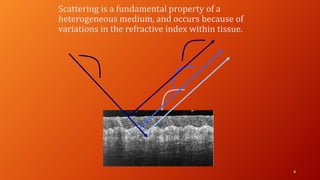
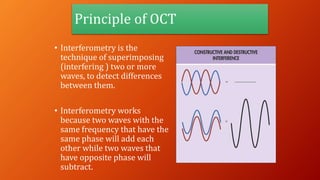
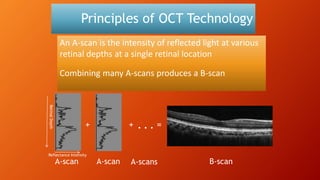
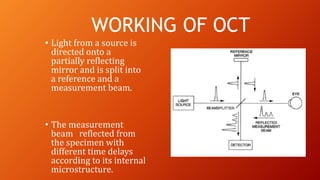
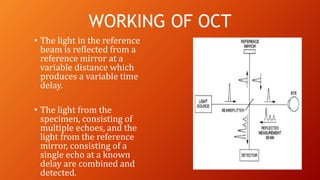
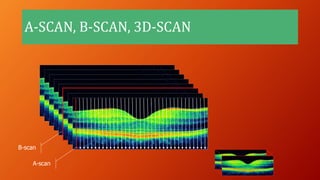
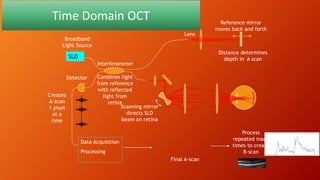
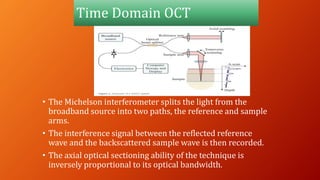
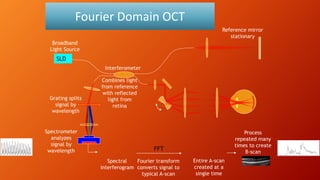
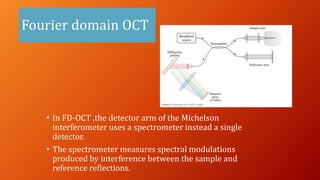
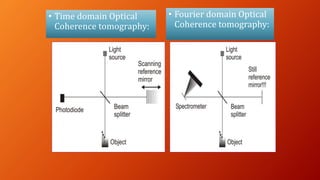
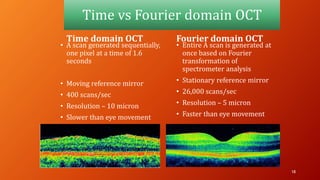
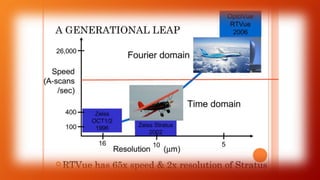
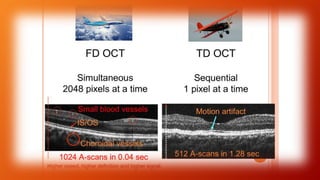
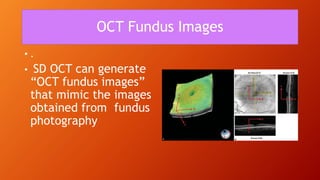
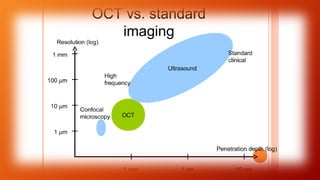
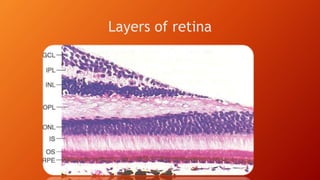
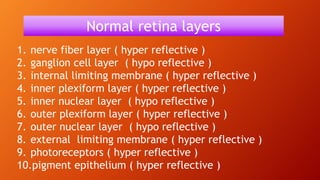
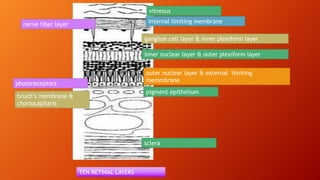
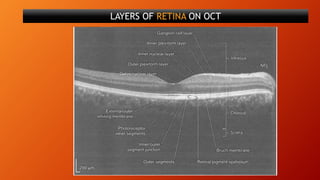
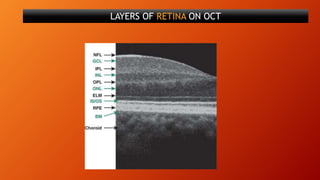
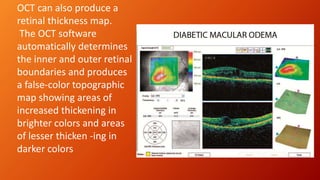
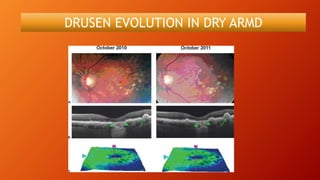
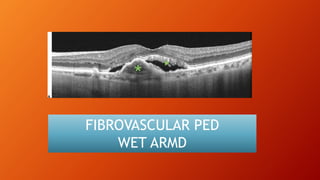
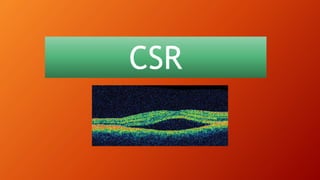
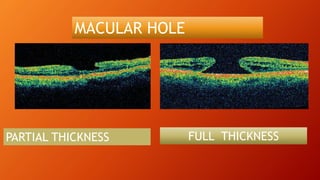
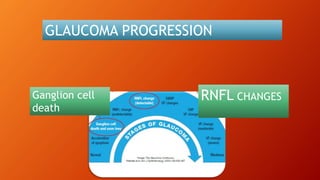
