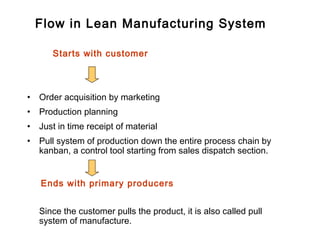
Lean manufacturing is a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste through continuous improvement by producing only what the customer needs. It aims to provide customers what they want, how they want it, where they want it, at a competitive price and always with expected quality. The core of lean manufacturing is reducing waste leading to improved quality, higher throughput, better efficiency and higher profitability. It utilizes tools like just-in-time, total productive maintenance, 5S, and visual controls to maximize flow and minimize waste.