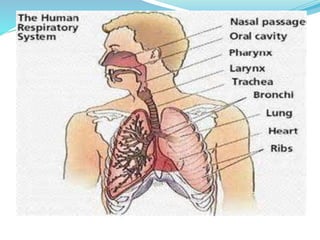
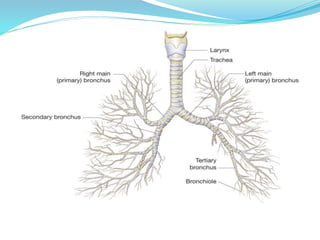
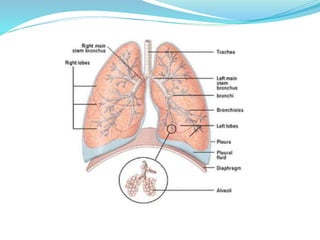
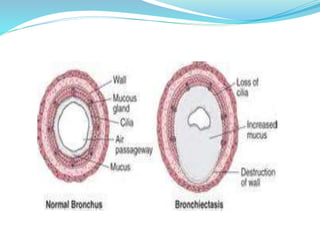
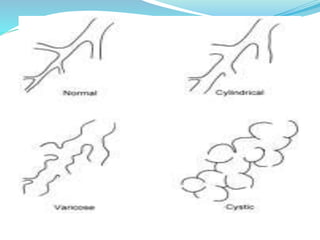
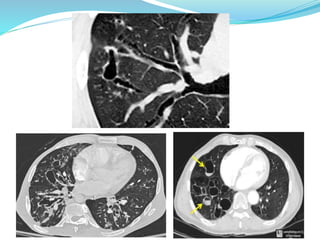
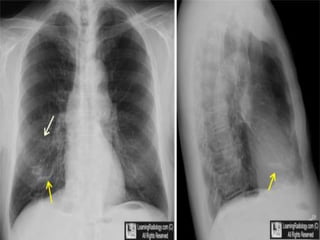
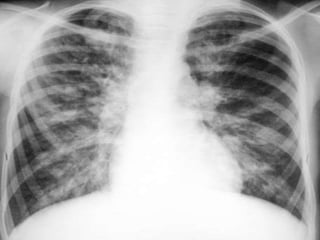
This document provides information about bronchiectasis, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and management. It describes bronchiectasis as an abnormal permanent dilation of the bronchi due to destruction of the bronchial wall muscles and elastic tissue. Common causes include infection, aspiration, obstruction, and genetic conditions like cystic fibrosis. Symptoms include chronic cough, sputum production, and recurrent lung infections. Diagnosis is made through clinical history and characteristic findings on CT scan. Management focuses on controlling infections with antibiotics, clearing secretions, and treating underlying causes.