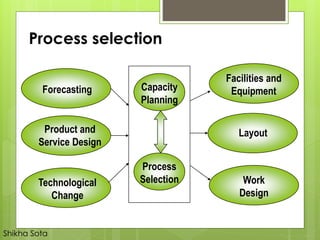
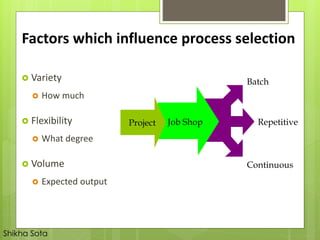
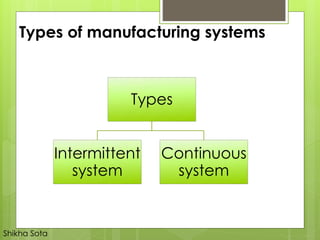
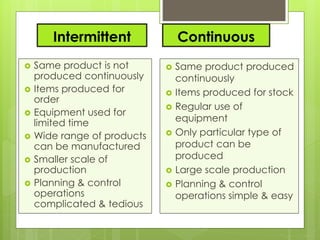
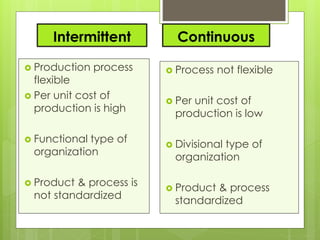
The document discusses different types of production systems and factors that influence process selection. It describes four main types of production systems: project, job, batch, and mass production. It also discusses intermittent and continuous manufacturing systems. Key factors that influence process selection include variety, volume, flexibility, and expected output. Process selection impacts capacity planning, facility layout, equipment design, and work design.