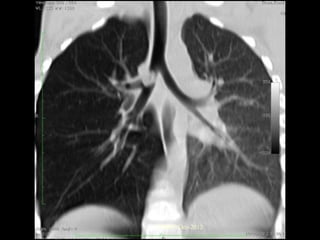
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung condition characterized by abnormal dilation of the bronchi and bronchioles. It can be caused by bronchial obstruction, congenital defects, or necrotizing pneumonia. Symptoms include cough, copious foul-smelling sputum, and recurrent lung infections. Long-term complications can include lung abscesses, lung damage, and heart failure. Treatment involves airway clearance and antibiotics to prevent infections.




![Causes:
Bronchial obstruction –
Tumor
Foreign body
Mucous impaction [complication of atopic
asthma, chronic bronchitis]
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-7-320.jpg)

![Causes : cont…..
Congenital / Hereditary conditions
• Congenital bronchiectasis (developmental anomaly)
• Cystic fibrosis
• Immunodeficiency states
• Immotile cilia & Kartagener syndromes
Necrotizing pneumonia
[Post infective bronchiectasis - TB, Staph, mixed
infection]
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-12-320.jpg)
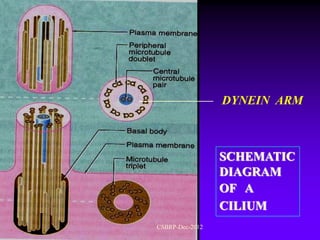
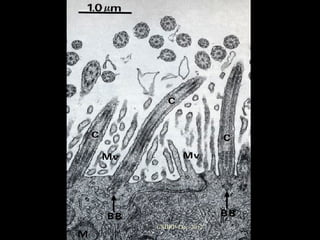
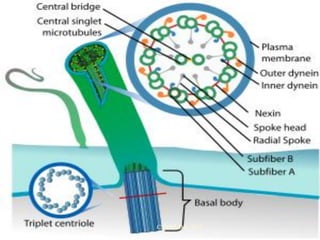
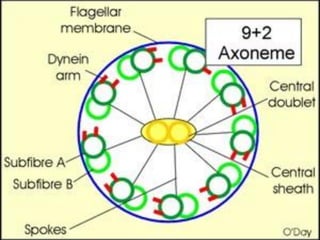
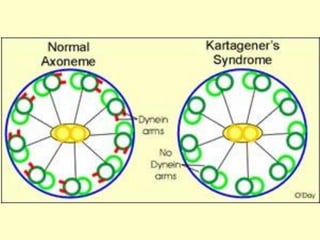
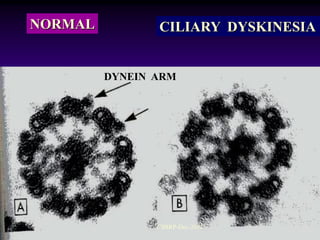
![Ciliary dyskinesia:
[Immotile cilia syndrome]
[Kartagener’s syndrome]
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-13-320.jpg)
![Ciliary dyskinesia:
[Immotile cilia syndrome]
[ Kartagener syndrome ]
Ciliary beating
Mucociliary clearance
Increased susceptibility to infections
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-14-320.jpg)


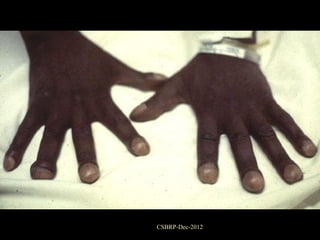
![Clinical features of
Ciliary dyskinesia:
Repeated bouts of otitis & sinusitis
Recurrent chest infections
Situs inversus - [ 50% ]
[ Kartagener syndrome - triad ]
Males --- Infertility
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-22-320.jpg)


