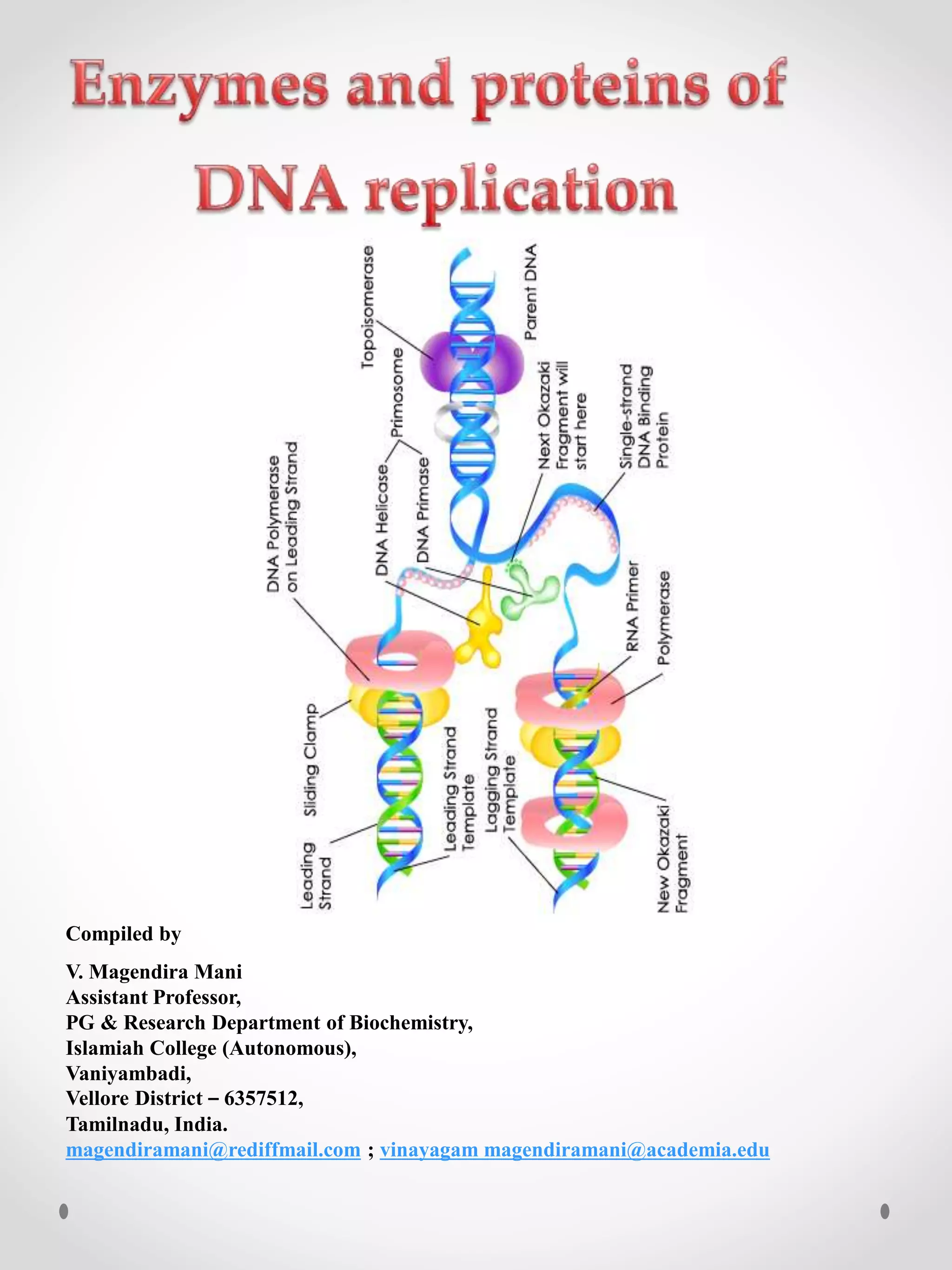
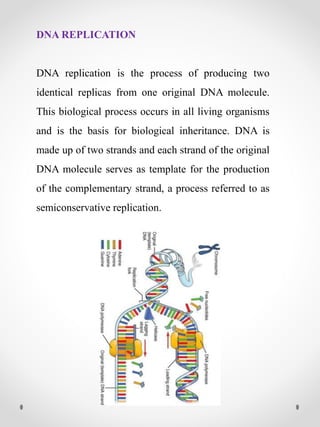
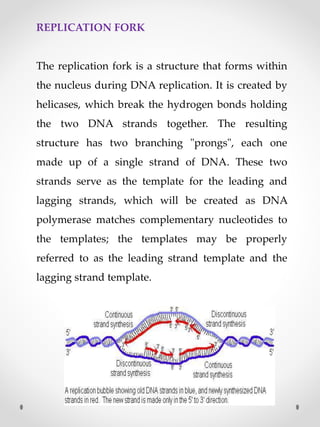
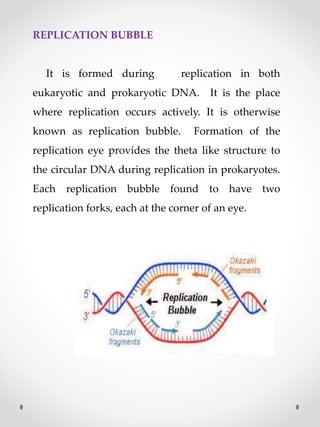
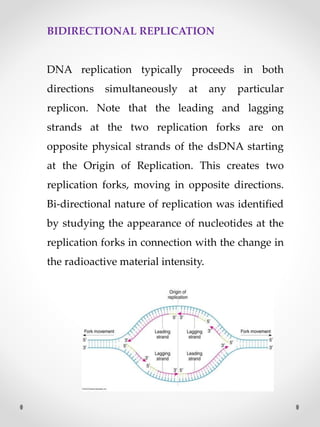
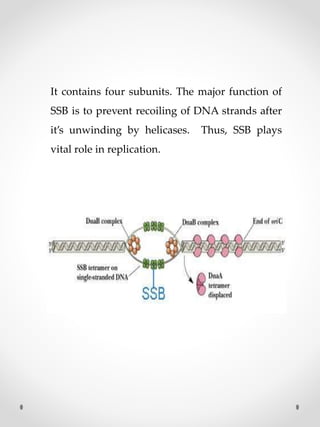
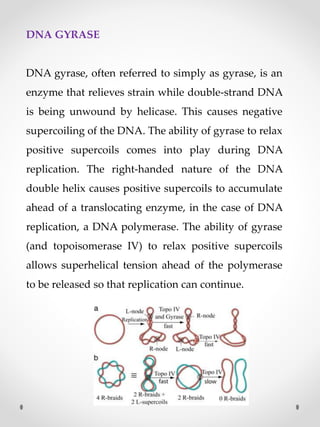
