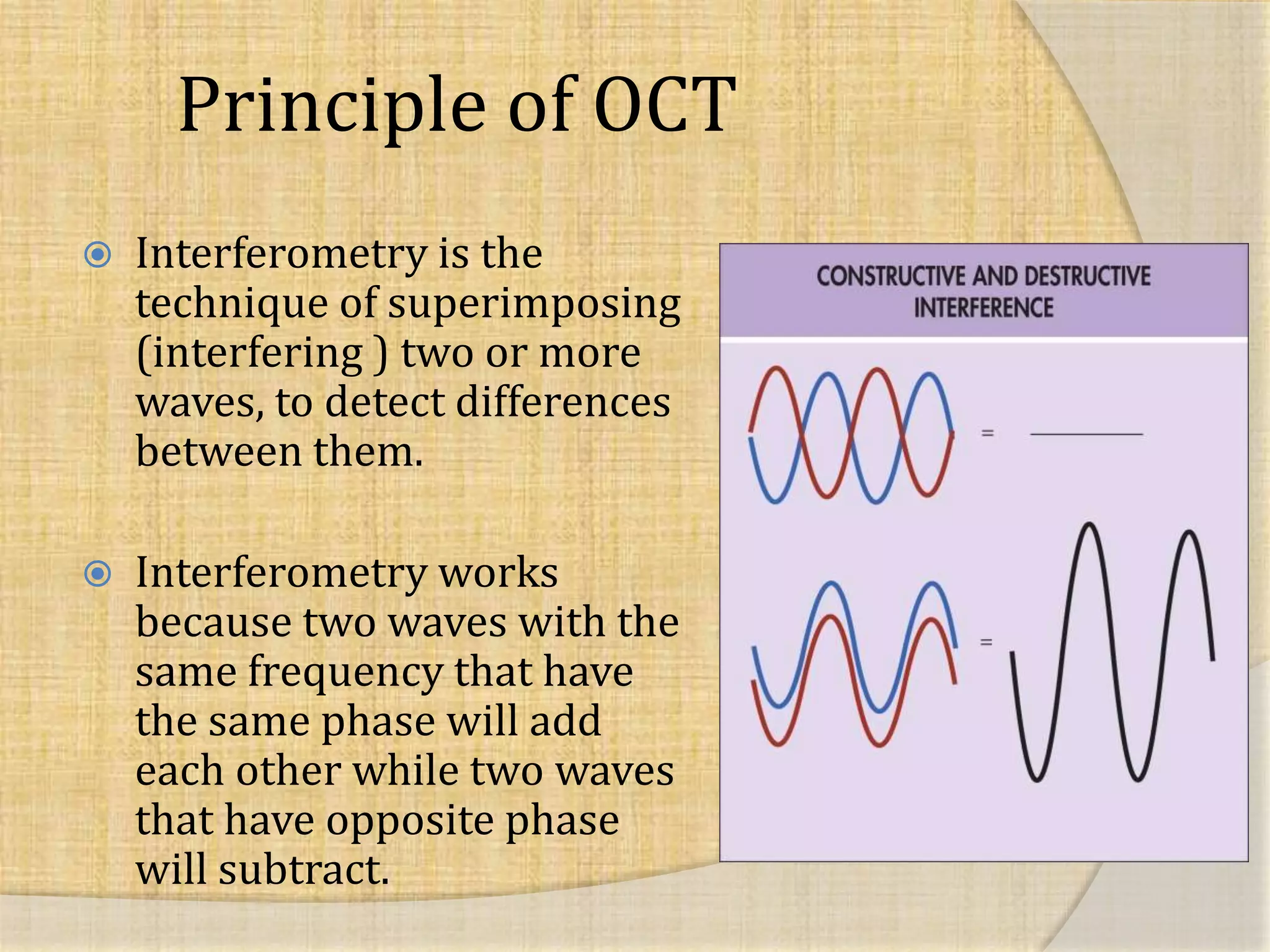
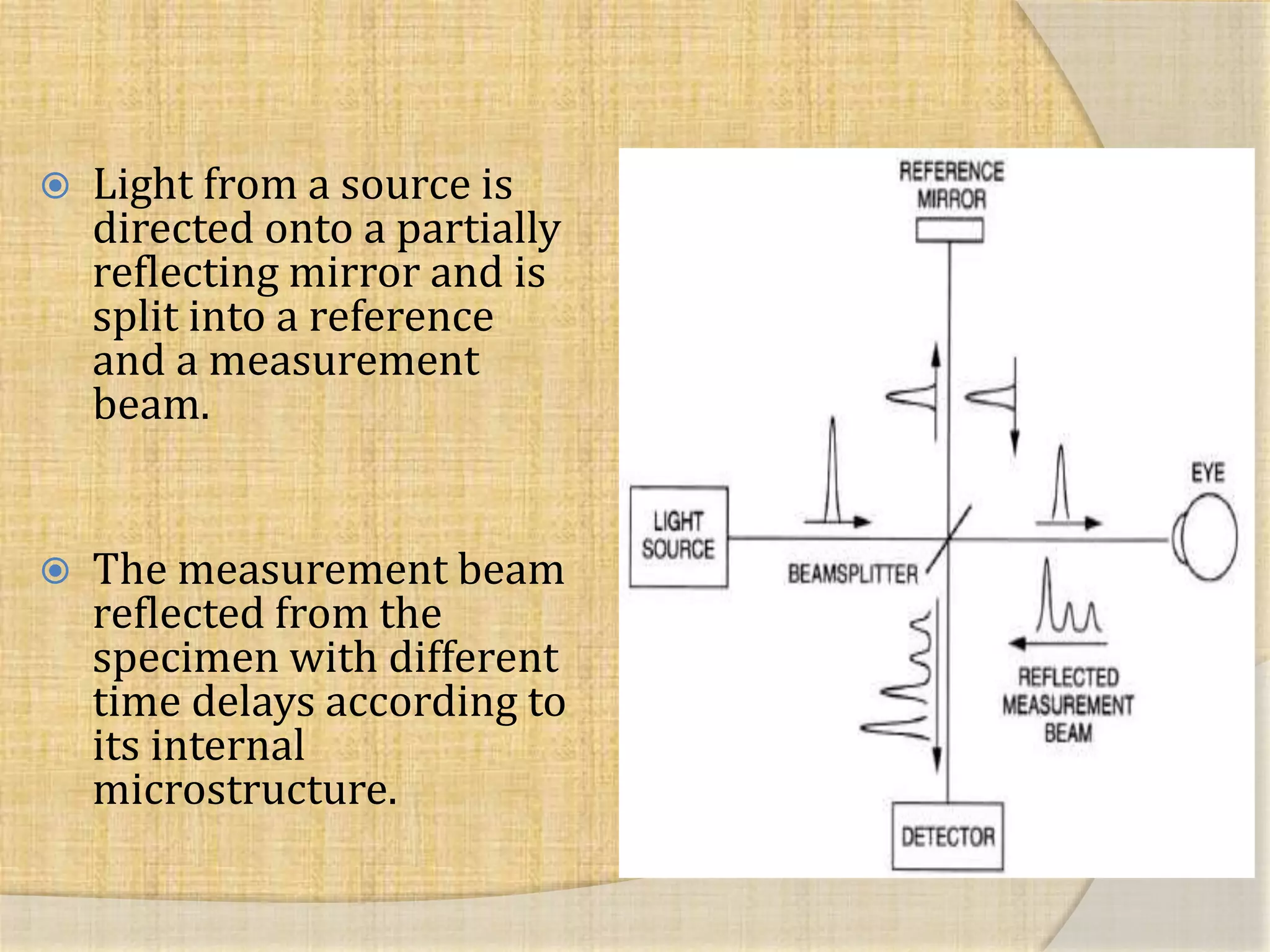
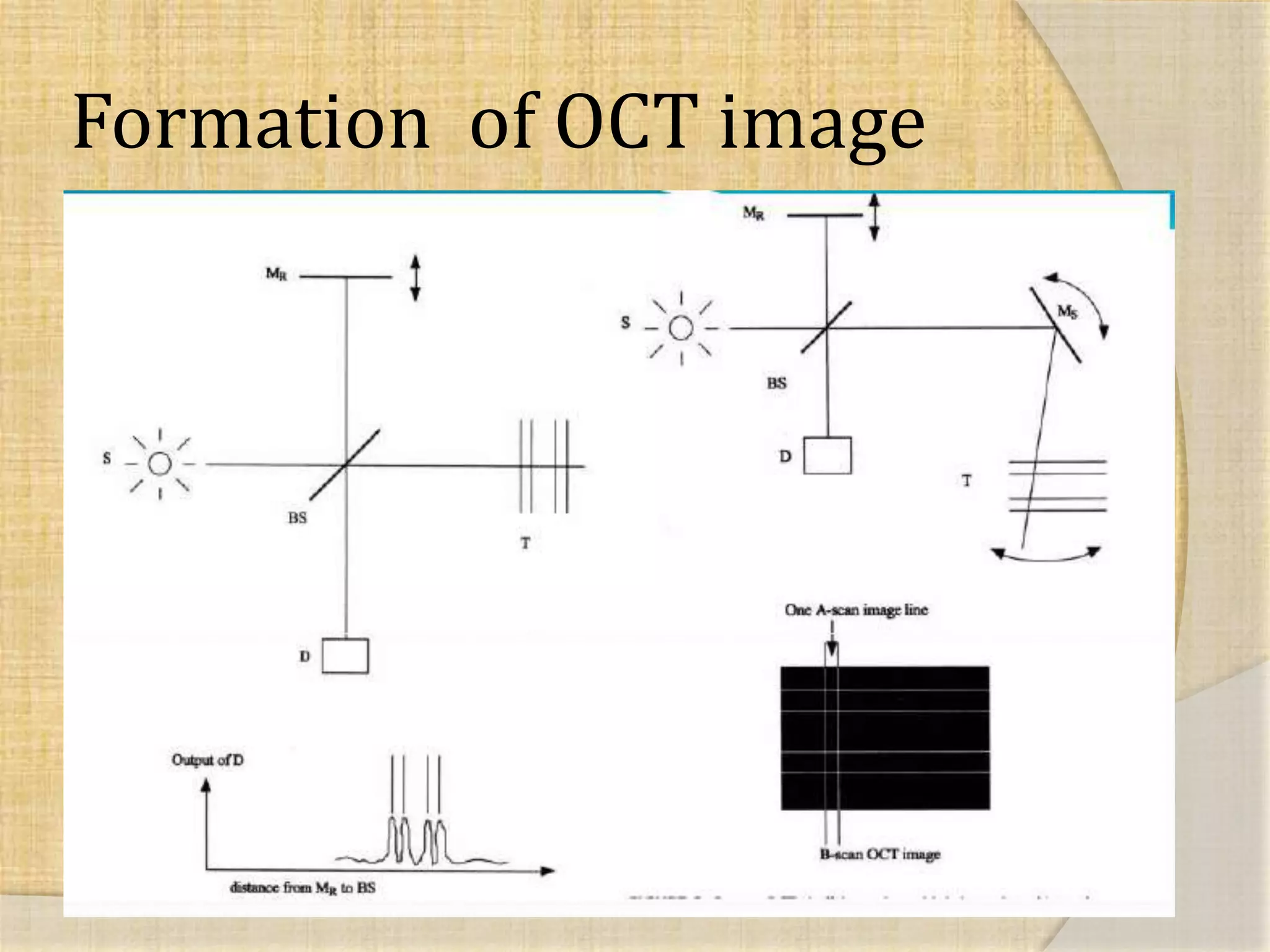
