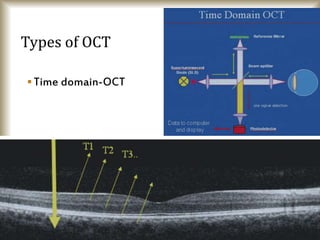
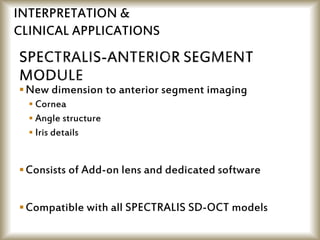
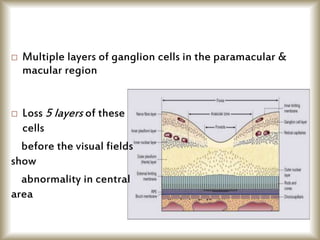
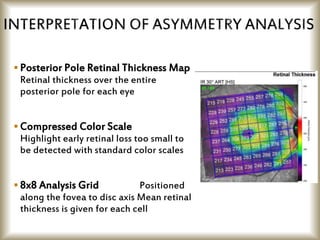
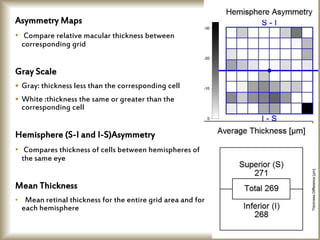
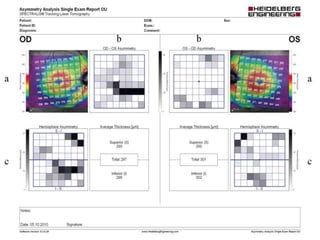
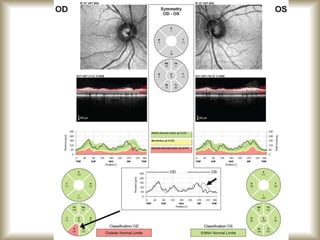
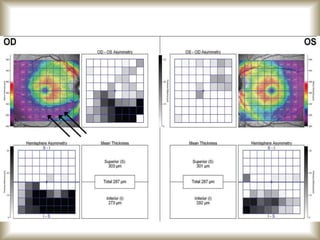
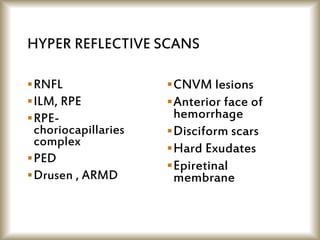
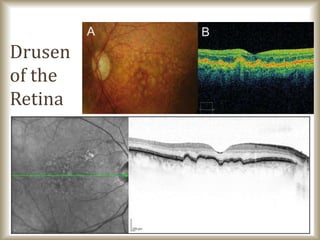
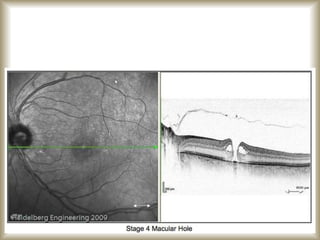
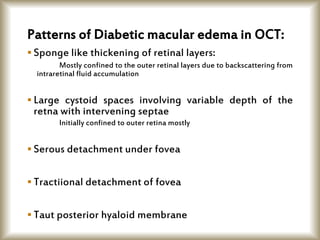
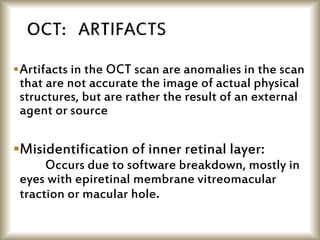
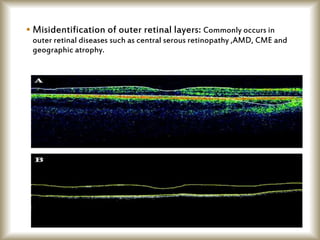
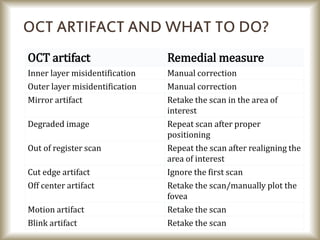
This document provides an overview of optical coherence tomography (OCT), including its history, principles, types, interpretation, clinical applications, limitations, and recent developments. OCT is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses infrared light to generate high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina and anterior segment. Newer spectral domain OCT systems provide faster scanning speeds and higher resolution compared to earlier time domain OCT systems. OCT is useful for diagnosing and monitoring retinal diseases like glaucoma as well as anterior segment conditions. Interpretation of OCT images involves identifying layers and structures that appear as various colors based on reflectivity. Recent advances include enhanced depth imaging to view deeper choroidal structures and software to quantify retinal thickness and nerve fiber layer measurements.