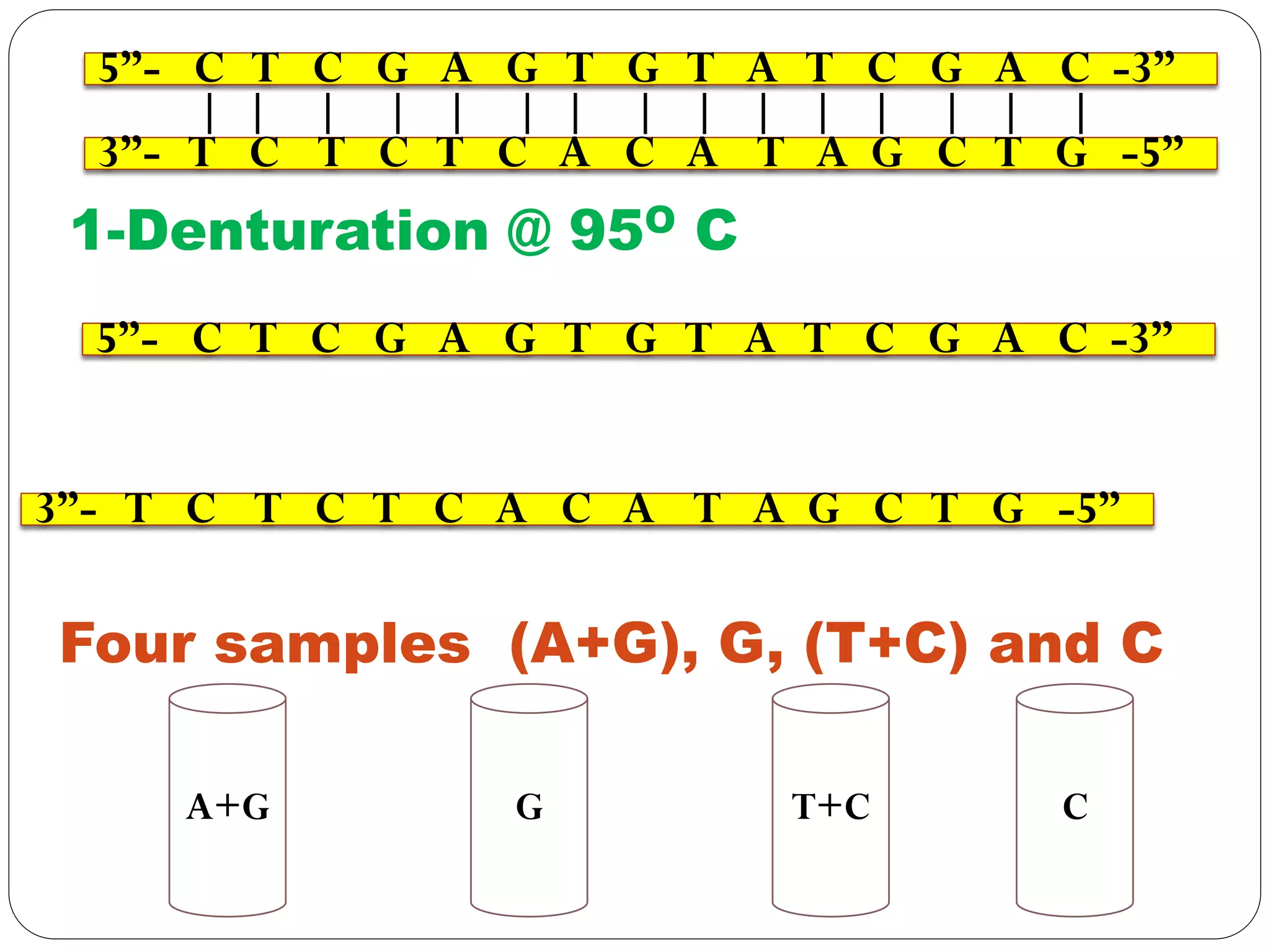
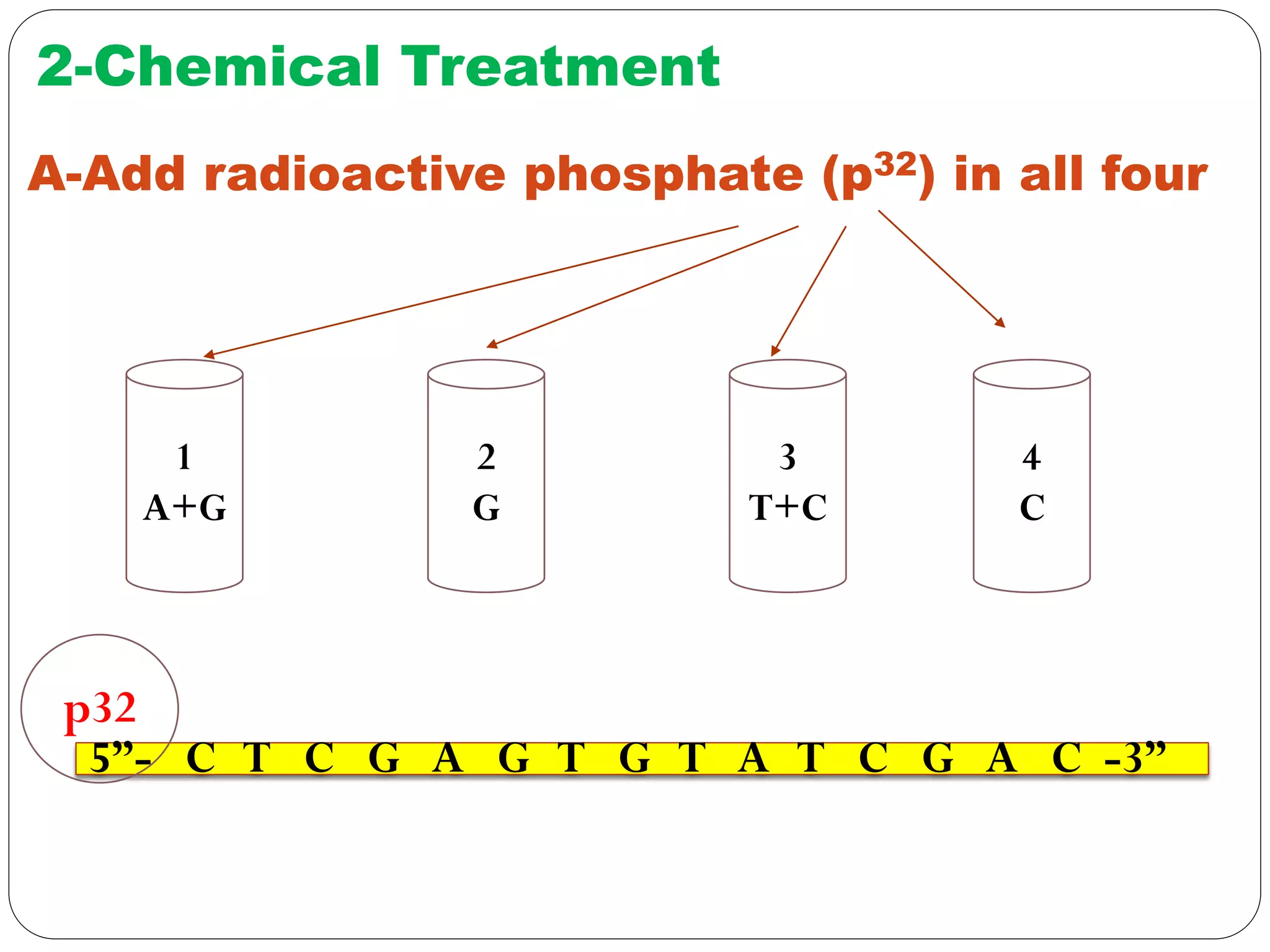
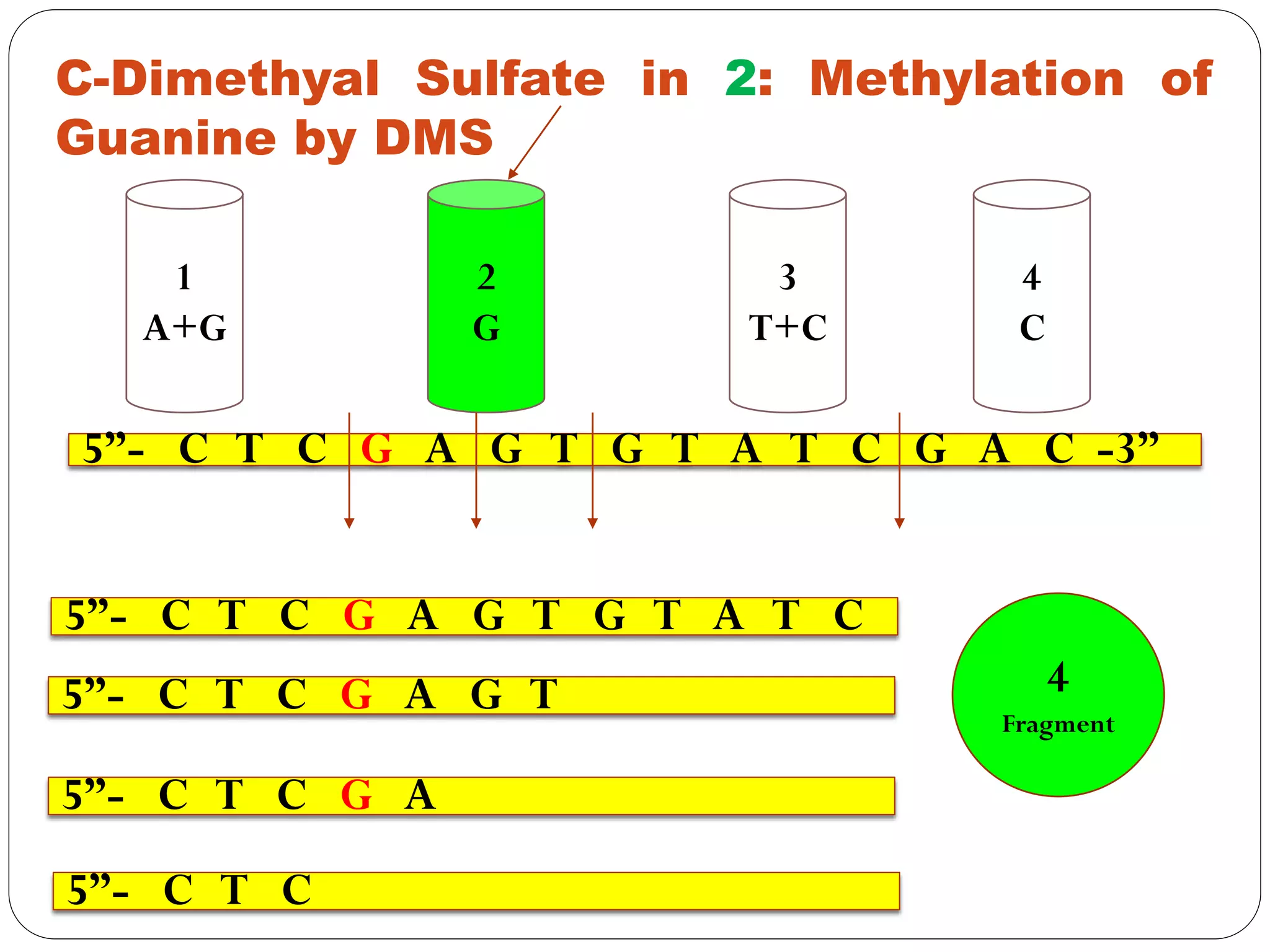
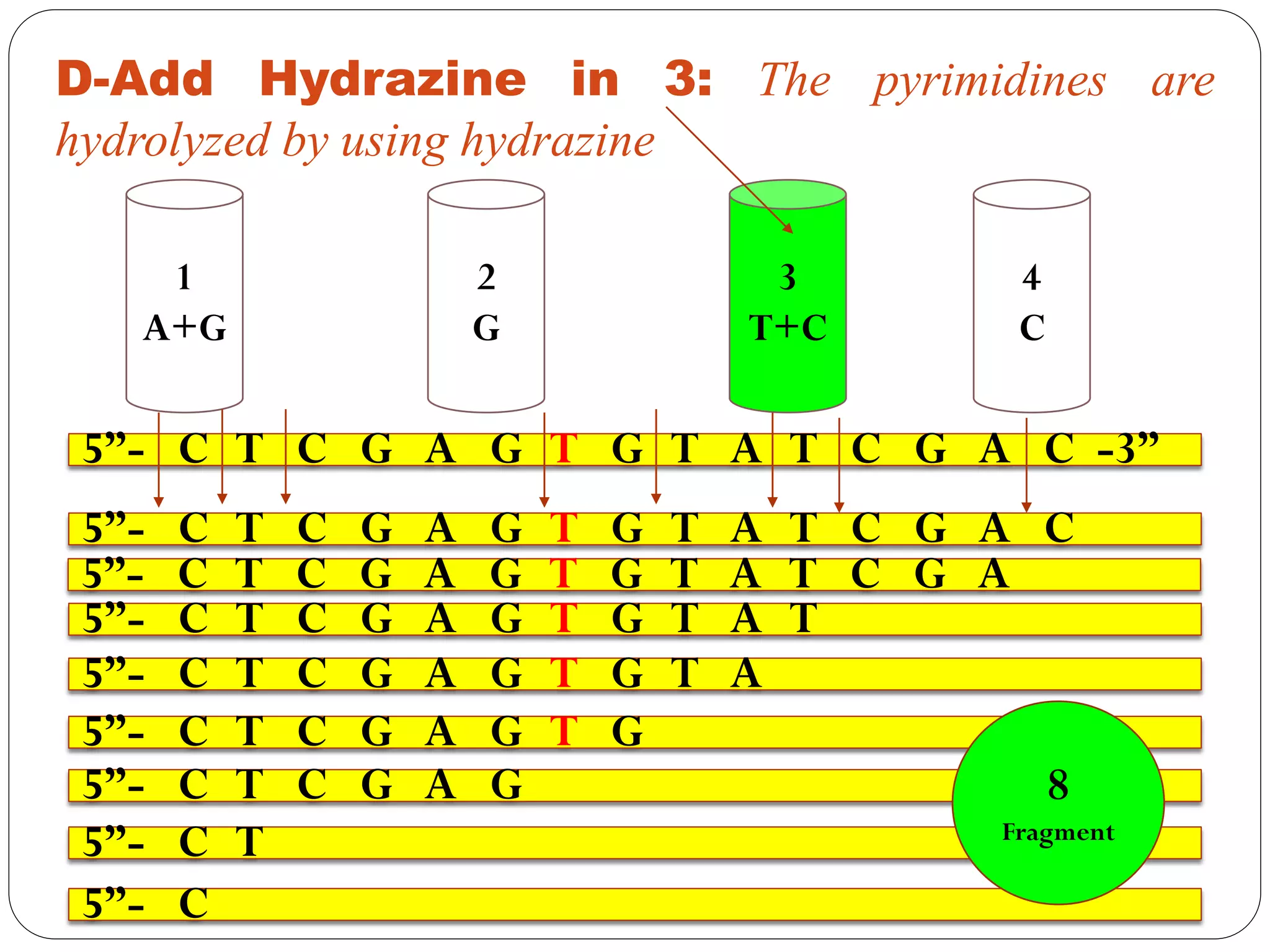
