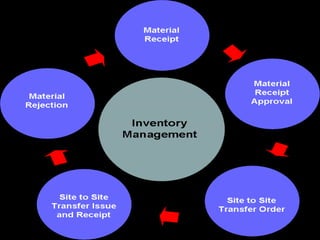
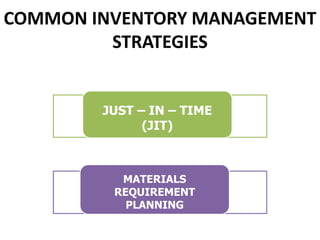
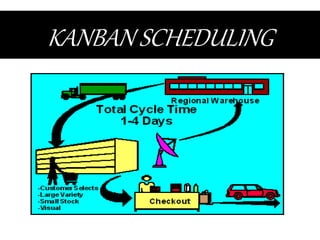
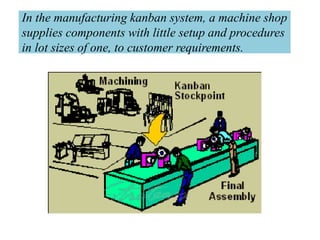
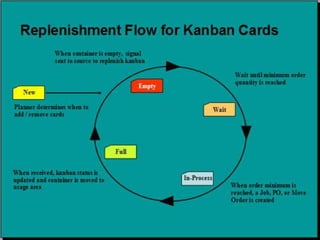
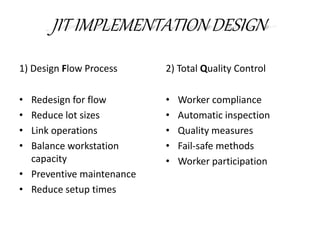
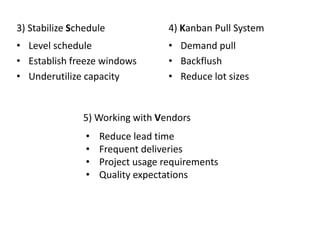
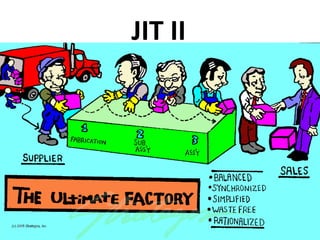
This document discusses inventory management strategies like just-in-time and kanban. It defines inventory, inventory management, and common strategies. It also discusses how mismanagement can lead to financial and supply problems. Key terms are defined, like kanban cards and the kanban scheduling system. Implementation of strategies at companies like Toyota and Dell are summarized, noting how both effectively deliver products when needed through supply chain visibility and minimal inventory.