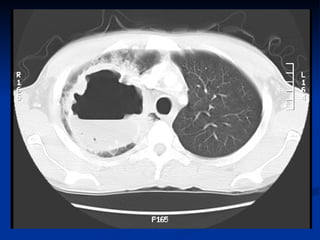
Lung abscess is a localized area of lung destruction caused by infection, typically by aspiration of oropharyngeal bacteria. It appears on imaging as a cavity containing air-fluid levels. The infection can start as necrotizing pneumonia that progresses to microabscesses and larger cavitary lesions over time. Risk factors include dental/sinus infections, impaired swallowing, or pre-existing lung disease. Treatment involves antibiotics targeting common aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Therapy typically lasts 4-6 weeks until imaging shows resolution, though surgery may be needed for large or resistant abscesses. Complications can include empyema, bronchopleural fistula, or distant infections if not properly treated.