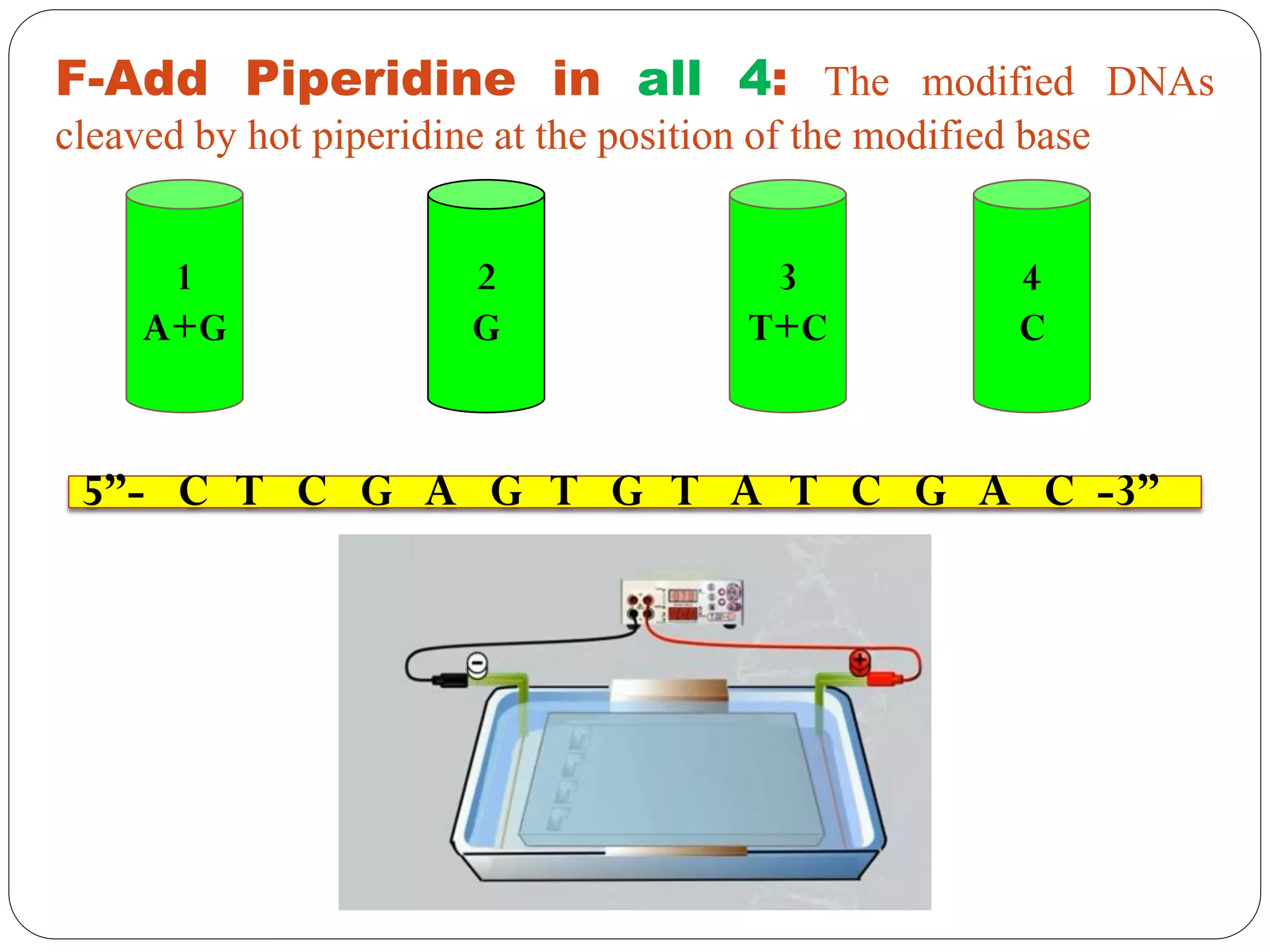
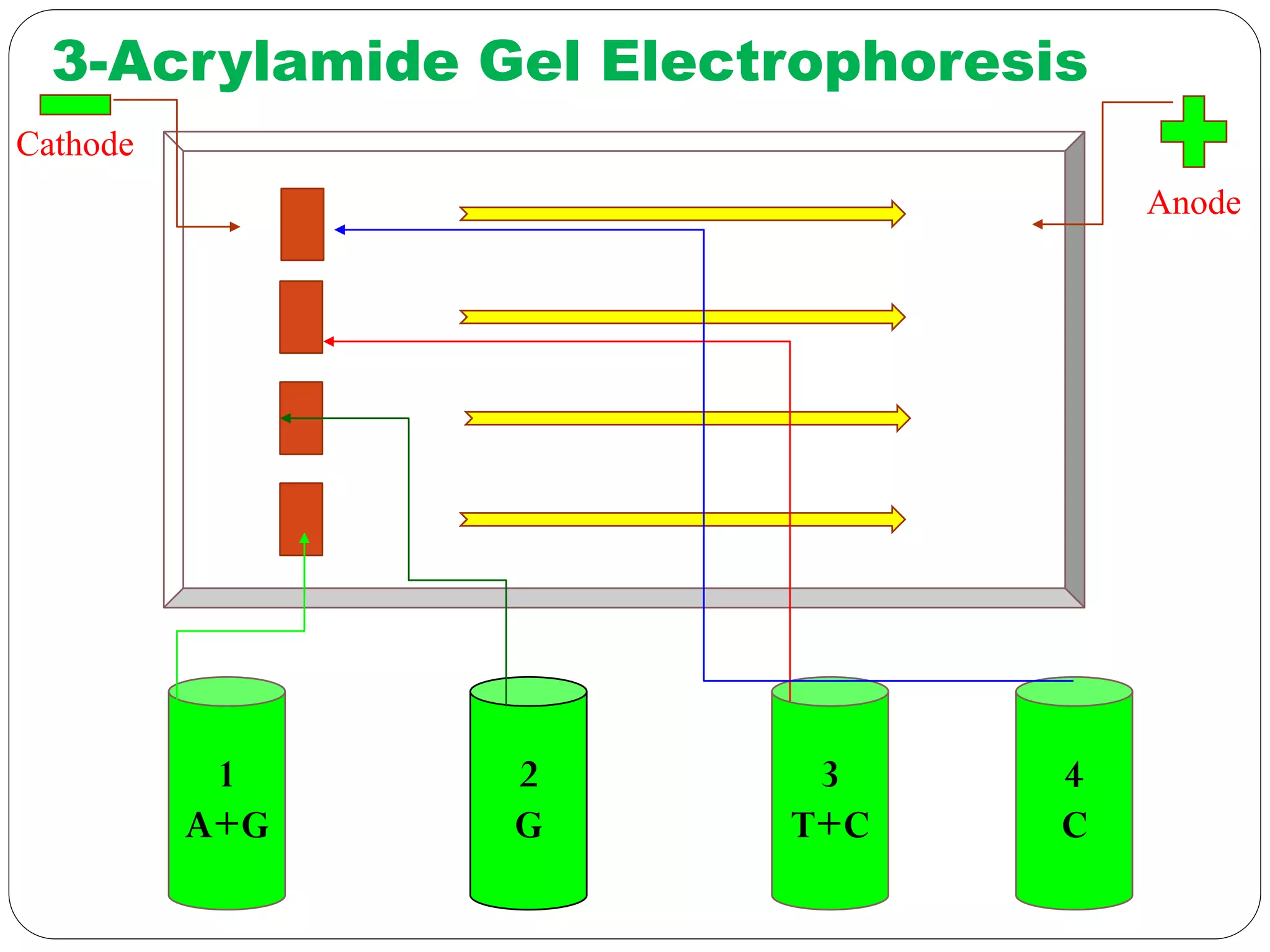
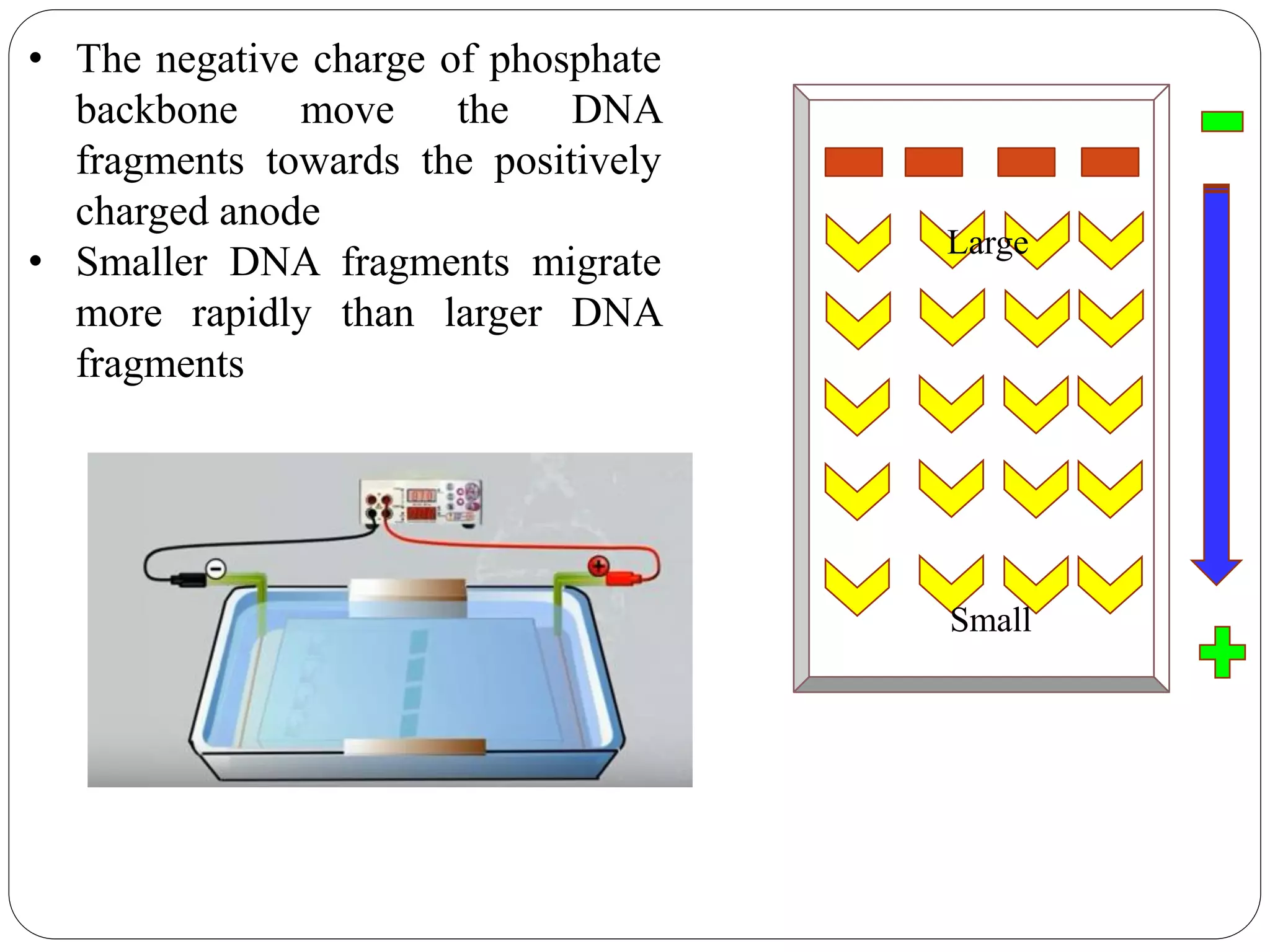
