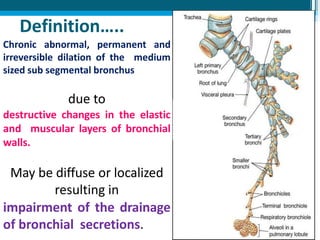
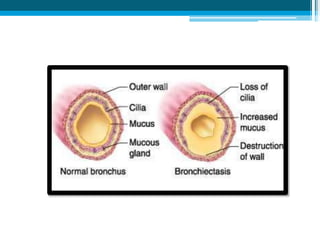
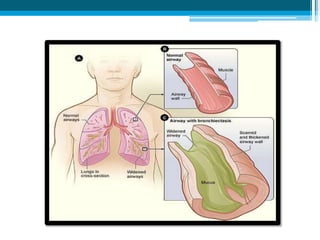
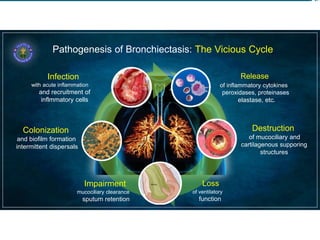
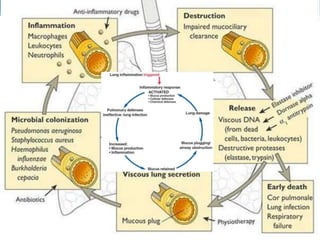
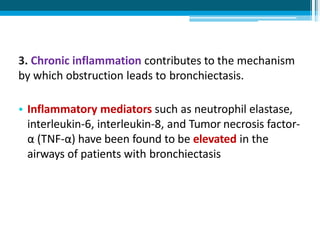
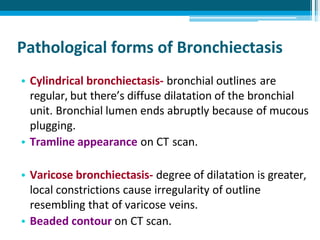
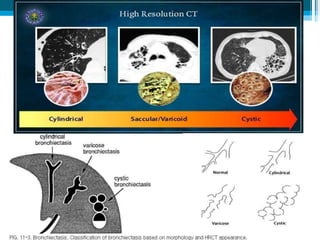
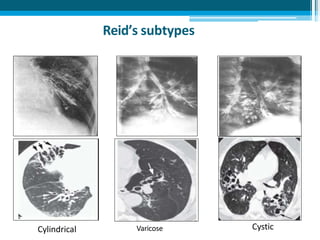
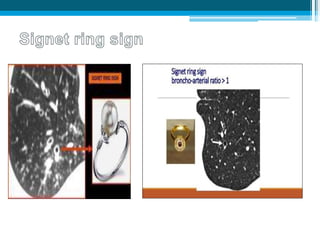
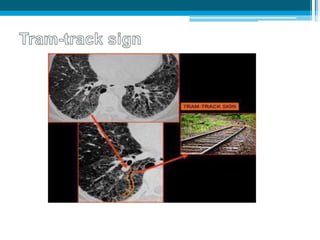
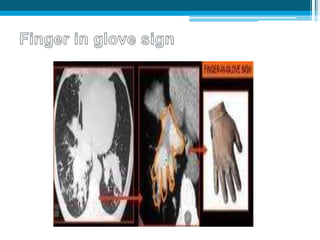
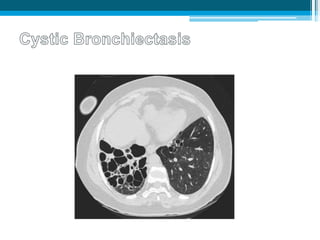
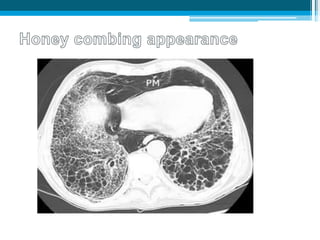
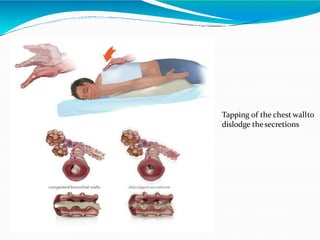
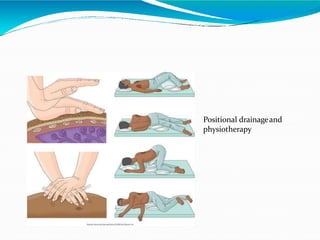
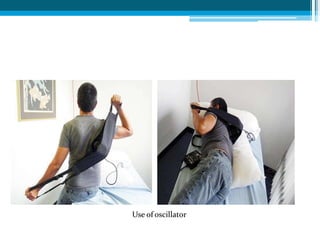
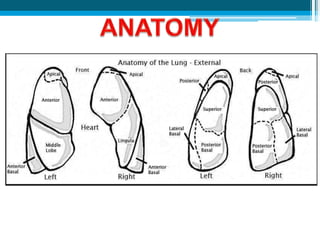
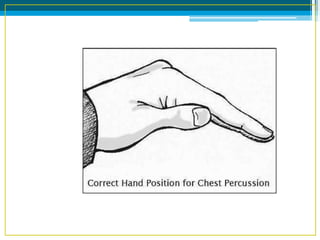
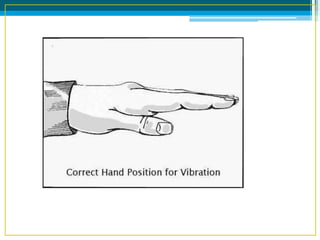
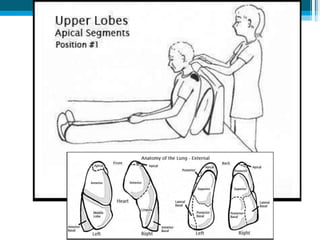
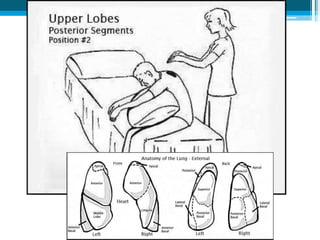
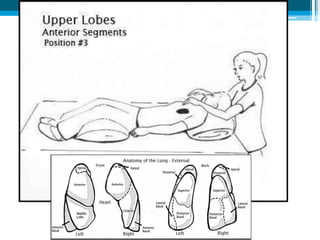
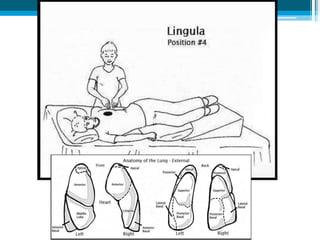
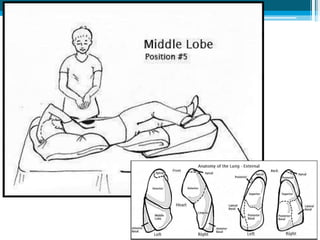
