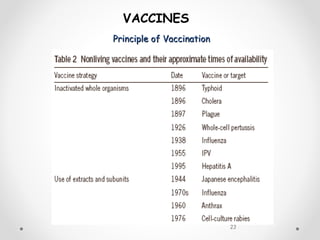
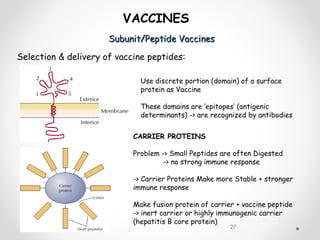
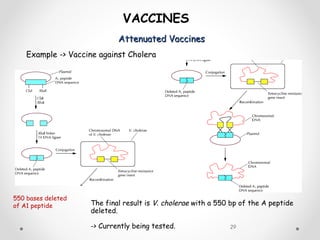
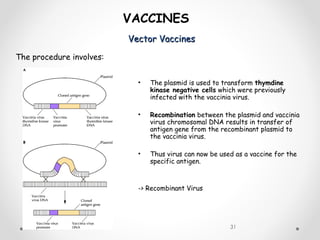
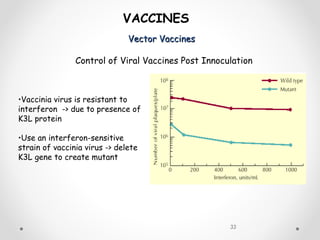
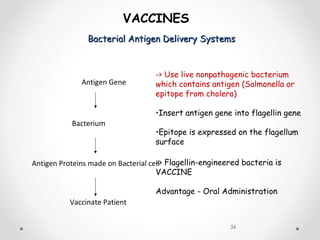
Vaccines work by exposing the immune system to antigens from a pathogen. This triggers the production of antibodies and memory cells that can recognize and quickly eliminate the pathogen if exposed in the future. There are several types of vaccines, including those using whole inactivated or attenuated pathogens, as well as newer subunit and vector vaccines that deliver just the antigenic components. Vaccine development and approval is a rigorous process to ensure safety and efficacy.



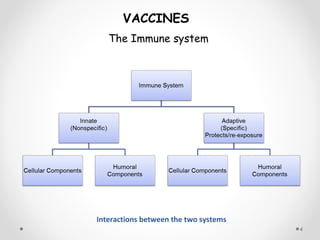
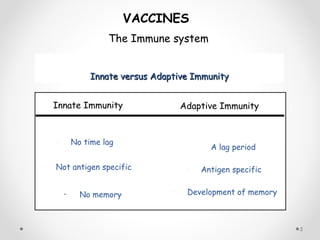

![The Immune SystemThe Immune System
10
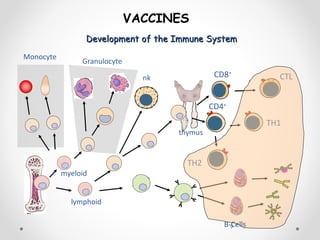
VACCINES
What Happens during an infection?
• Innate Immunity activated
– macrophages slip between cells [extravasation] to arrive
– cytokine chemicals attract other “troops” [chemotaxis]
– histamine chemicals dilate blood vessels for easier access to injury
[vasodilatation]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcs-vacation-170826005148/85/Vaccine-and-immunization-10-320.jpg)
![The Immune SystemThe Immune System
11
VACCINES
Macrophages (The “big eaters”)
• Phagocytic cells -
able to ingest small foreign invaders
– neutrophils
– monocyte
• they release cytokines that enhance the immune
response
• Mast cells /basophils
– release histamine that dilates blood vessels
– causes redness [erythrema], swelling
[edema], and heat [fever]
• Call for help from the ADAPTIVE IMMUNE System
-> results in a coordinated successful defense !
• Major players . . . the B lymphocytes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcs-vacation-170826005148/85/Vaccine-and-immunization-11-320.jpg)
![The Immune SystemThe Immune System
12
VACCINES
The Adaptive Immune system
1. Humoral immune system: -> acts against bacteria and viruses using immunoglobulins
(also known as antibodies) -> produced by B cells.
2. Cellular immune system: -> destroys intracellular pathogens (such as virus-infected
cells and mycobacteria – causing tuberculosis) using T cells (also called "T
lymphocytes"; "T" means they develop in the thymus).
There are two major types of T cells:
Cytotoxic T cells (TC cells): -> recognize infected cells by using T cell receptors to
probe cell surfaces (-> Major Histocompatability Complex [MHC]) . If they
recognize an infected cell, they release granzymes (proteases) to trigger that
cell to become apoptotic ("commit suicide")
Helper T cells (TH cells): -> activate macrophages and also produce cytokines
(interleukins) that induce the proliferation of B and T cells.
-> recognize infected cells of the immune system by using HelperT cell
receptors to probe cell surfaces (-> Major Histocompatability Complex [MHC])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcs-vacation-170826005148/85/Vaccine-and-immunization-12-320.jpg)
![The Immune SystemThe Immune System
13
VACCINES
The Adaptive Immune system
Activated B cells differentiate into . . .
– Antibody producing cells [attack mode]
– Memory cells [remembers & future protection]
Antigen & T-helper cell
memory
antibodies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcs-vacation-170826005148/85/Vaccine-and-immunization-13-320.jpg)