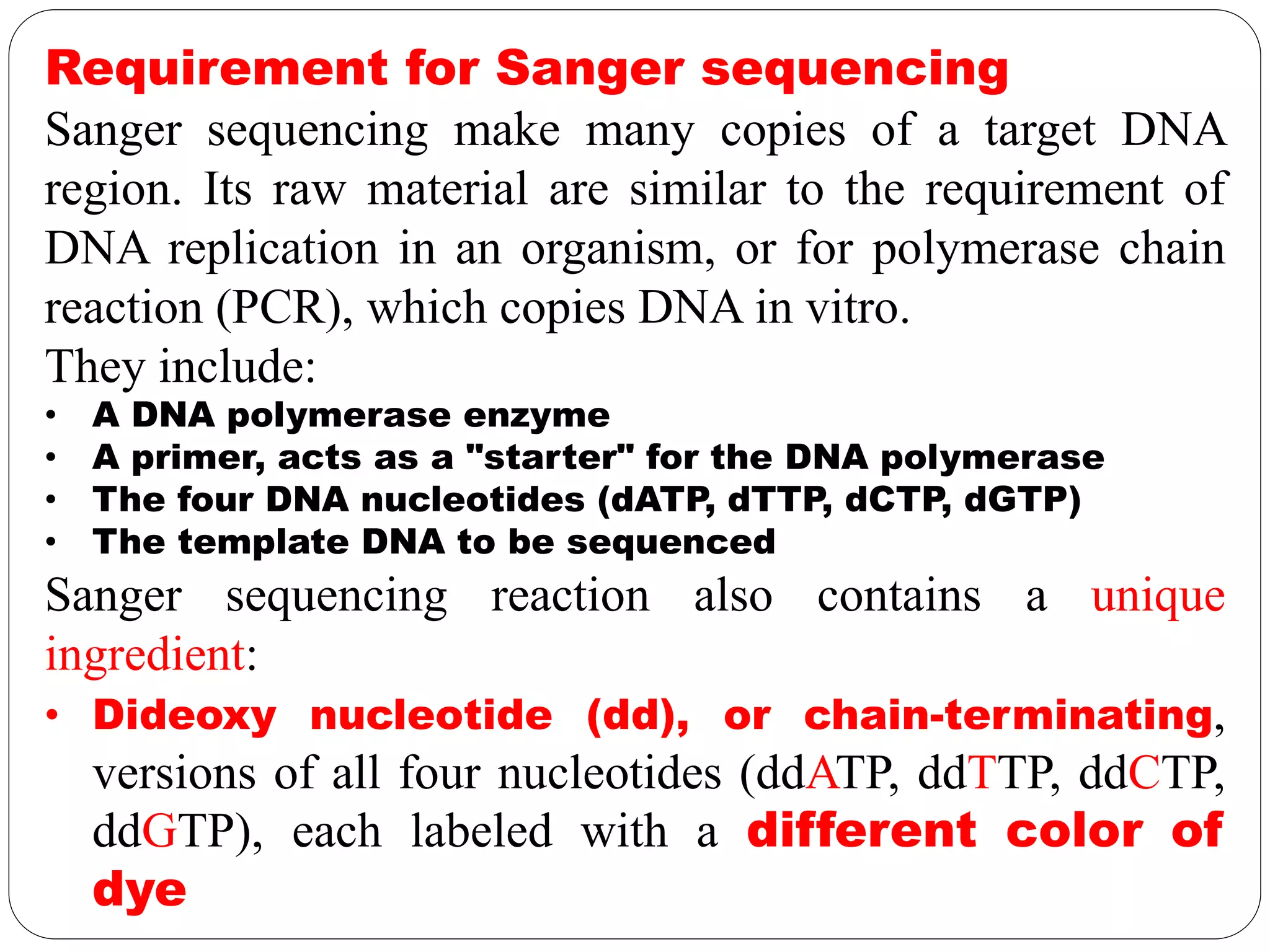
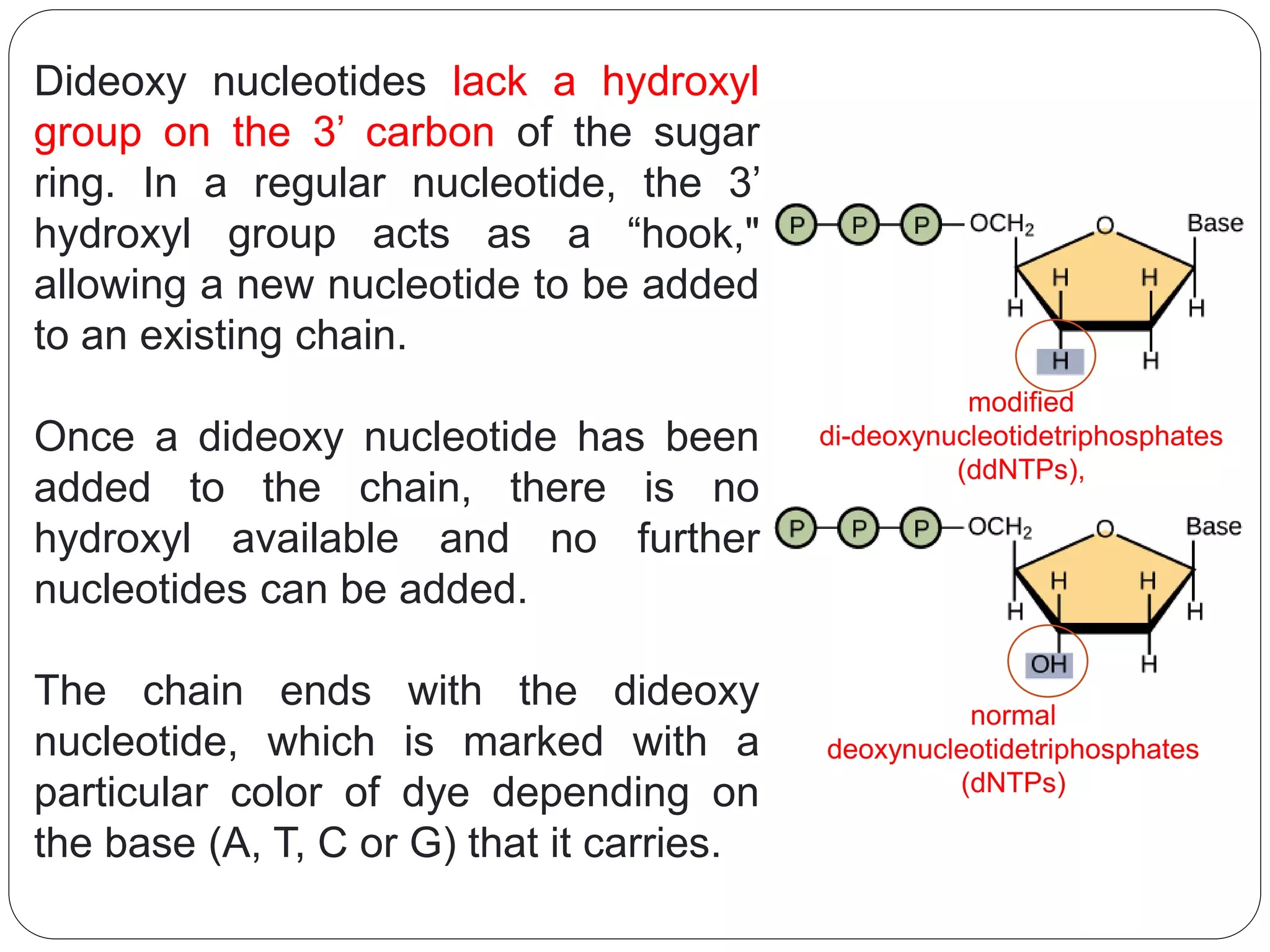
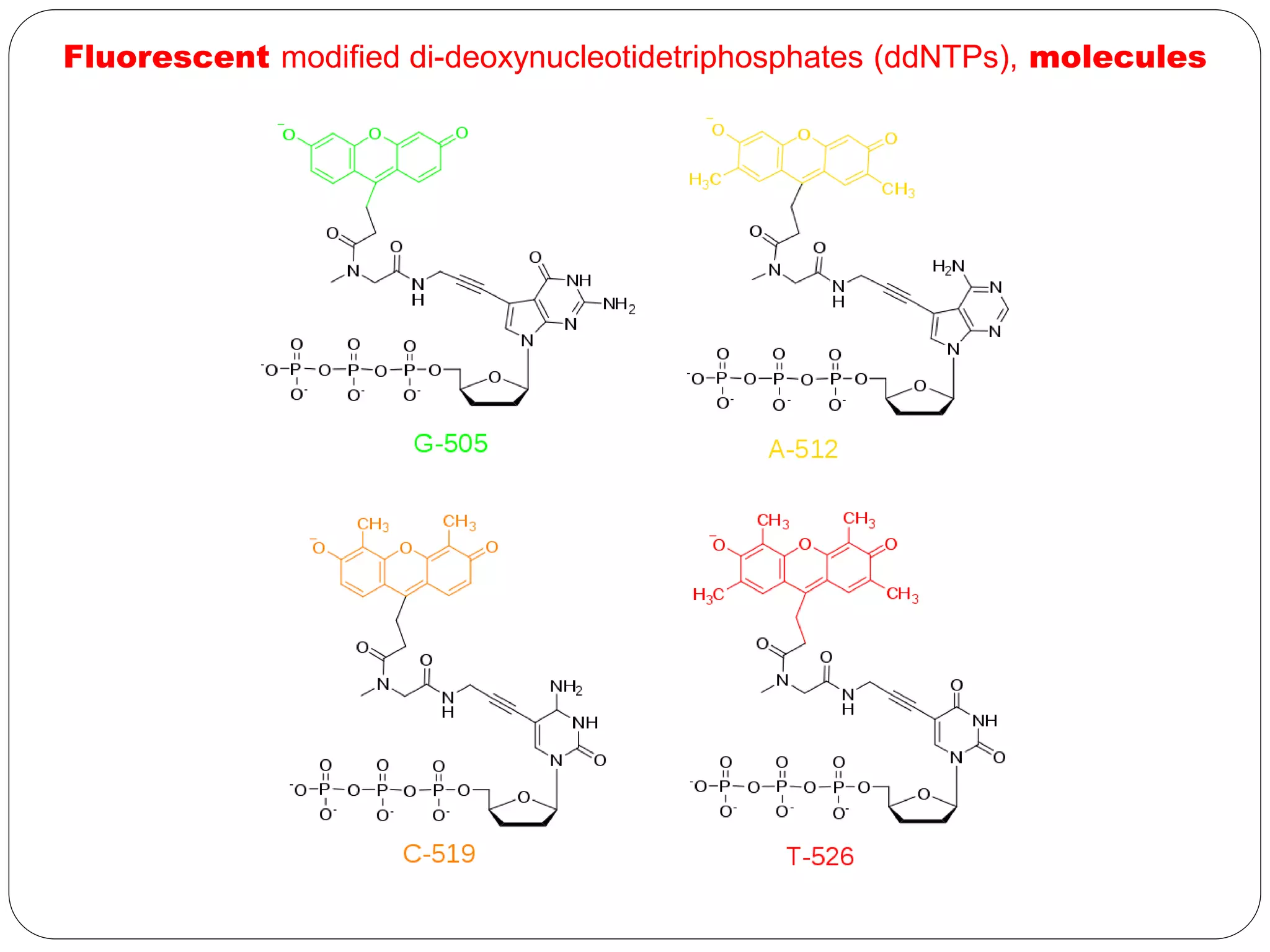
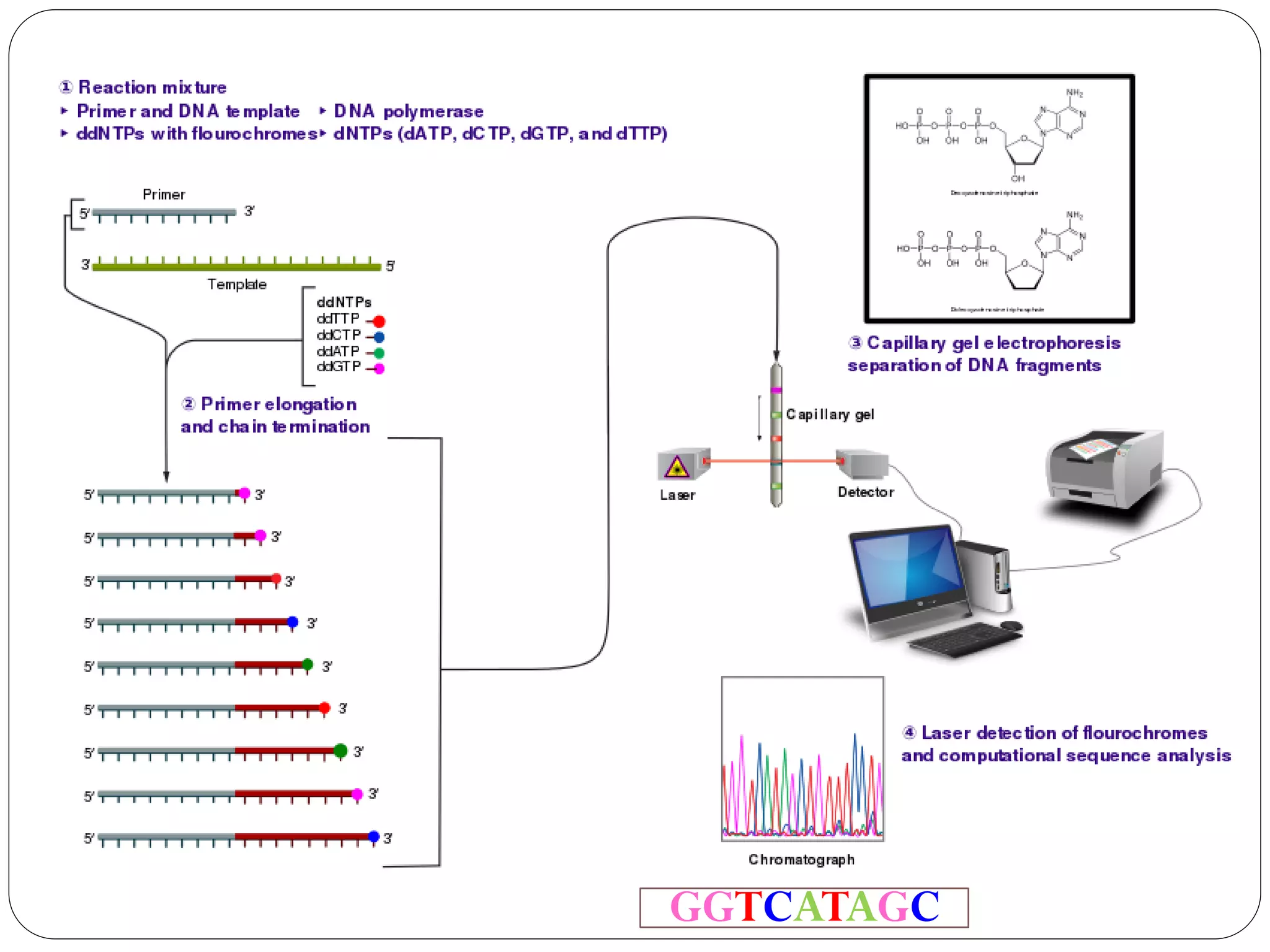