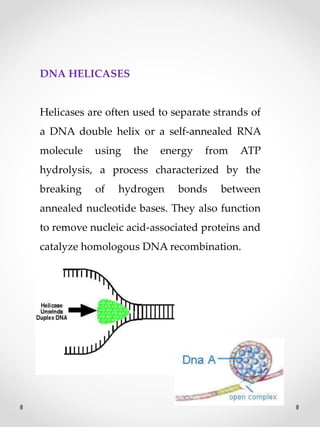
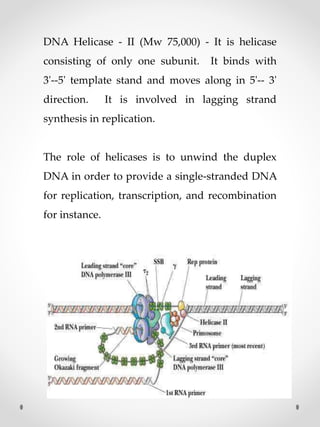
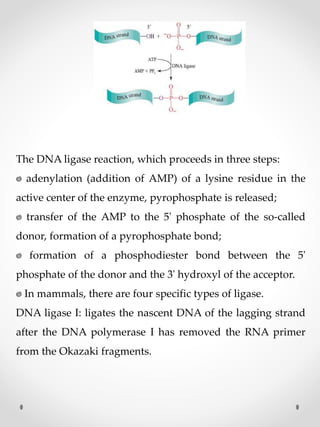
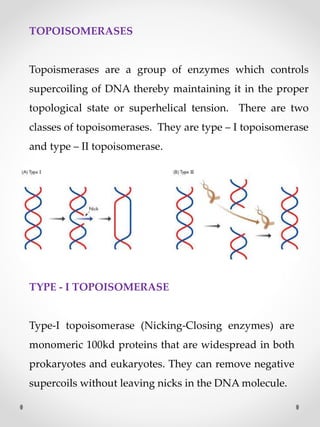
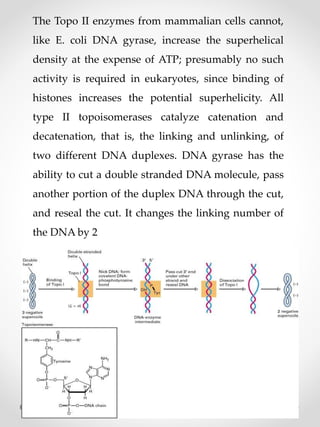
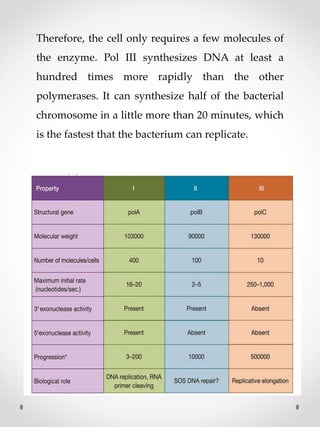