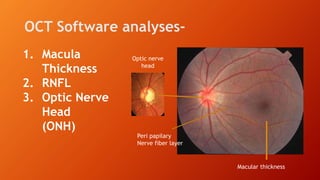
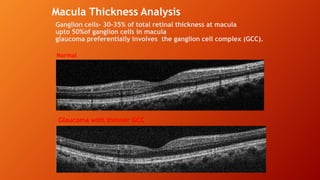
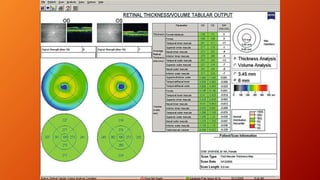
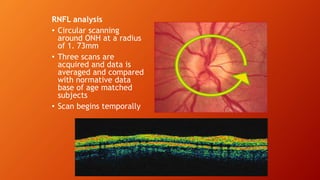
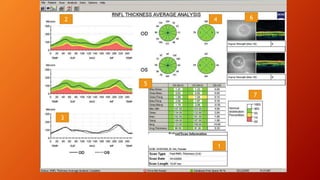
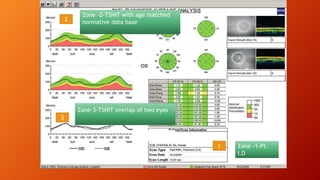
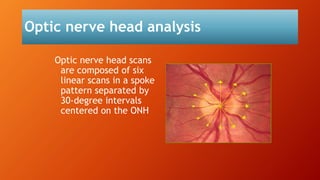
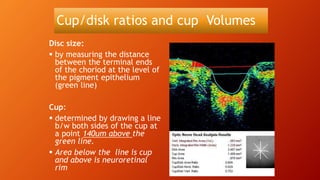
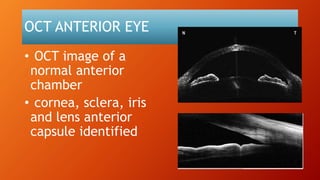
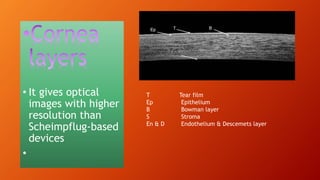
OCT provides high-resolution, cross-sectional imaging of the retina and anterior segment of the eye in a non-invasive manner. It works on the principles of interferometry and low coherence reflectometry to obtain micrometer-level resolution images. Time domain OCT uses a moving reference mirror while Fourier domain OCT obtains entire scans simultaneously using a spectrometer. OCT is useful for diagnosing and monitoring various retinal diseases like macular edema, glaucoma, age-related macular degeneration and corneal pathologies by visualizing intraretinal layers and thickness maps. It has become the gold standard for evaluation and management of diseases affecting the retina.