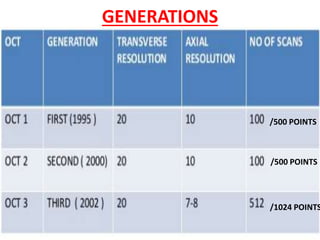
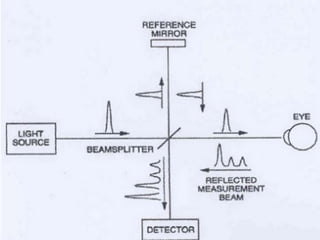
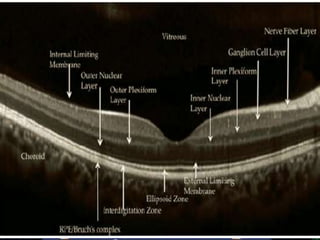
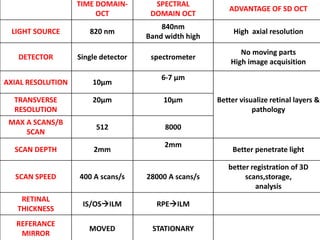
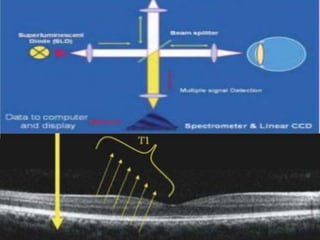
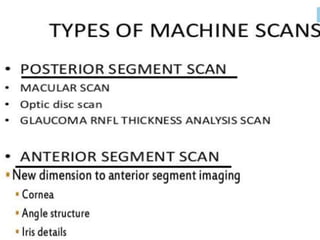
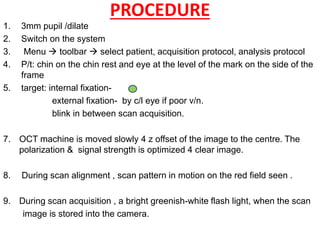
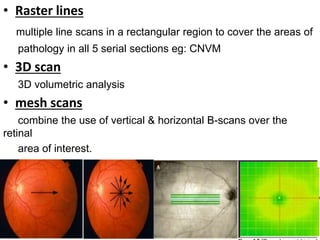
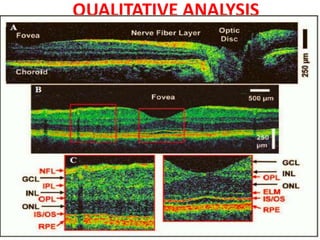
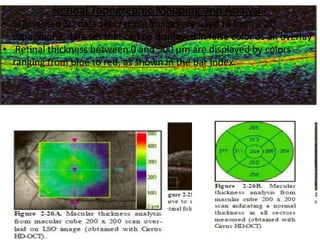
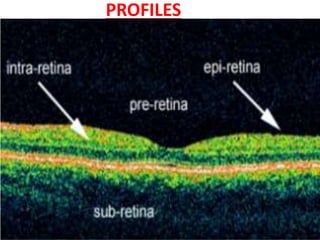
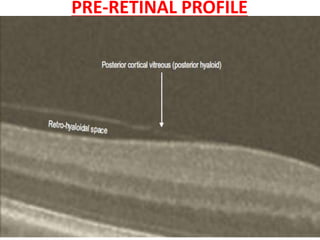
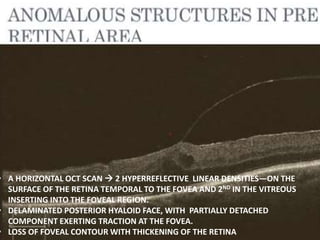
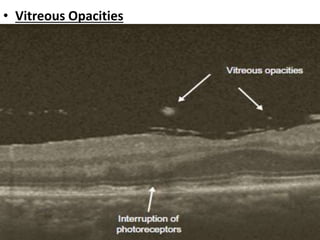
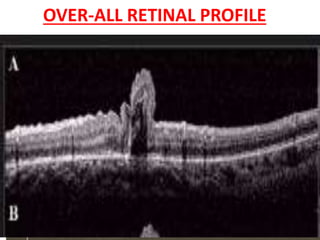
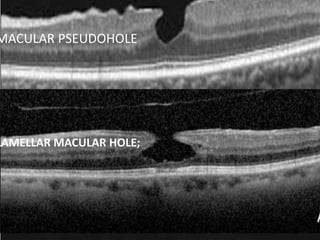
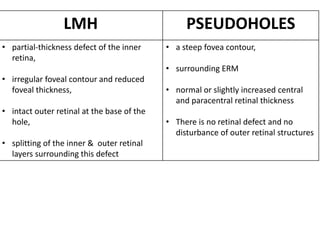
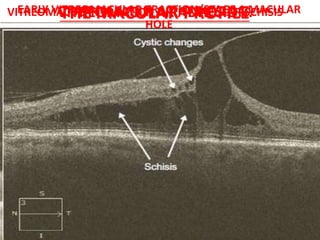
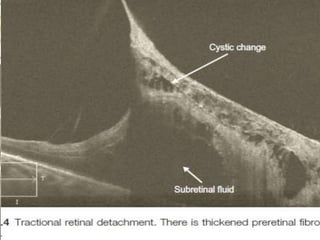
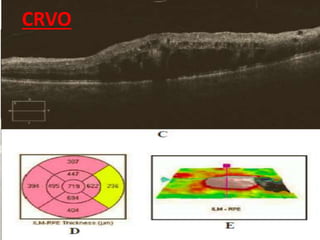
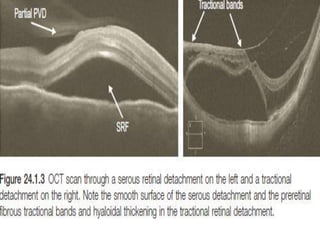
