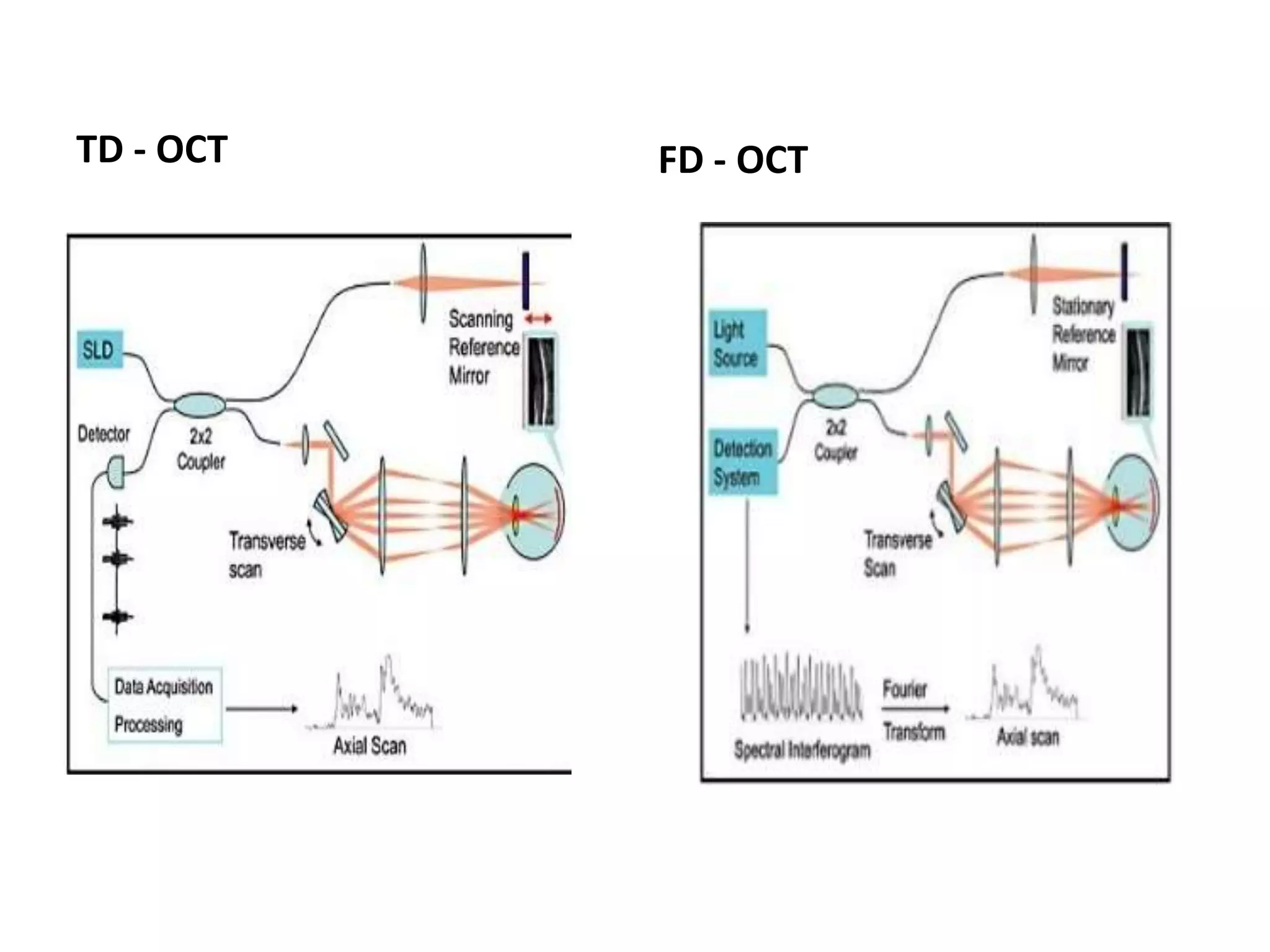
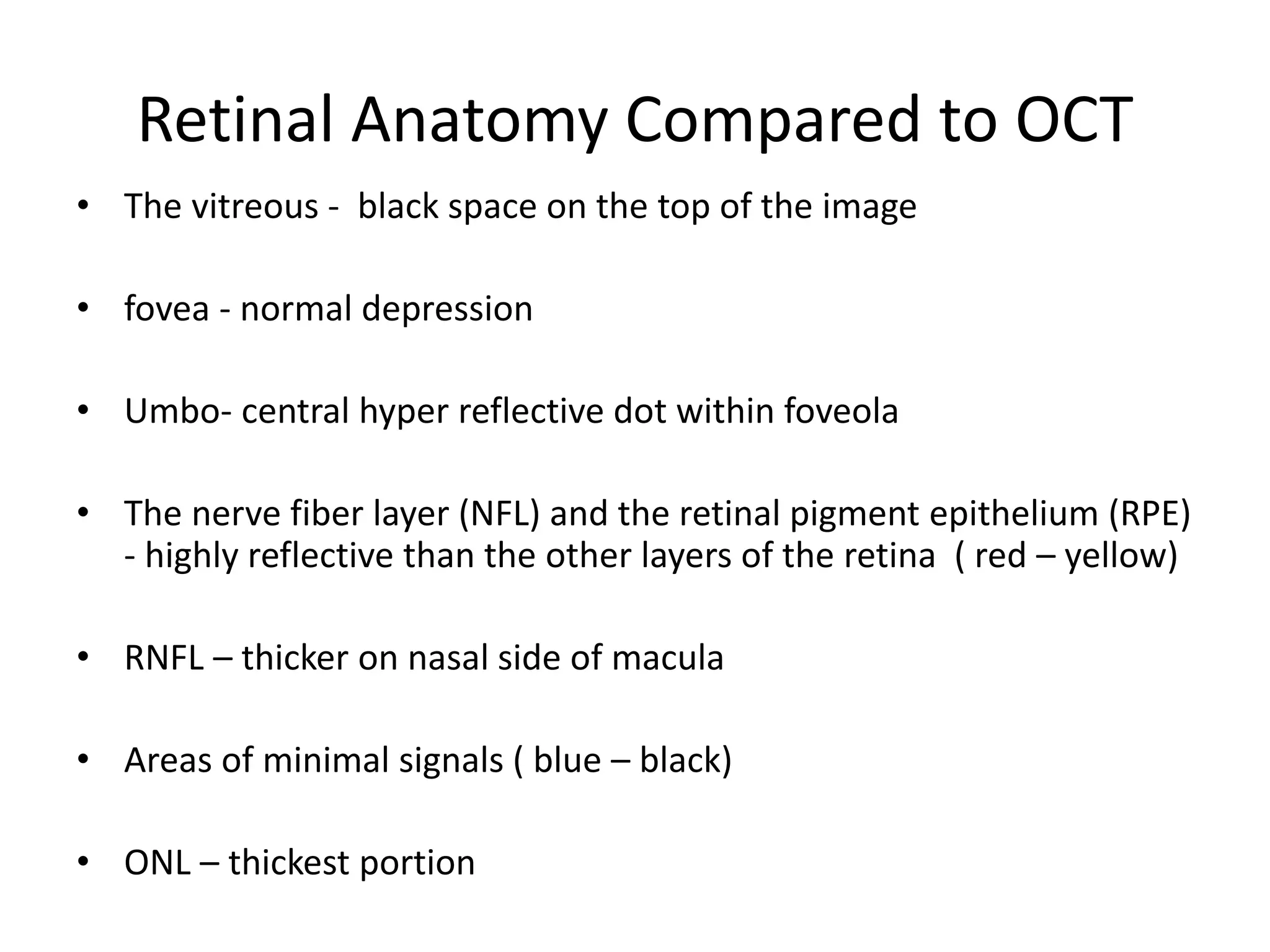
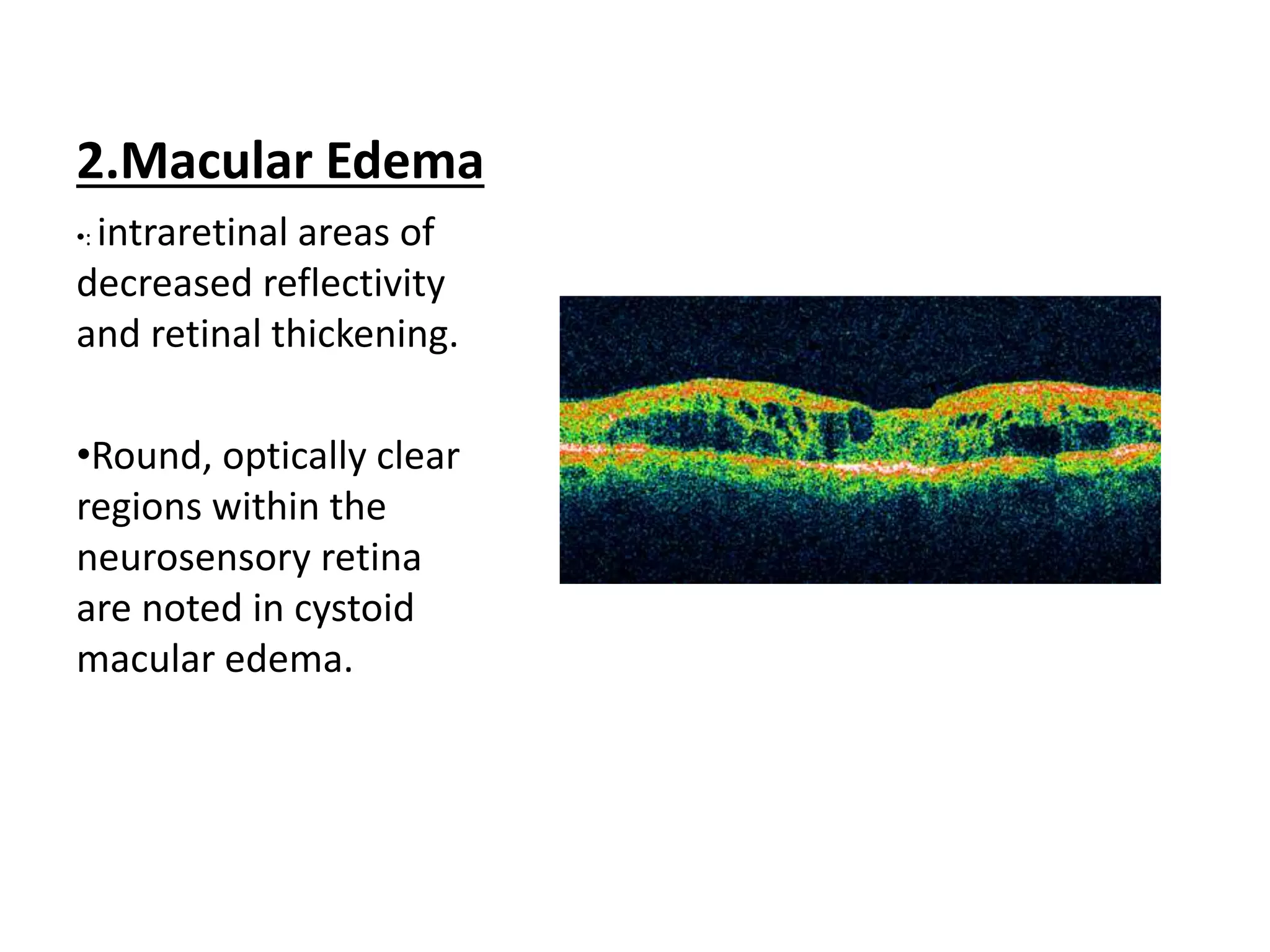
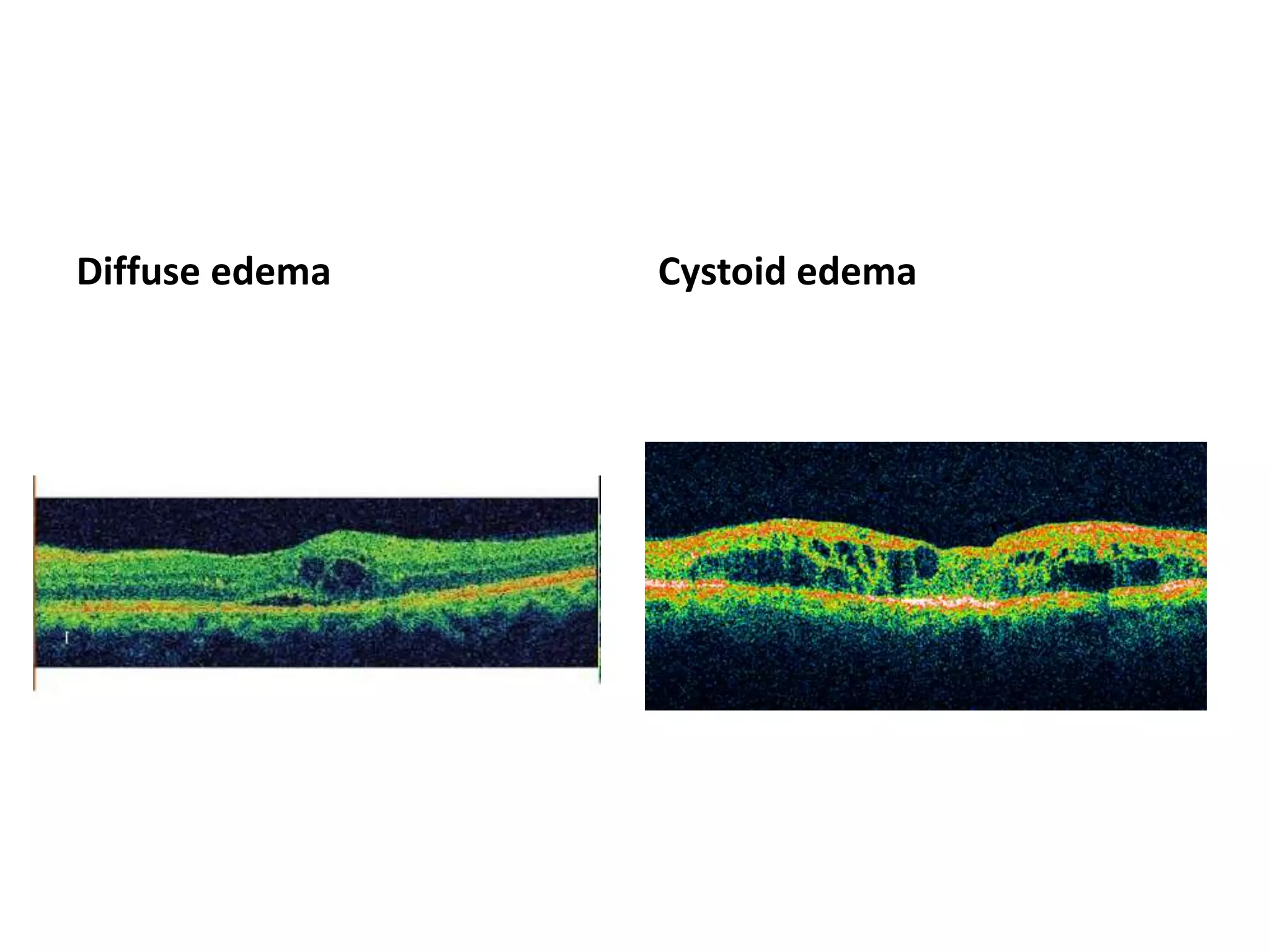
The document discusses Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), detailing its history, principles, types, and factors related to its usage in retinal examinations. It explains the technological evolution of OCT, including various scan protocols and the anatomical analysis of the retina through OCT images. Additionally, it covers clinical applications, limitations, and the interpretation of OCT results in diagnosing and monitoring retinal conditions.