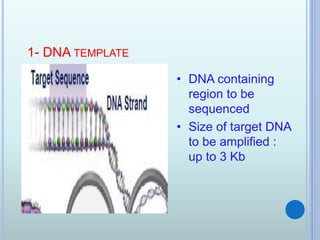
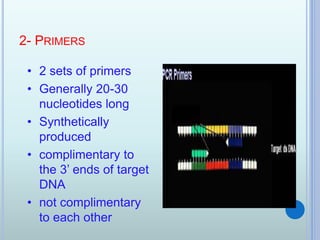
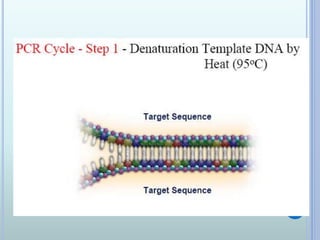
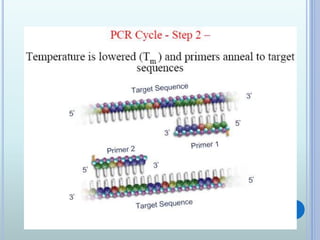
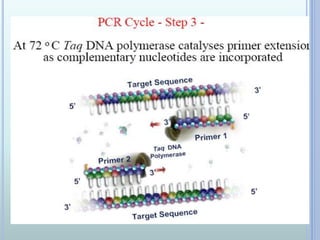
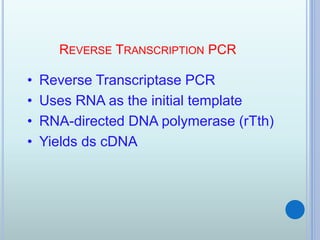
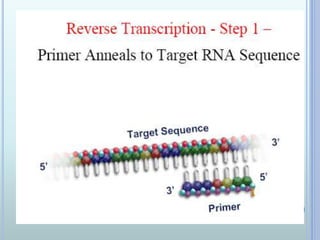
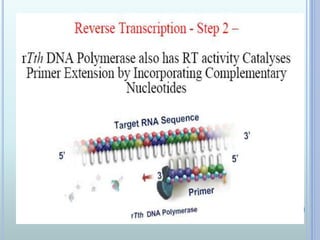
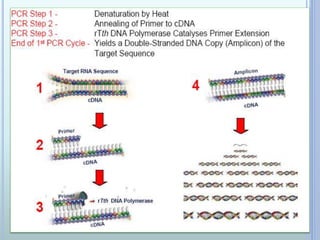
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an in vitro technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA. It involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample in the presence of primers, DNA polymerase, and dNTPs. Each cycle doubles the amount of target DNA. Real-time PCR permits both amplification and simultaneous quantification of the target DNA by using fluorescent dyes. It has various applications including disease diagnosis, gene expression analysis, and food testing.