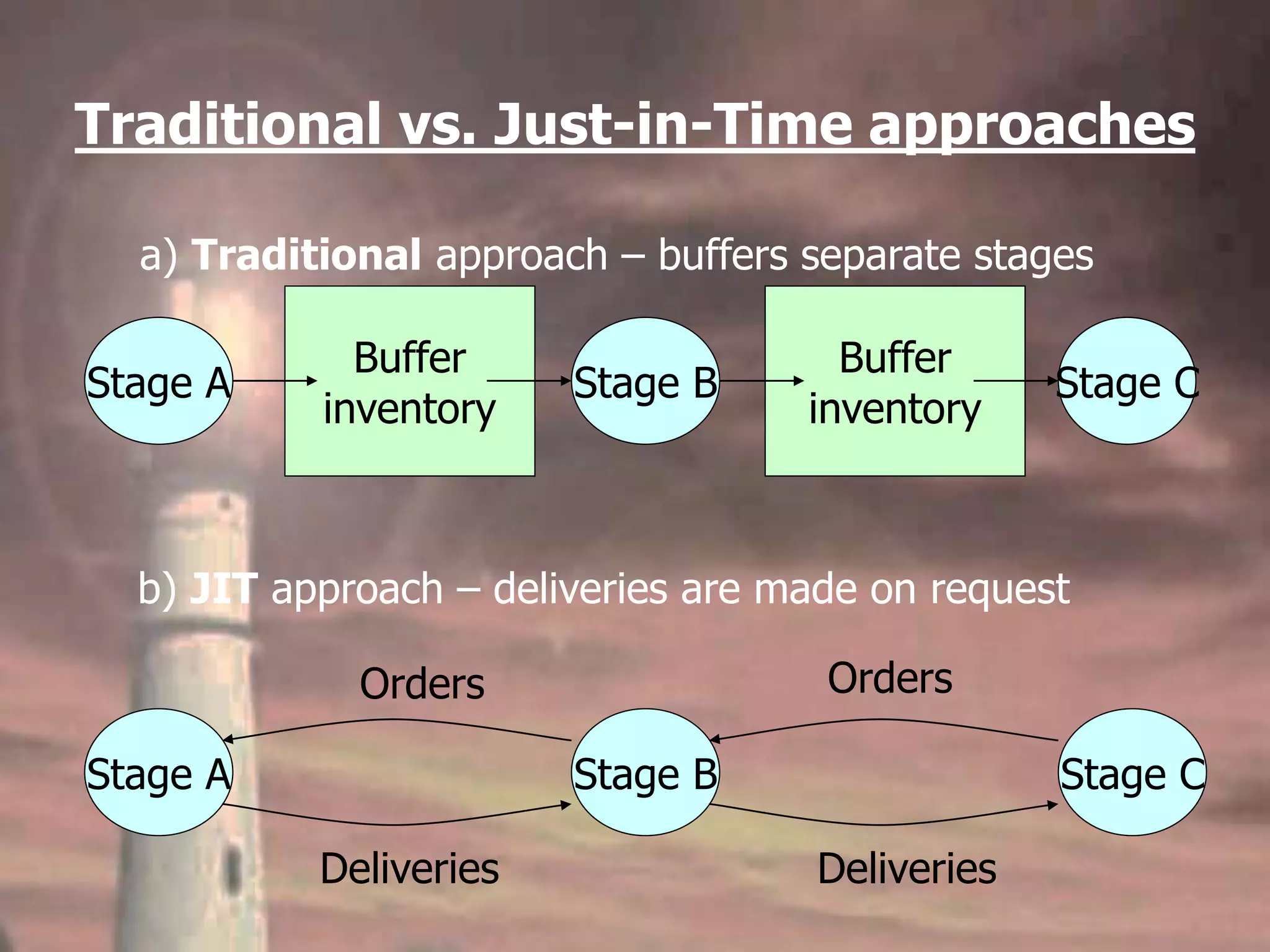
Lean operations aim to remove all non-value adding activities to deliver a faster, more dependable, higher quality and lower cost operation that is more responsive to customers. Just-in-time means producing goods exactly when needed to avoid inventory waste. The lean philosophy focuses on eliminating waste, involving everyone, and continuous improvement. Key lean techniques include visual management, small batch production, pull scheduling, total productive maintenance, and design for manufacturability. Lean and MRP planning approaches can be combined if their advantages are understood and preserved.