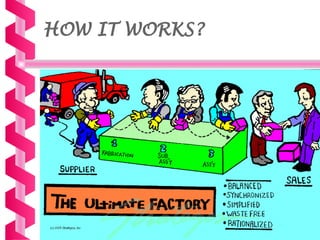
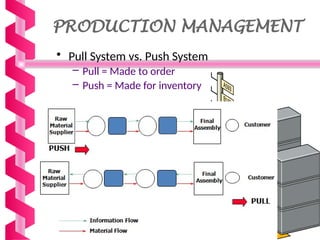
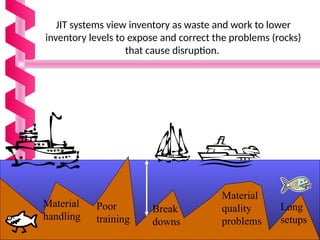
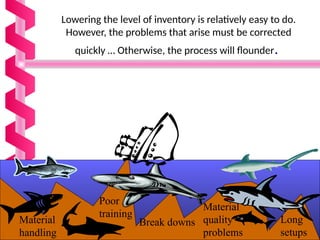
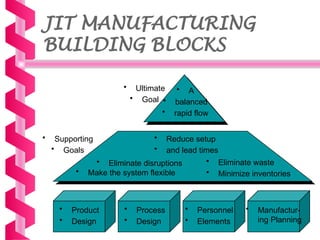
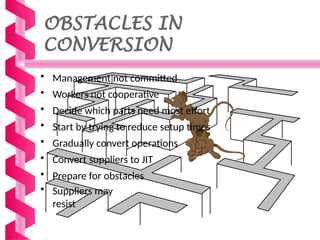
Just-in-time (JIT) is a manufacturing philosophy aimed at producing goods with minimal inventory for efficiency, developed in Japan by Taiichi Ohno at Toyota post-World War II. It emphasizes the elimination of waste, quality management, and a pull production system, while also establishing strong supplier relationships and fostering employee involvement. JIT has various advantages, including high quality and flexibility, but presents challenges such as supply risks and management commitment.