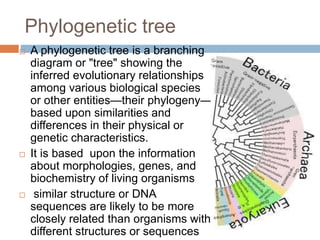
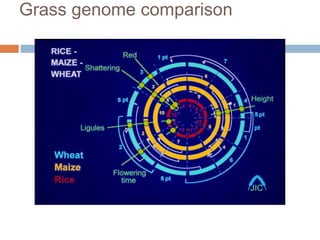
Genomic variation refers to slight differences in genetic material between organisms. It includes mutations, which are mistakes in DNA copying, and polymorphisms, where multiple alleles exist for a gene. Variations are found throughout genomes and are not evenly distributed. Studying genomic variation helps with genome mapping and screening for genetic diseases. Phylogeny determines evolutionary relationships between species based on physical/genetic similarities from fossils, molecules, and genes. A phylogenetic tree shows inferred relationships in a branching diagram. Synteny refers to homologous genes occurring in the same order on chromosomes, showing closely related species have similar gene order and large syntenic regions. The document compares gene order and syntenic regions among rice, sorghum, maize, and