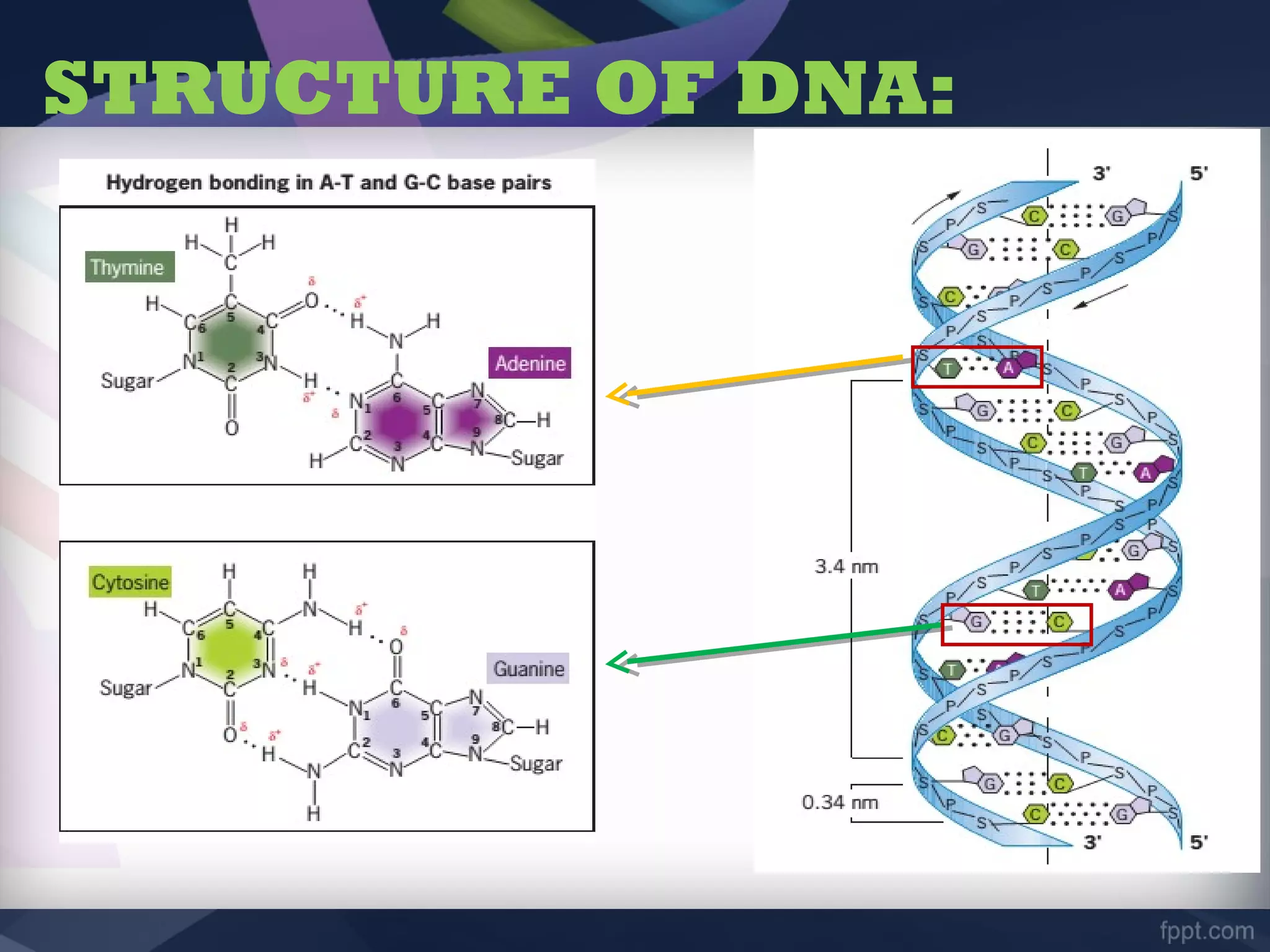
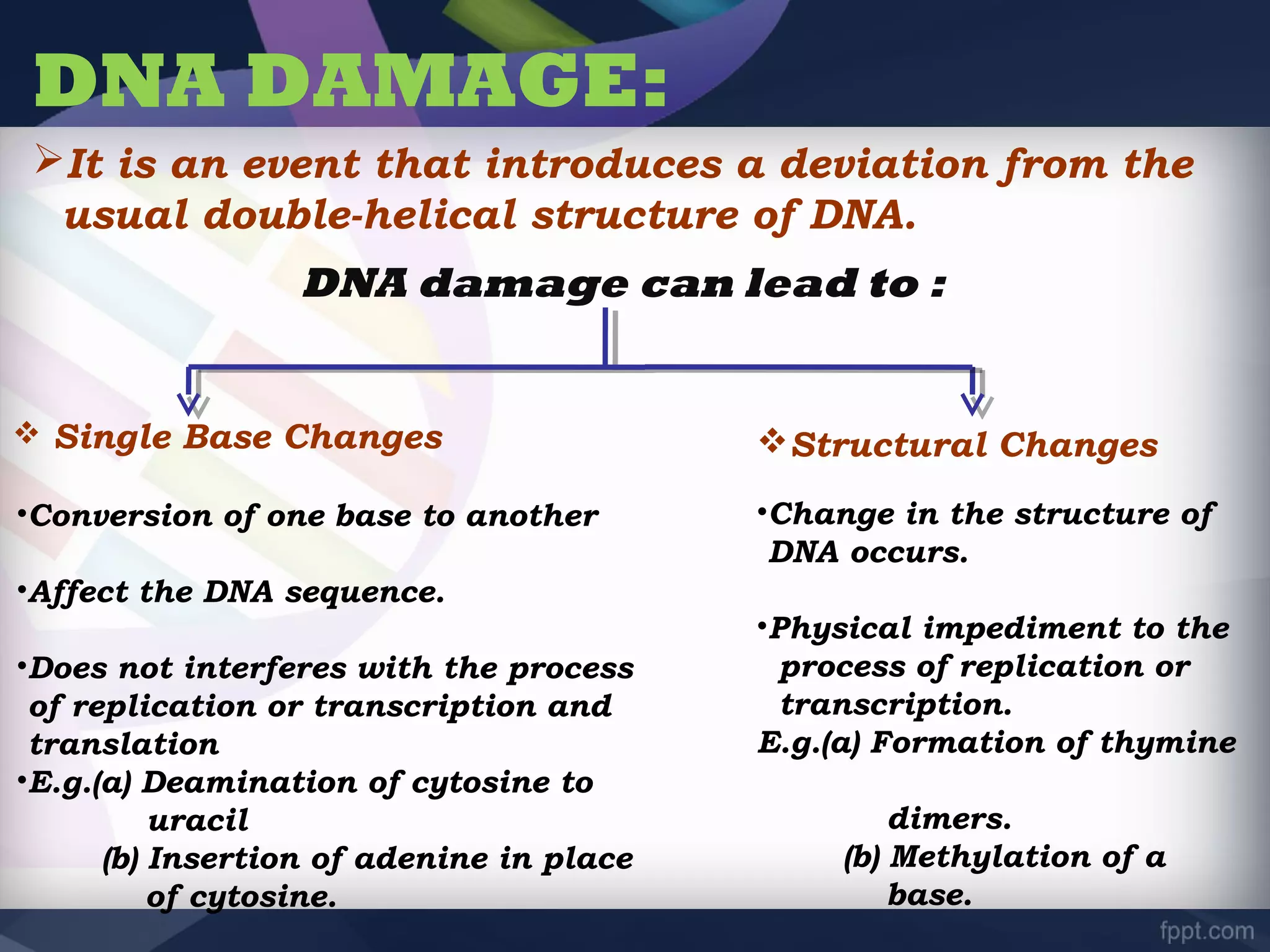
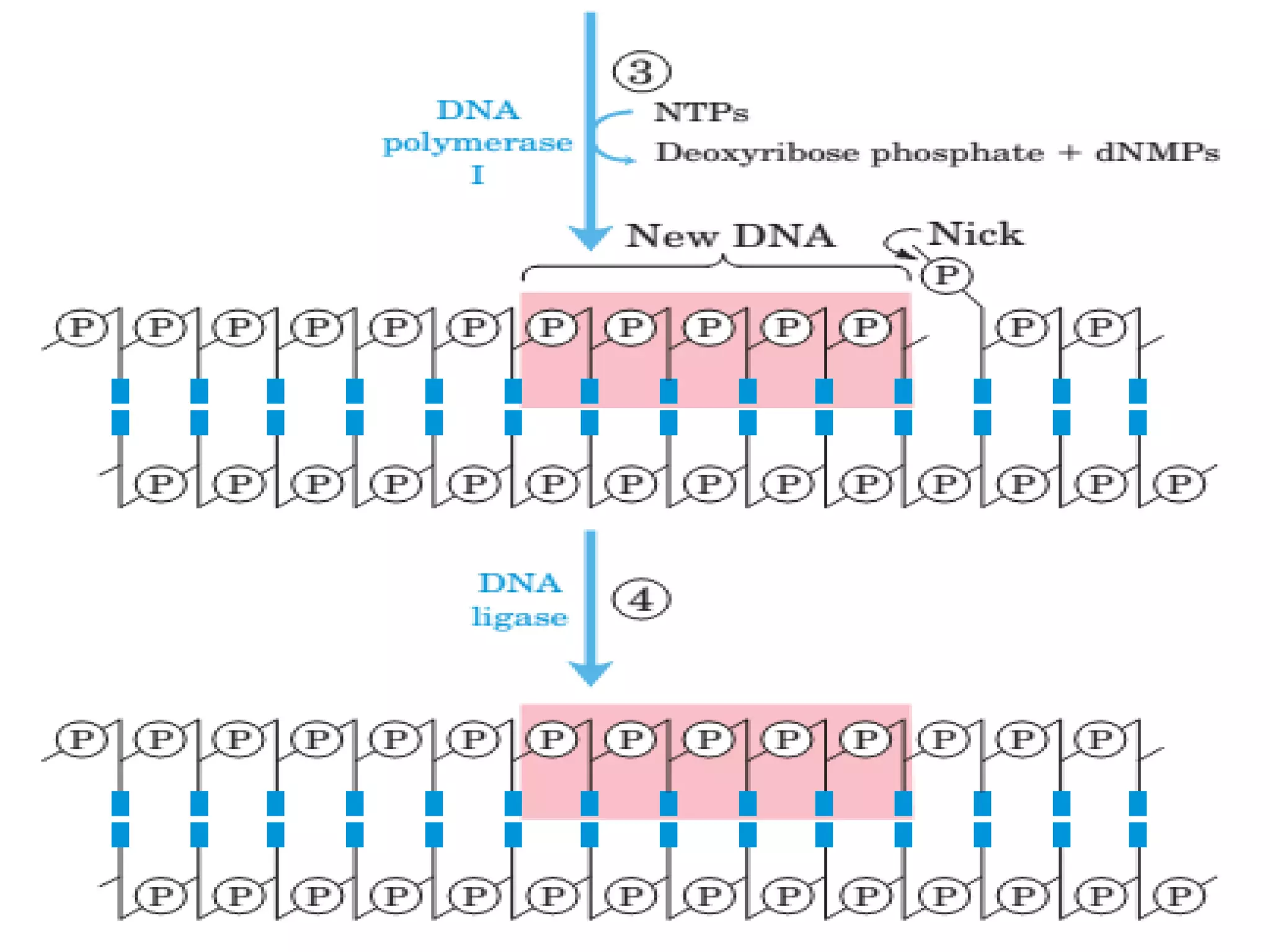
The document discusses the structure, damage, and repair mechanisms of DNA, outlining its significance as the genetic material in various organisms. It details types of DNA damage, such as single base changes and structural changes, and illustrates their causes and effects. Furthermore, it describes DNA repair mechanisms like mismatch repair, nucleotide-excision repair, and base-excision repair as essential systems to correct DNA injuries.