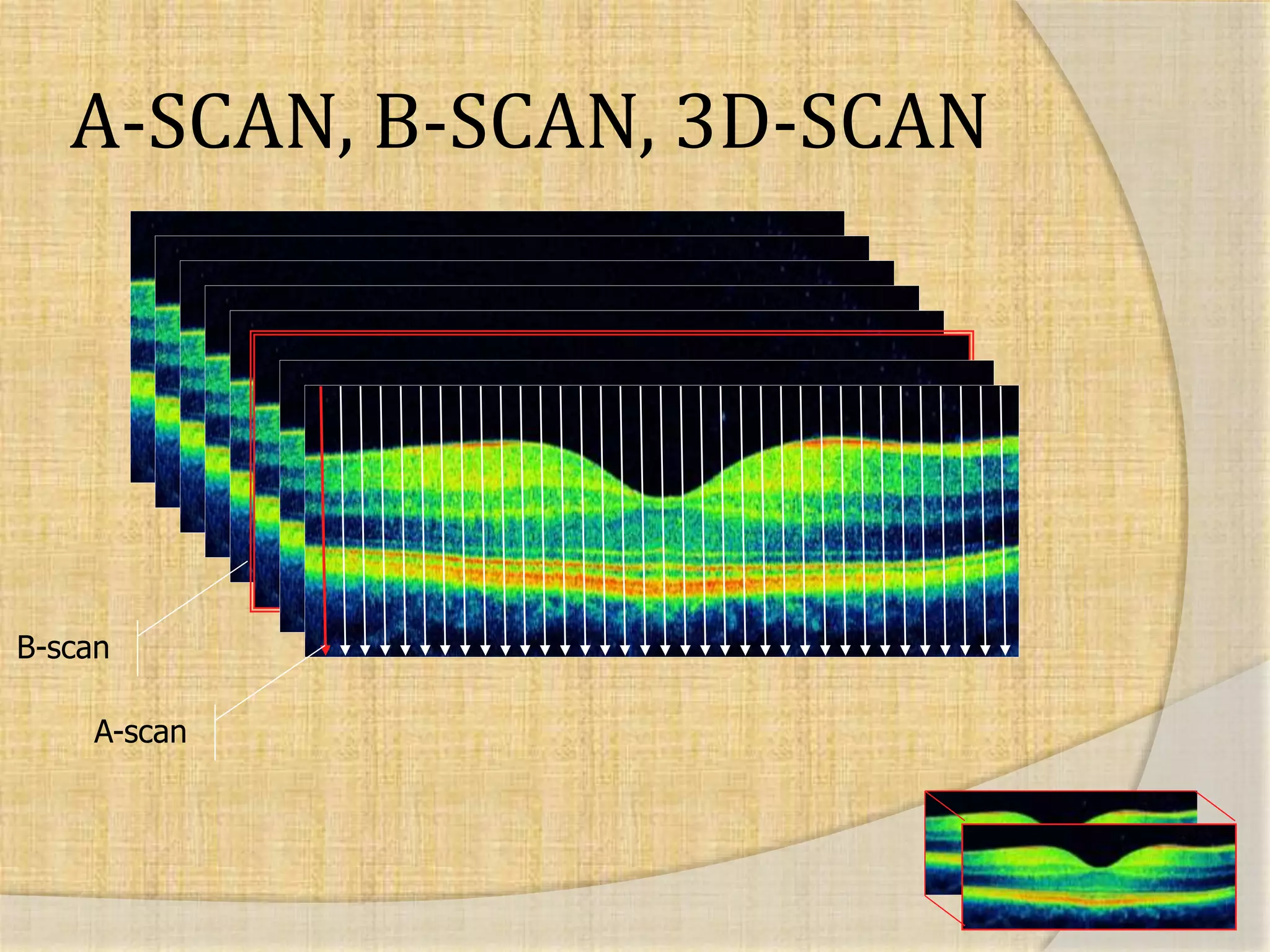
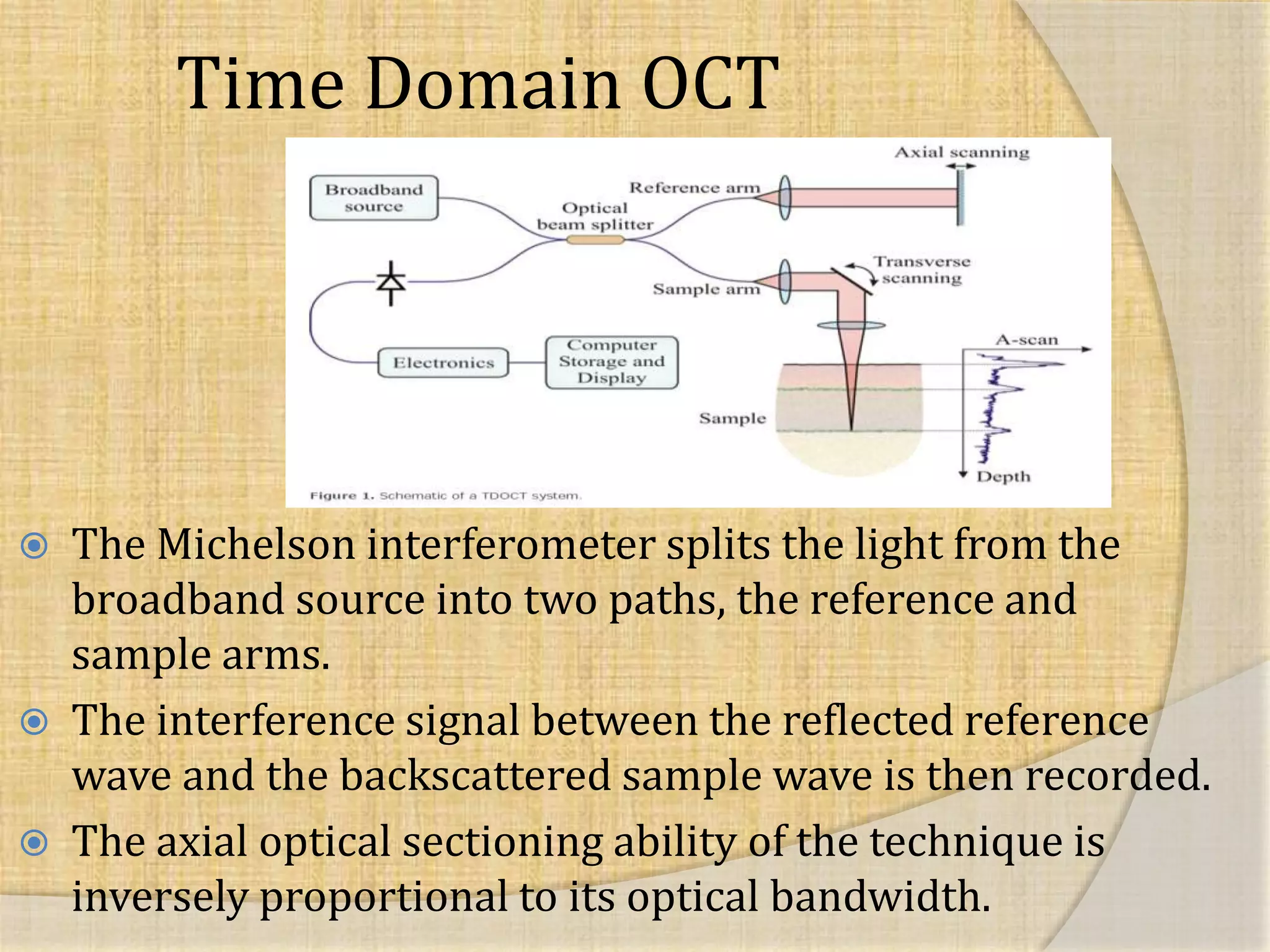
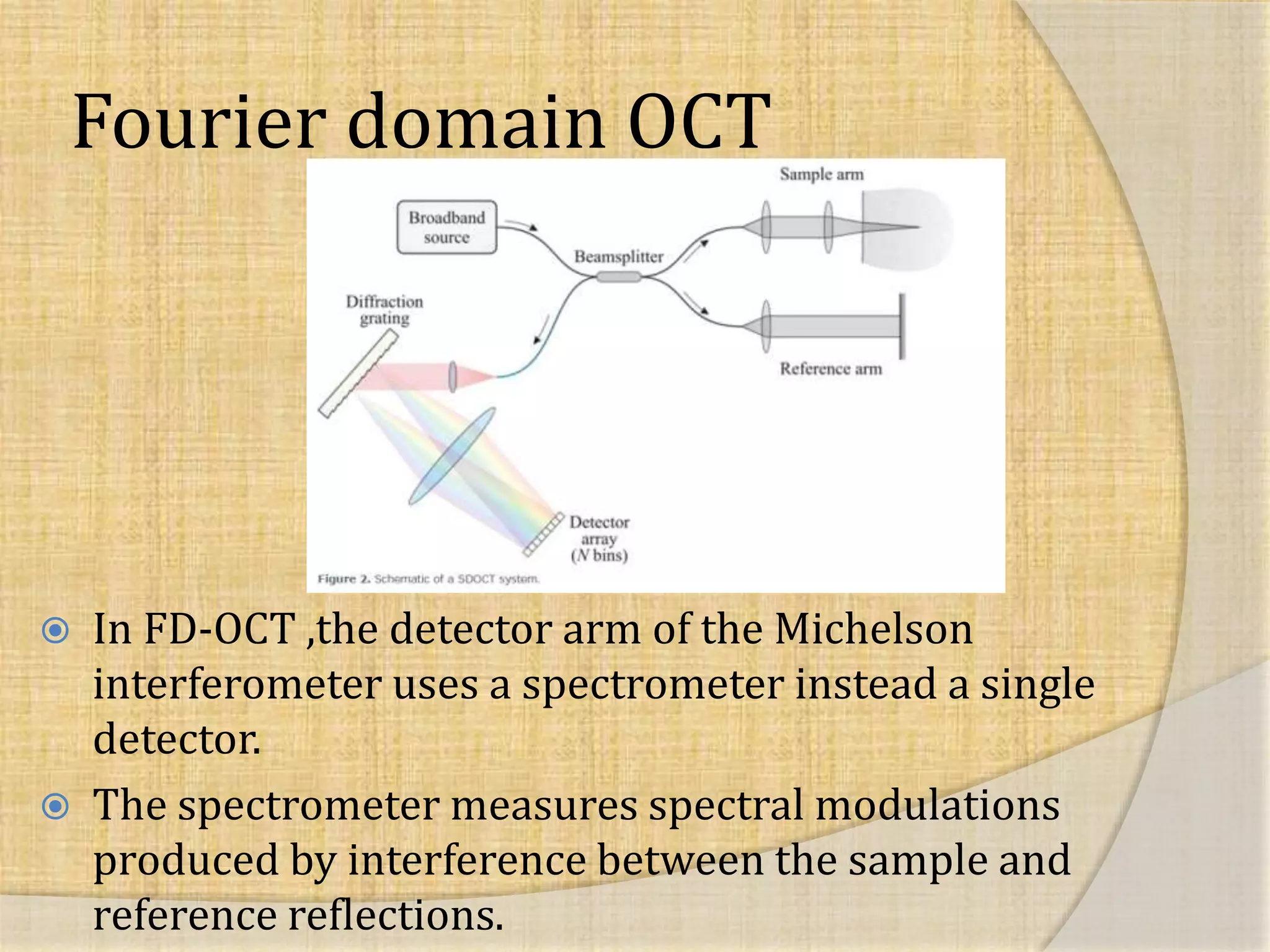
OCT uses interferometry to perform non-invasive imaging of biological tissues. The first OCT images of the retina were obtained in 1990. Time domain OCT works by scanning a reference mirror to measure echo time delays, while Fourier domain OCT measures spectral interference patterns without scanning. Fourier domain OCT allows for much faster acquisition speeds compared to time domain OCT. Integrating OCT with scanning laser ophthalmoscopy enables localization of OCT scans on fundus images.