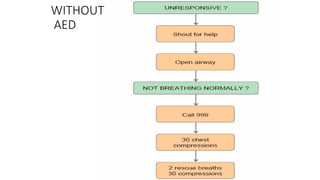
The document outlines the management of cardiac emergencies and trauma in general practice, detailing signs, symptoms, and appropriate responses for conditions like myocardial infarction. It emphasizes the importance of immediate medical assistance, assessing and managing airway, breathing, circulation, disability, and exposure in trauma care. The protocols include the use of medications, oxygen administration, and effective communication with receiving hospitals to improve patient outcomes.