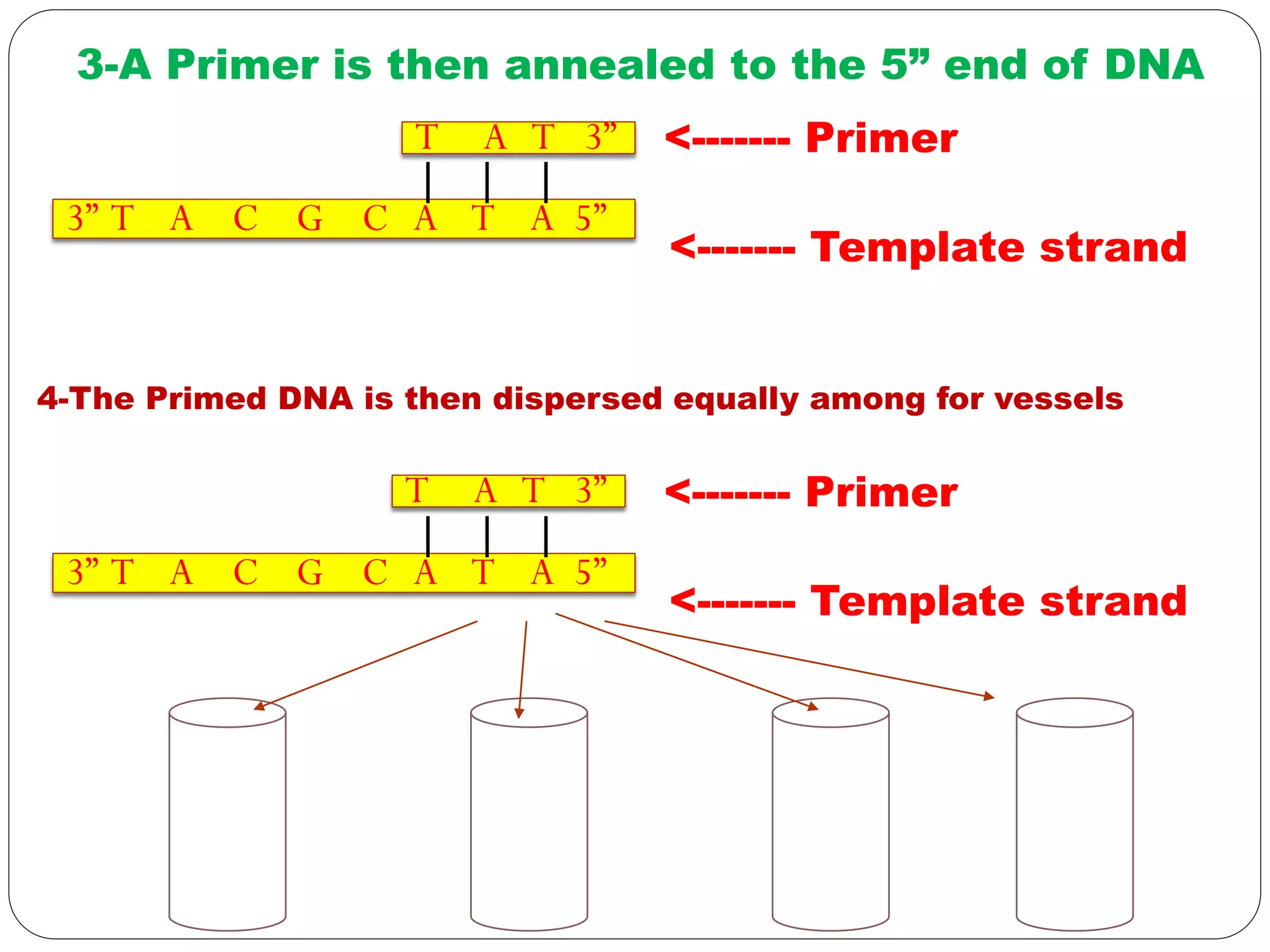
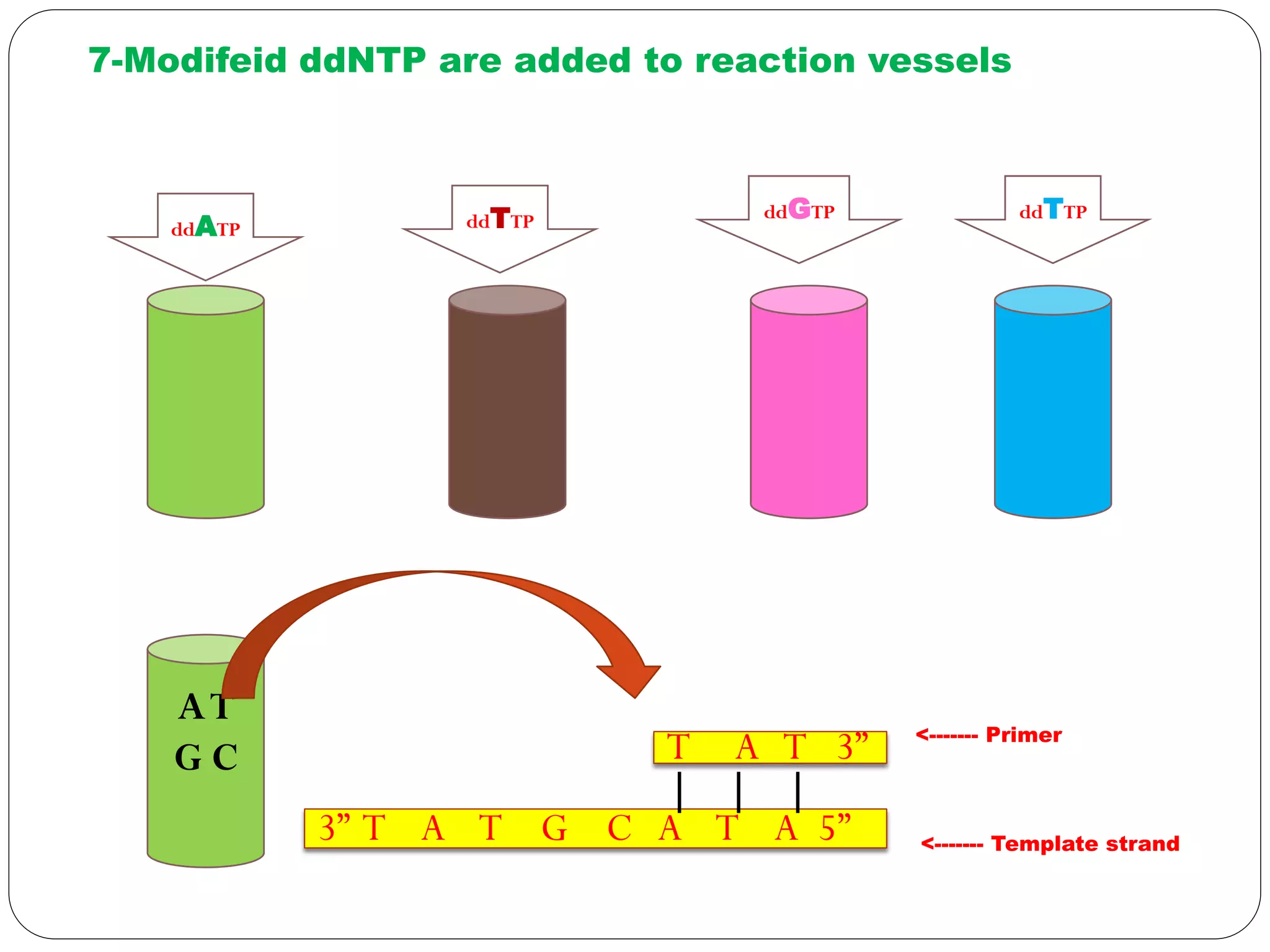
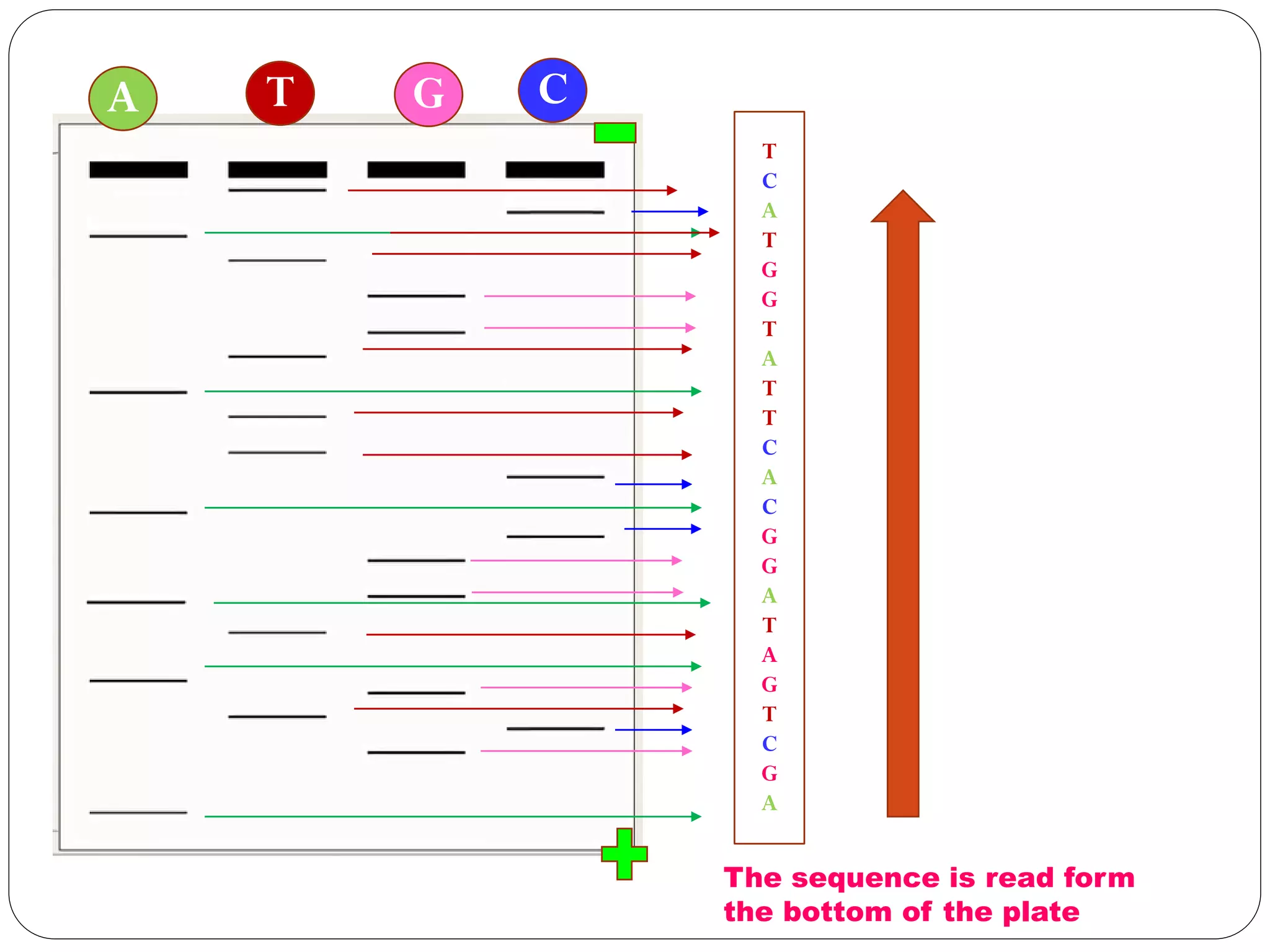
