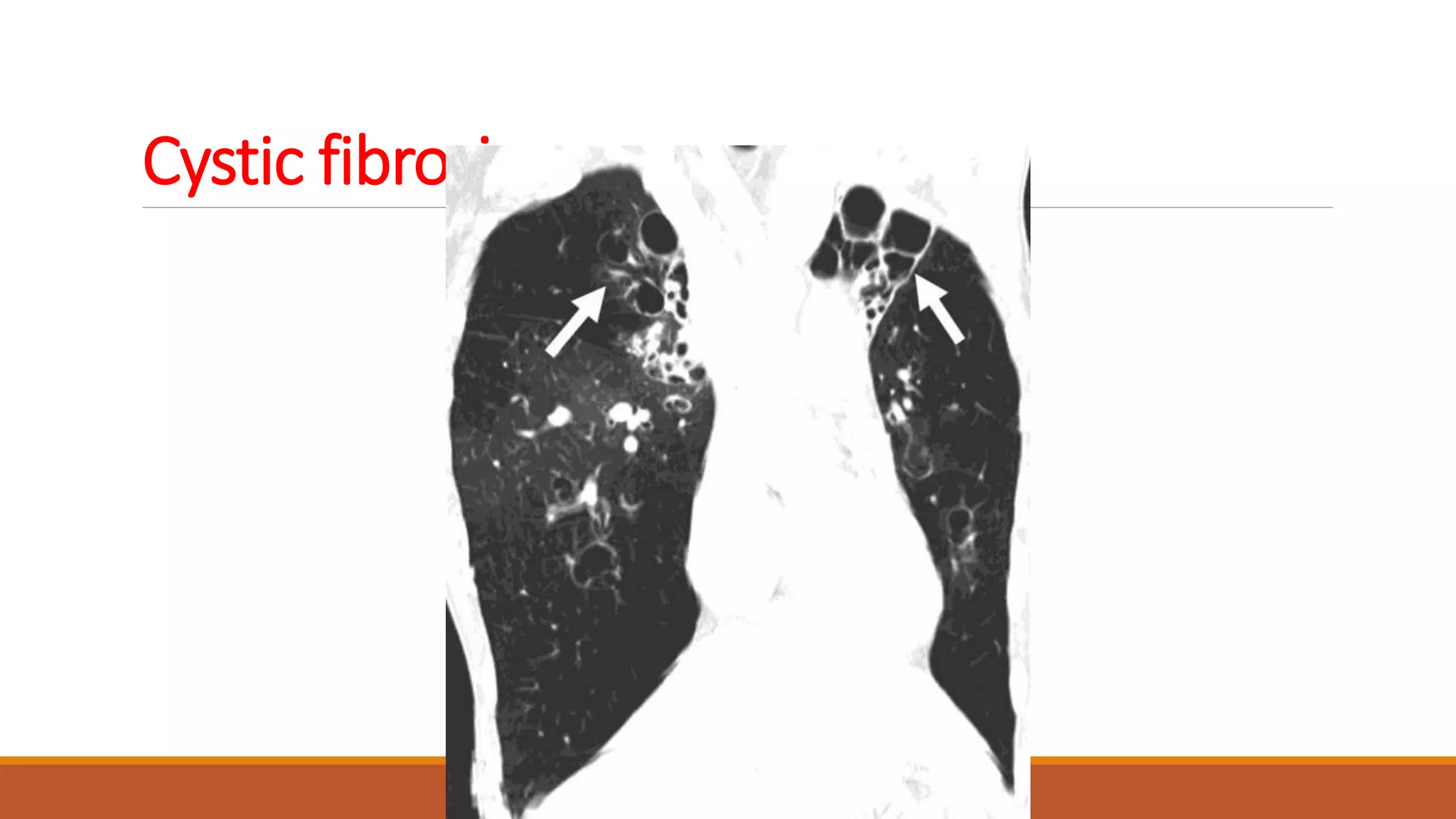
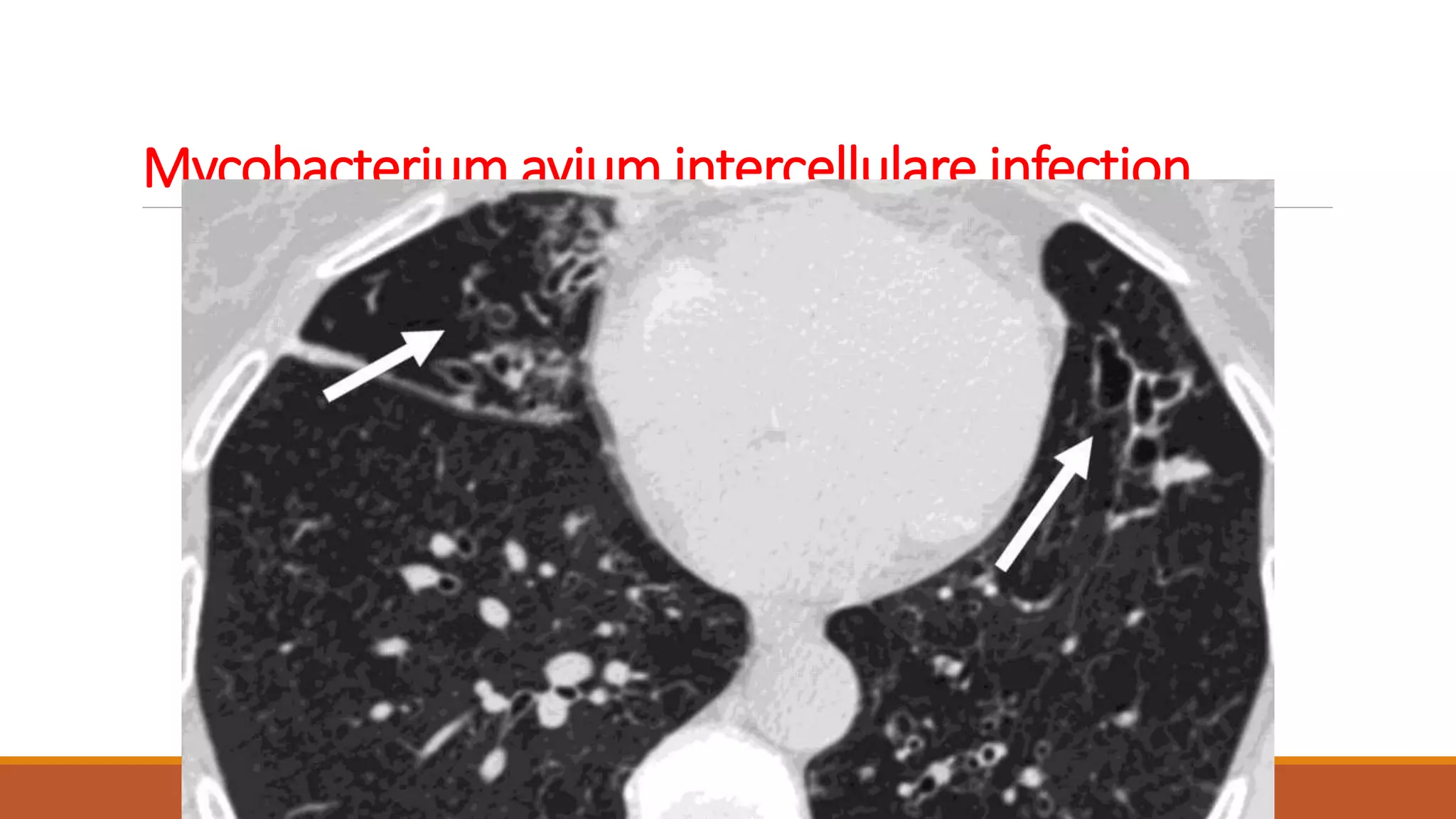
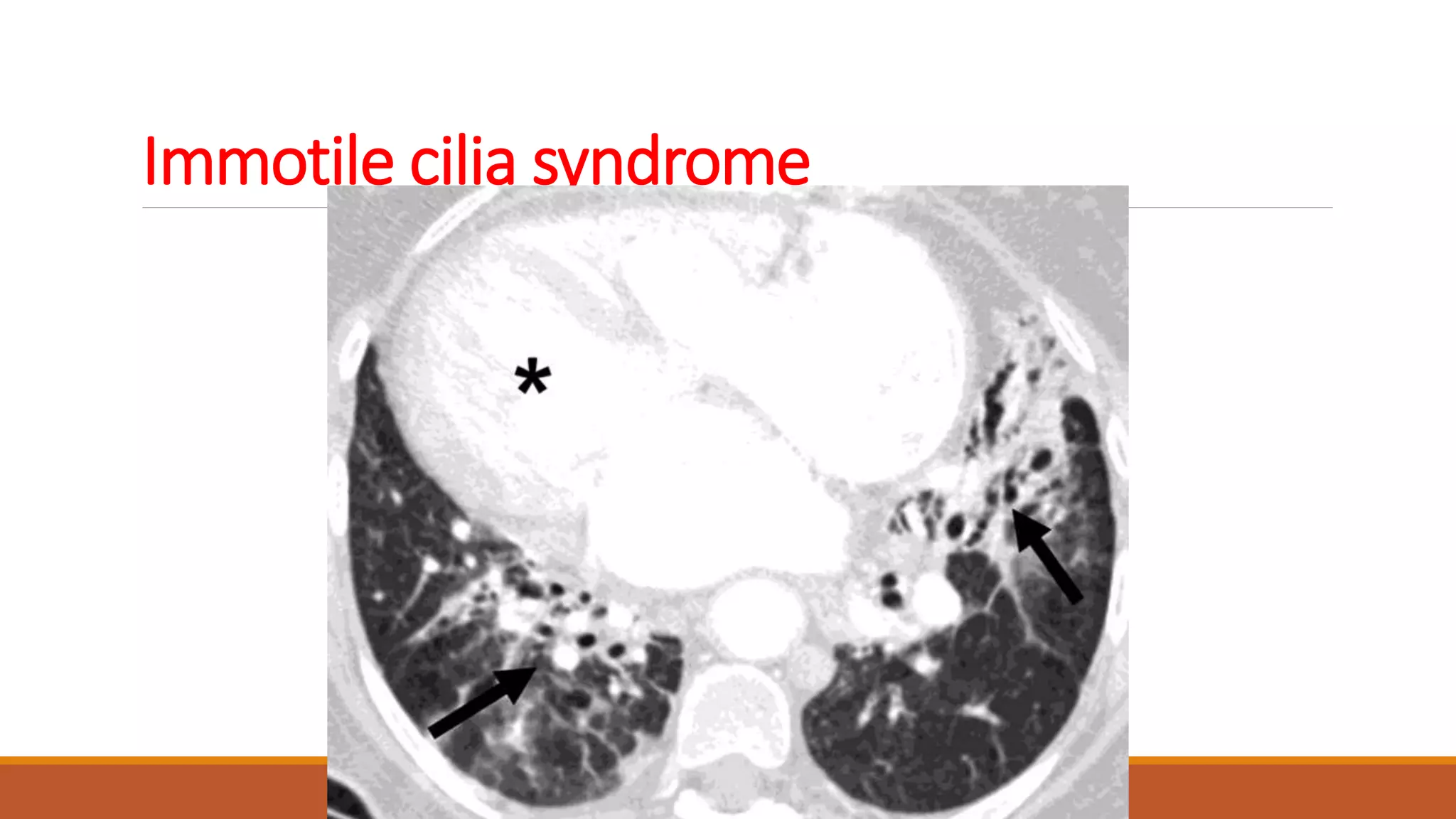
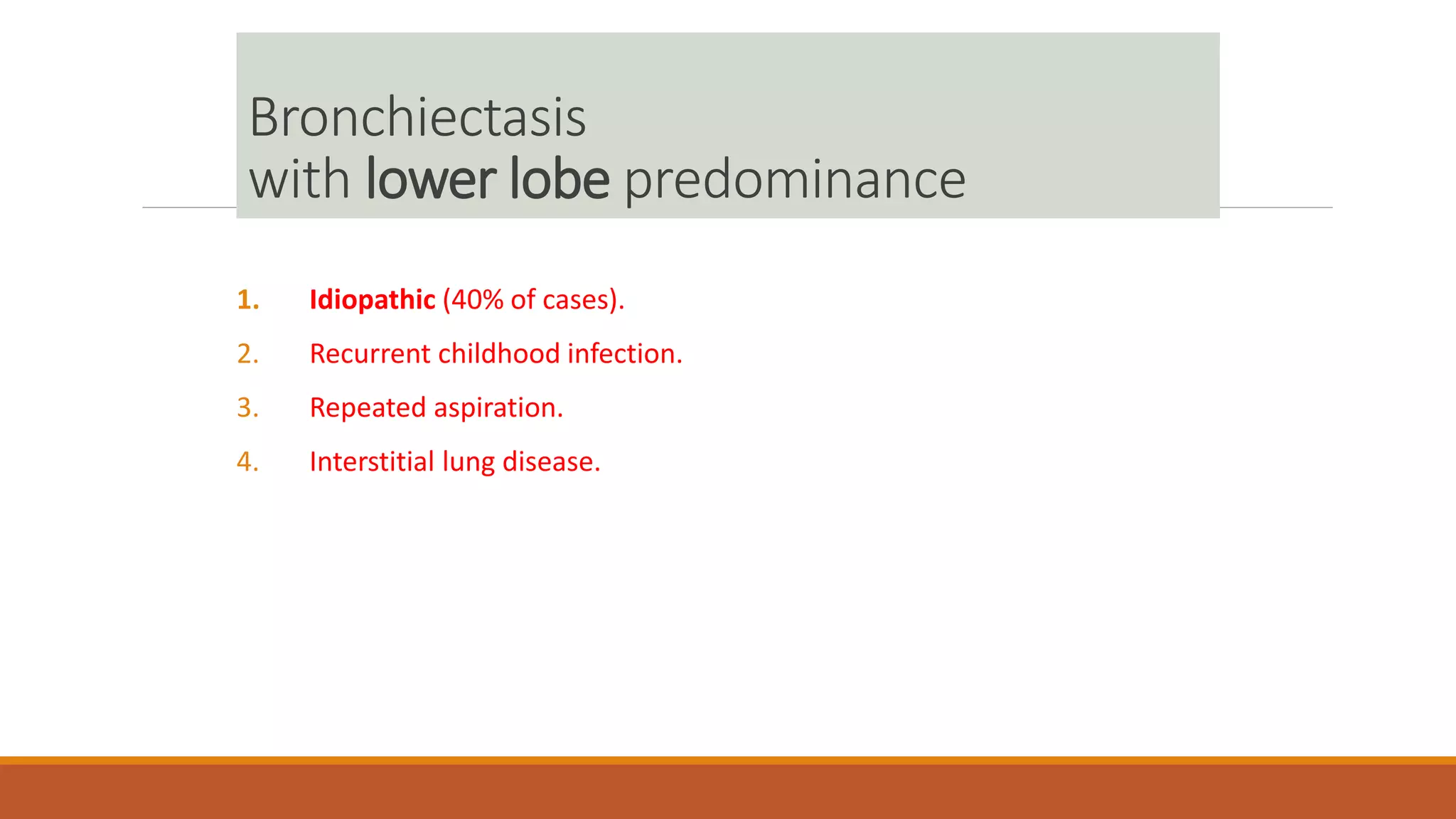
Bronchiectasis is the irreversible dilatation of the airways. It can be cylindrical, varicose, or cystic in appearance. Common causes include post-infection, infection by bacteria or mycobacteria, airway obstruction, and immunodeficiencies. Symptoms include persistent cough with sputum, hemoptysis, dyspnea, and wheezing. Diagnosis involves chest x-ray, CT scan, sputum culture, and lung function tests. Treatment goals are to eliminate the cause, improve airway clearance, control infection, and reverse airflow obstruction using antibiotics, chest physiotherapy, bronchodilators, and surgery in some cases.