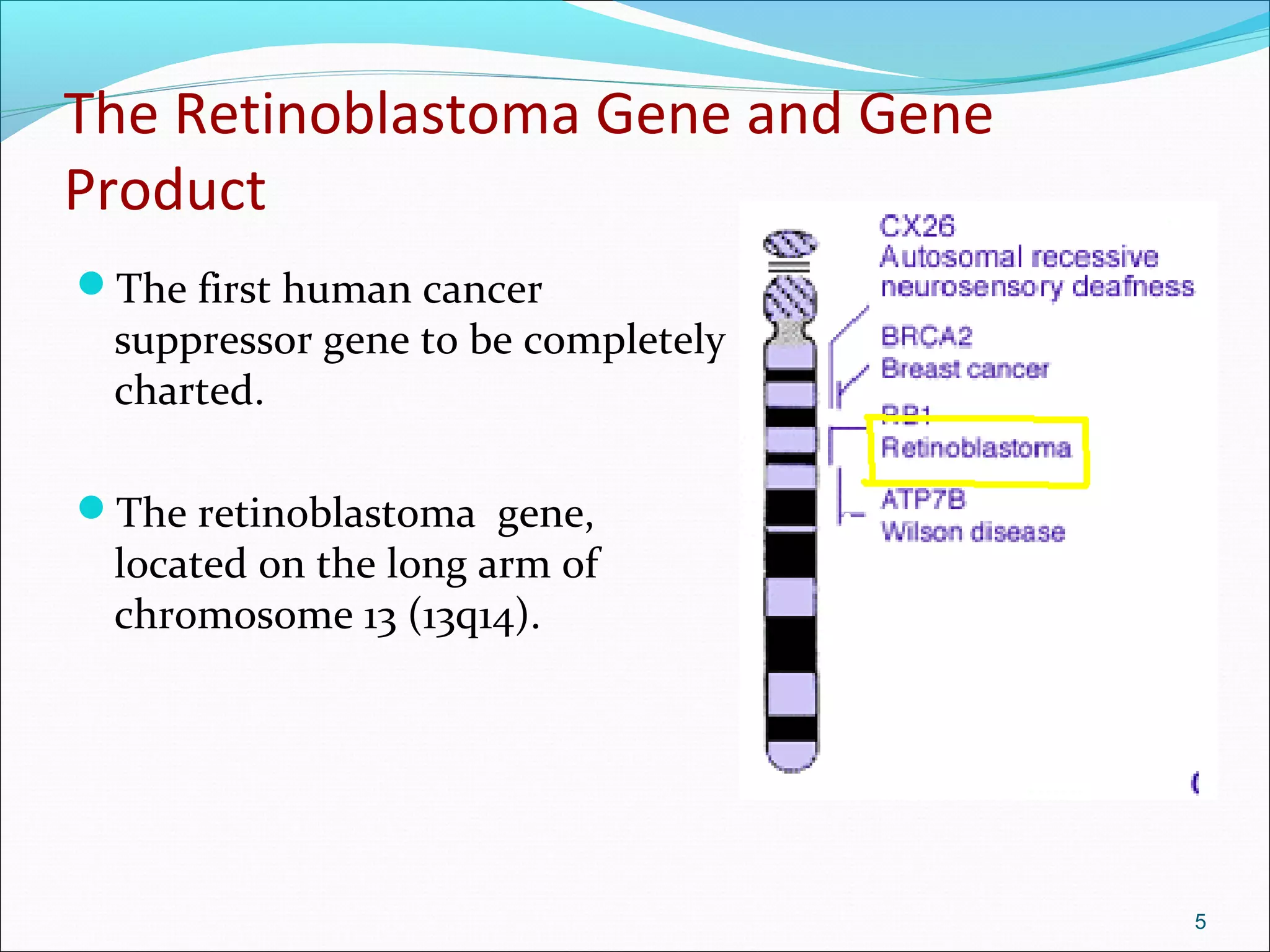
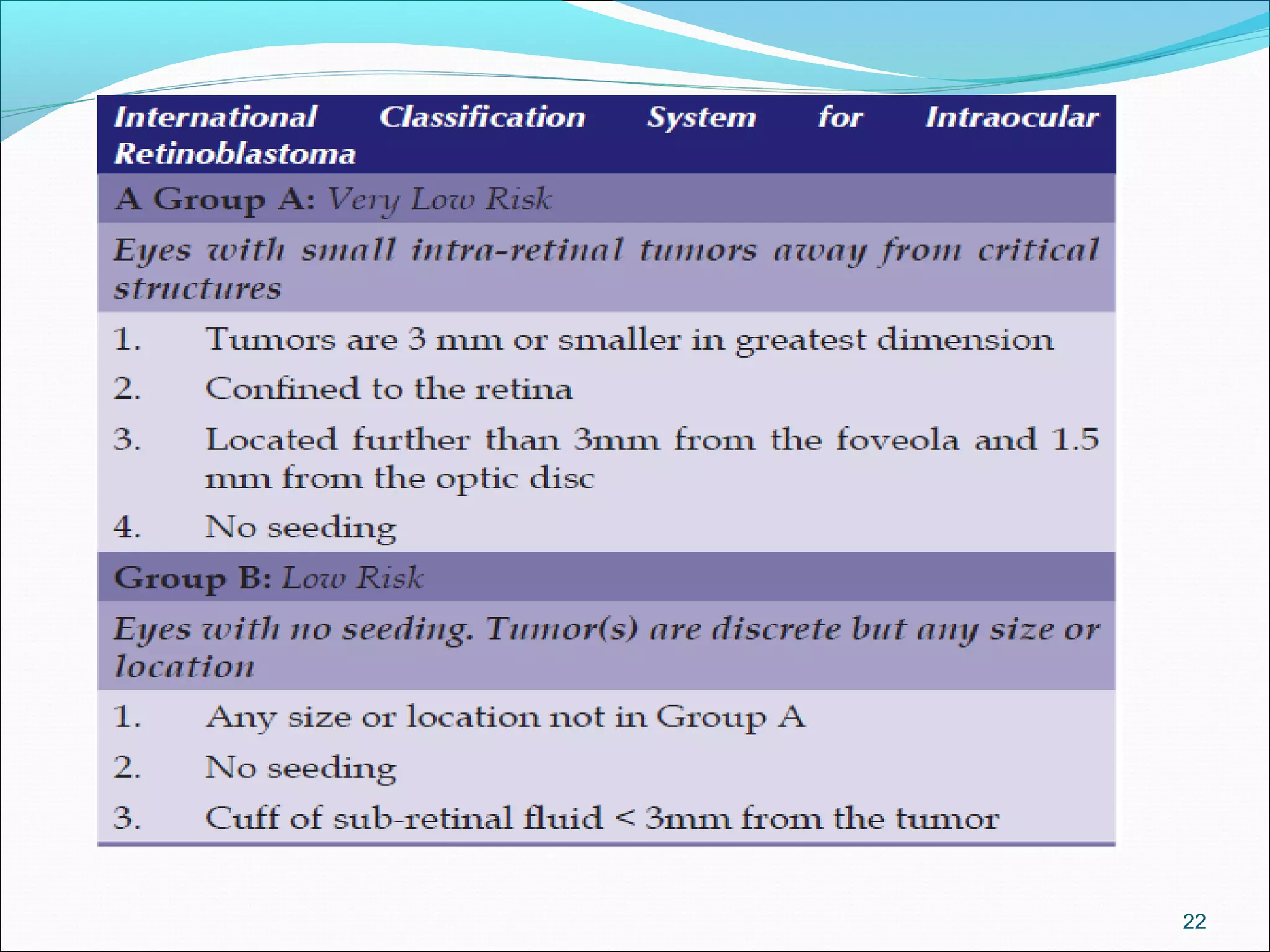
Retinoblastoma is a rare cancer that affects the retina. It is the most common eye cancer in children and its incidence ranges from 1 in 14,000 to 1 in 34,000 live births worldwide. The document discusses the epidemiology, genetics, pathology, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, classification systems, management options including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, cryotherapy and enucleation, and importance of genetic counseling for families with retinoblastoma.