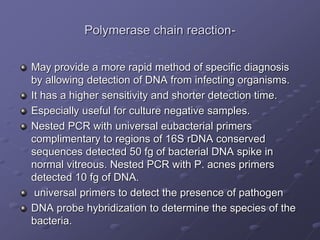
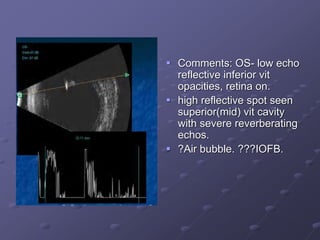
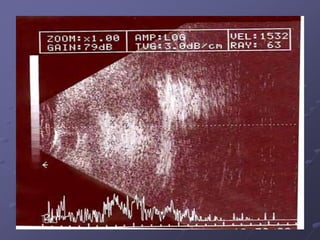
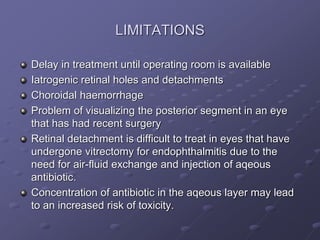
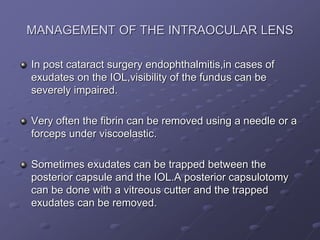
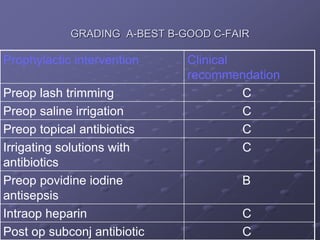
1. Early recognition and treatment of endophthalmitis is critical to prevent further spread and vision loss. Diagnosis involves a thorough ocular exam, microbiological investigations including aqueous or vitreous taps and cultures, as well as systemic workup to identify the source of infection.
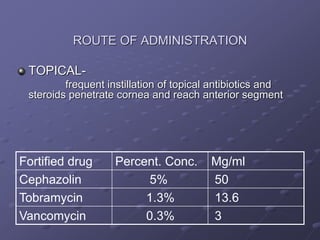
2. Treatment involves prompt administration of broad-spectrum intravitreal antibiotics targeting both gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. Vitrectomy may improve outcomes in cases with initial light perception vision or suspected fungal infection. Close monitoring is needed as repeat injections or surgery may be required if the infection persists or vision declines.
3. Risk factors like older age, diabetes, and poor initial vision portend worse visual outcomes,