![Cystic fibrosis (CF)
[Mucoviscidosis]
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-27-320.jpg)
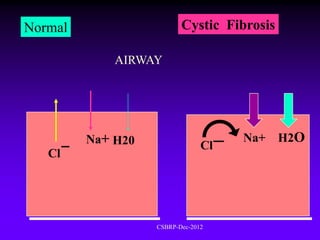
![Cystic fibrosis [Mucoviscidosis]
Systemic disease
Prevalence: 1 in 2500 live births
Common in western countries
Uncommon in Asians & Africans
Pulmonary involvement dominates
Inheritance - AR
95% deaths - pulmonary disease
[ Bronchiectasis ]
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-28-320.jpg)
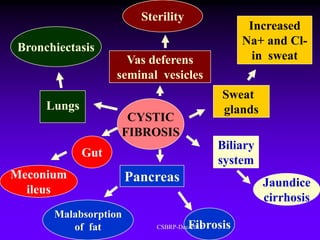
![Pathogenesis of CF:
Thick viscous mucus
Impaired mucociliary clearance
Repeated bouts of pulmonary infections
Parenchymal fibrosis
[ Bronchiectasis ]
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-30-320.jpg)
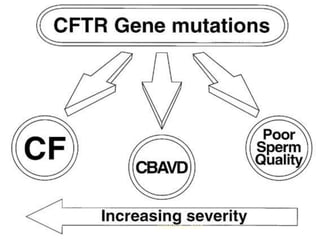
![Molecular defect:
Gene - CFTR
Chromosome - 7q31 - 32
Function - Anion channel
Defect in cystic fibrosis ( 550 mutations )
--- deletion of codon 508 [phenylalanine]
CFTR: Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance Regulator
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-31-320.jpg)






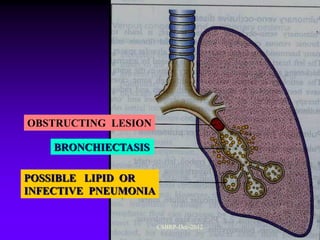
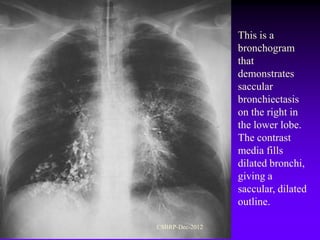
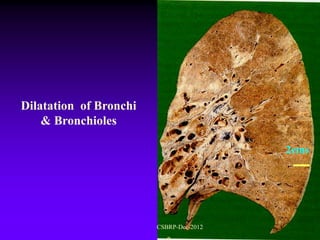

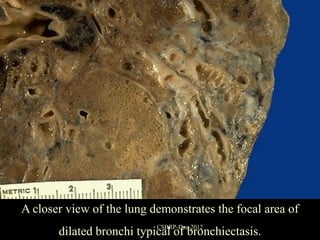

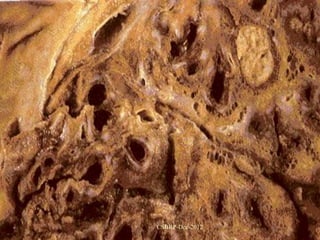
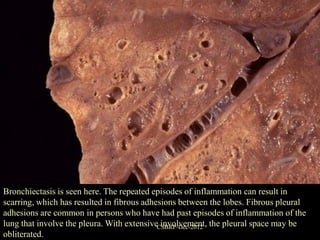
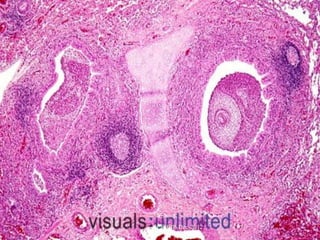
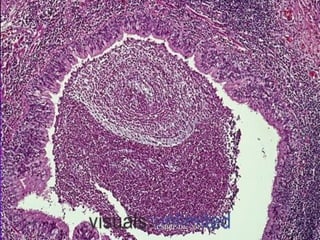
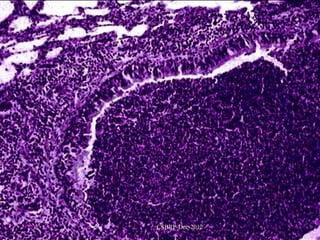

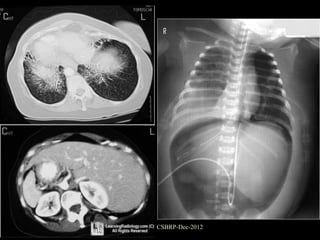
![Complications of
bronchiectasis:
Metastatic abscesses ( brain abscess)
Recurrent pulmonary infection
Right sided cardiac failure
[ chronic cor pulmonale ]
Massive haemoptysis
Reactive systemic amyloidosis
[ Nephrotic syndrome ]
CSBRP-Dec-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bronchiectasis-csbrp-130111111739-phpapp01/85/Bronchiectasis-53-320.jpg)