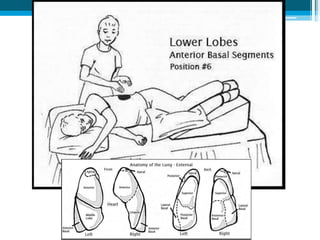
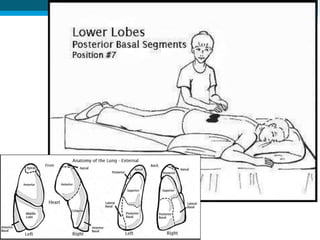
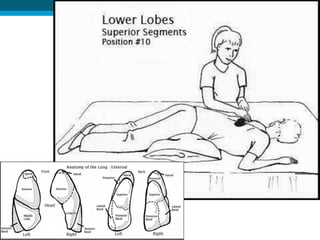
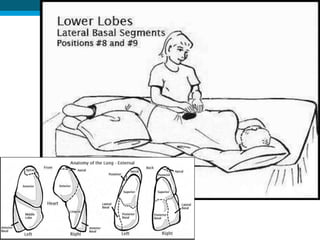
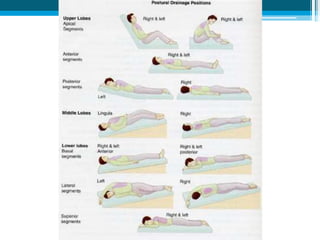
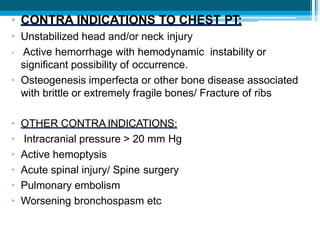
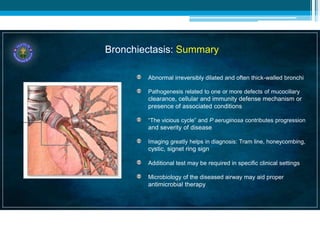
Bronchiectasis in children is an irreversible dilation of the airways caused by destructive changes to the airway walls. It has many causes including cystic fibrosis, infections, immunodeficiencies, and anatomical defects. The pathology involves a vicious cycle of impaired mucus clearance leading to recurrent infections, inflammation, and further airway damage. Symptoms include cough, sputum production, and breathing difficulties. Diagnosis is made through imaging like HRCT that shows changes to airway contours. Treatment focuses on airway clearance techniques and controlling infections with antibiotics. Management of underlying conditions and lung transplantation may be needed in severe cases.