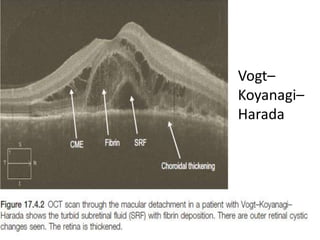
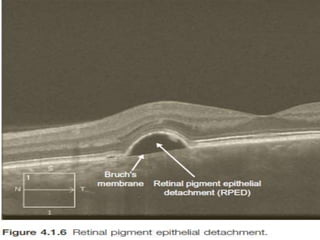
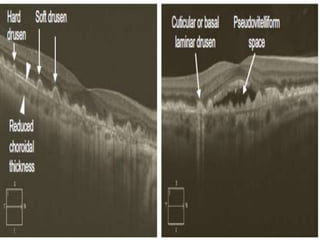
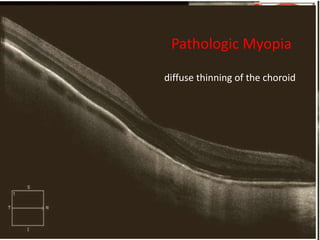
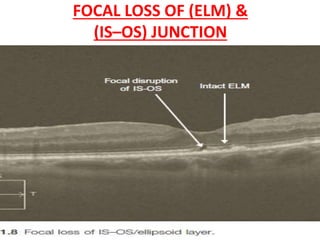
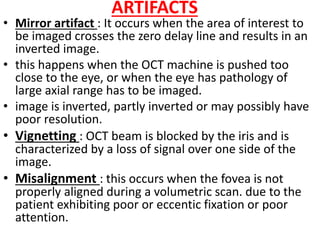
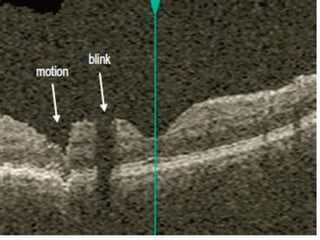
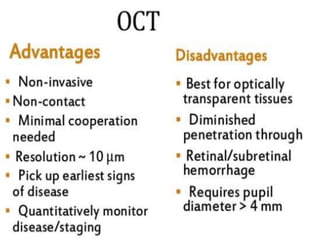
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) provides high resolution, cross-sectional images of the retina. OCT uses light waves to generate tomographic scans. Early OCT systems had axial resolutions of 10 μm and scan speeds of 400 scans/second. Newer spectral domain OCT systems have higher resolutions of 1-15 μm and faster scan speeds of up to 52,000 scans/second, allowing better visualization of retinal layers and pathology. OCT is used to qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate retinal morphology and thickness.