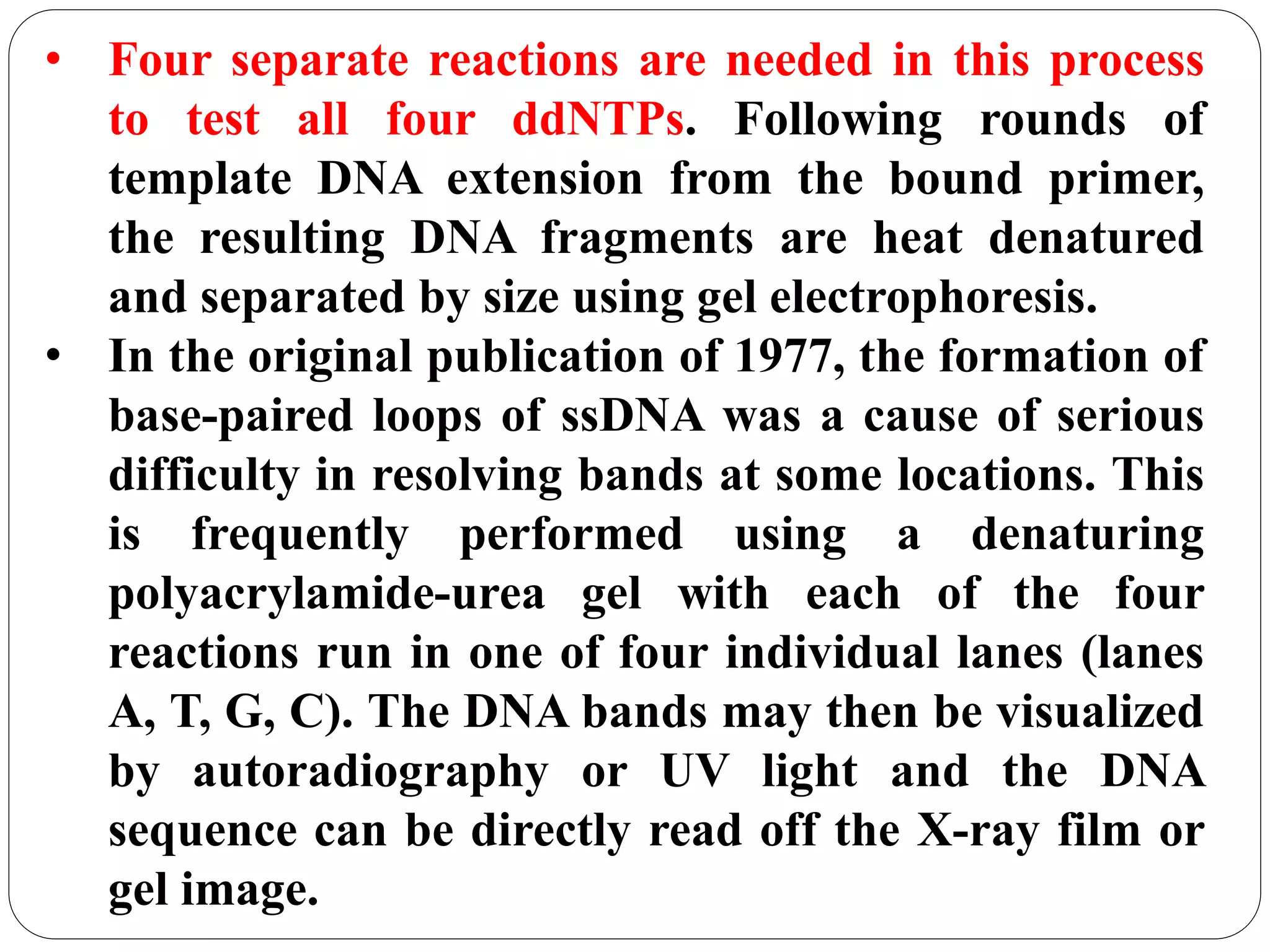
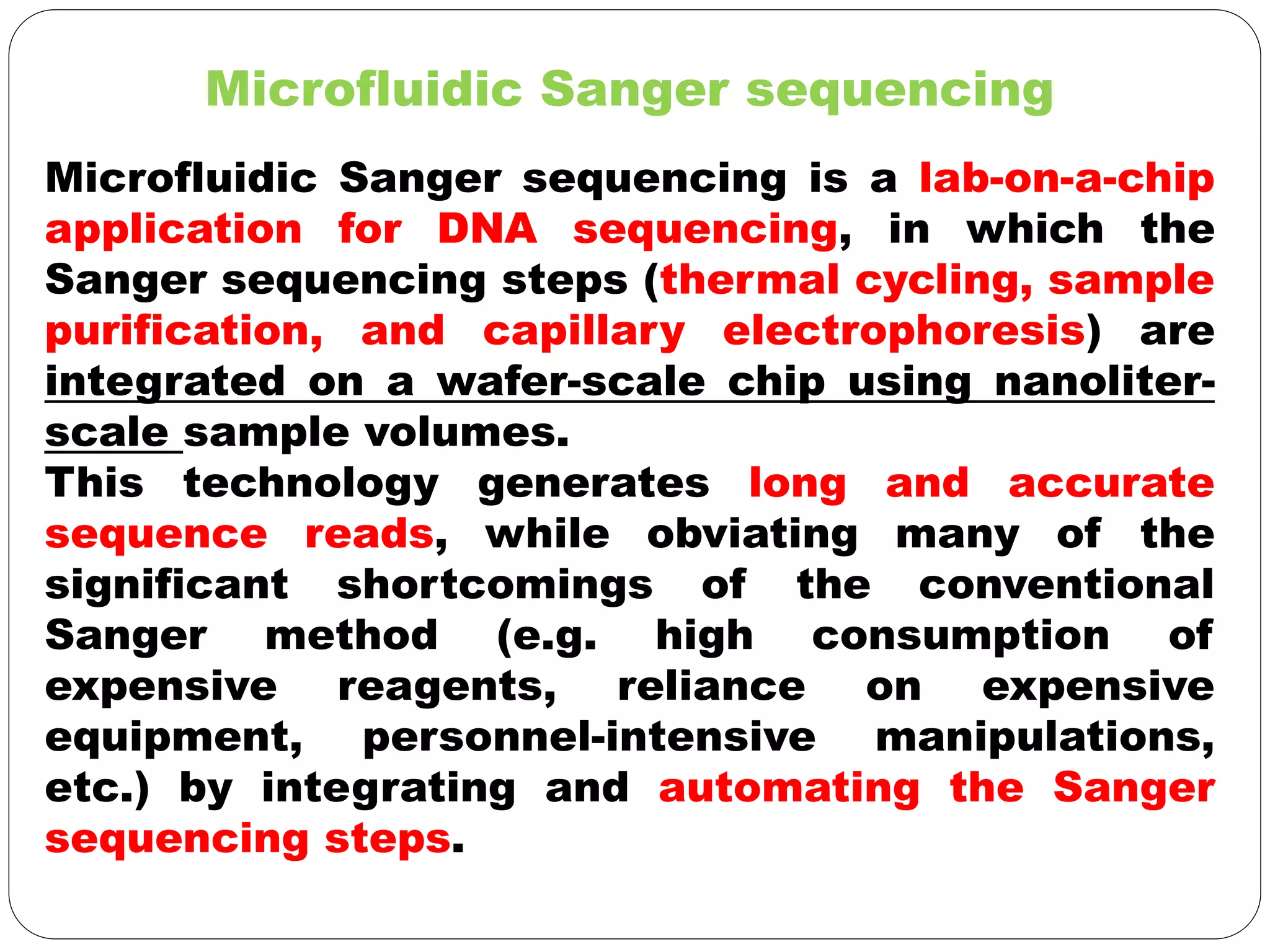
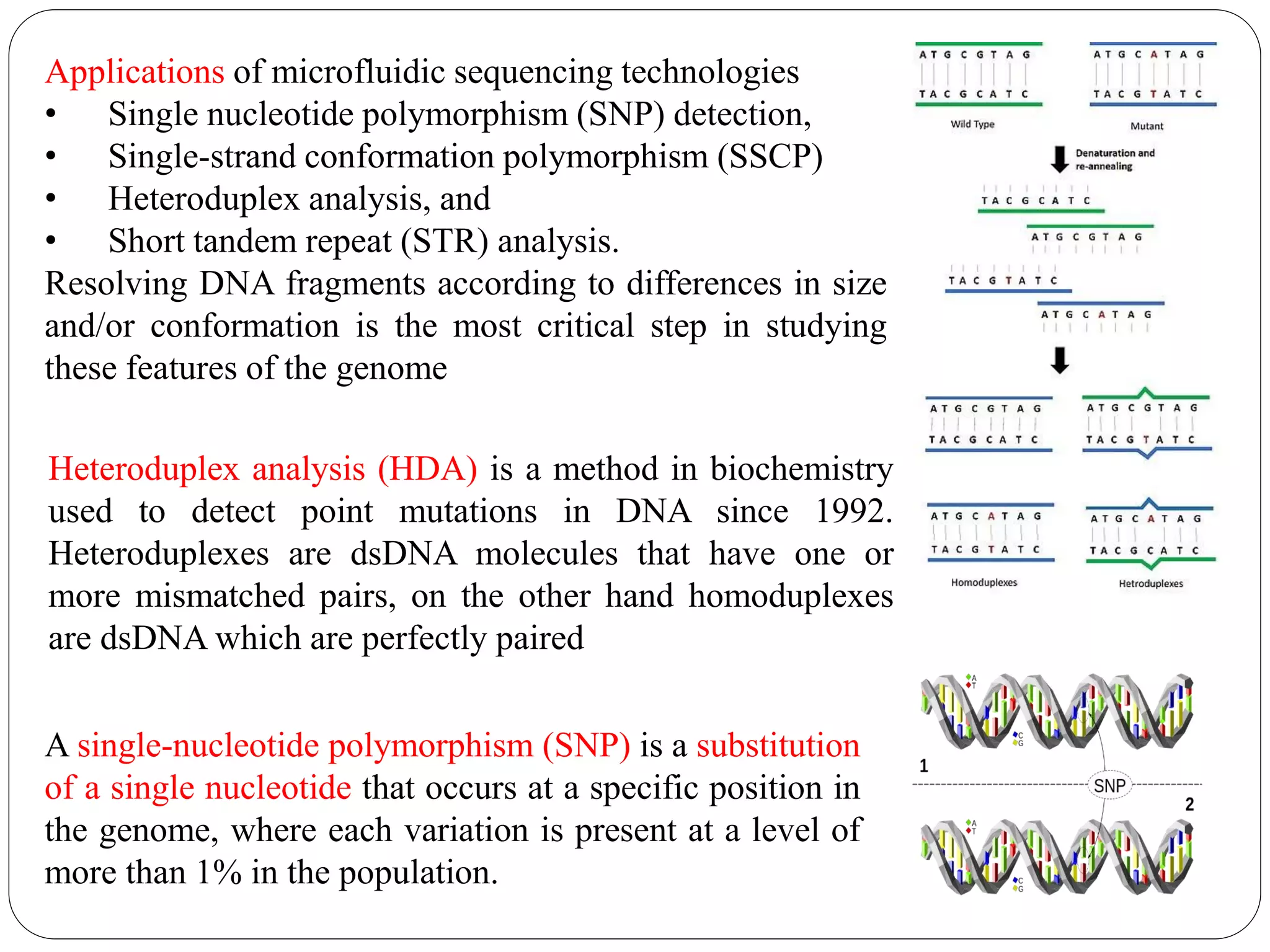
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotides in DNA, which has become faster and less expensive over the last two decades due to advances in technology. It is crucial for various fields, including medical diagnosis and biotechnology, enabling the comparison of healthy and mutated sequences to diagnose diseases. Key historical methods include Sanger sequencing and Maxam-Gilbert sequencing, both pivotal in the progression of genome sequencing techniques.