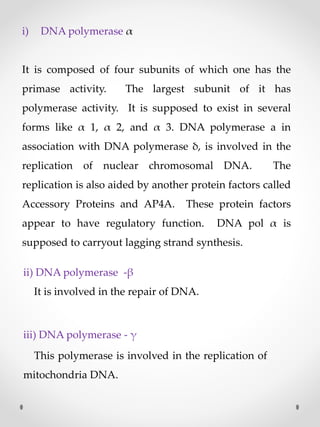
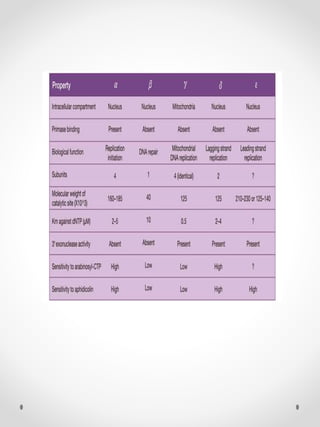
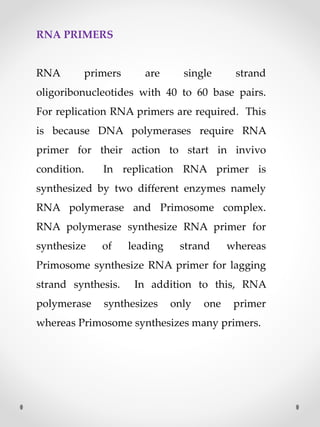
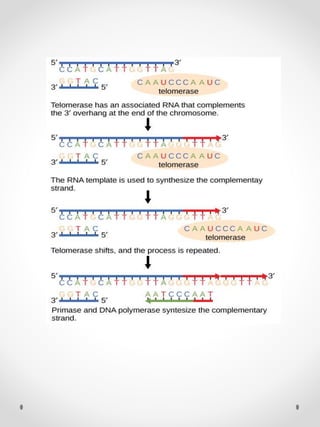
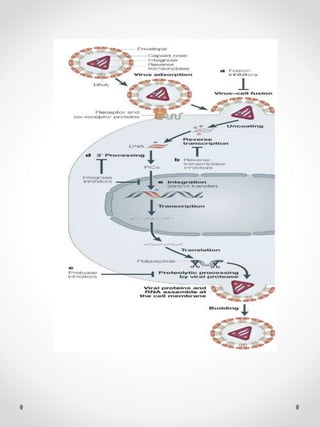
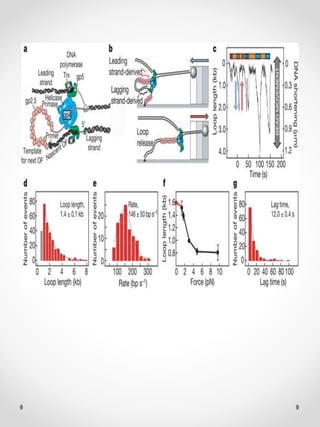
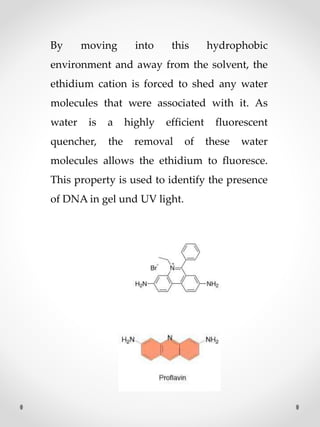
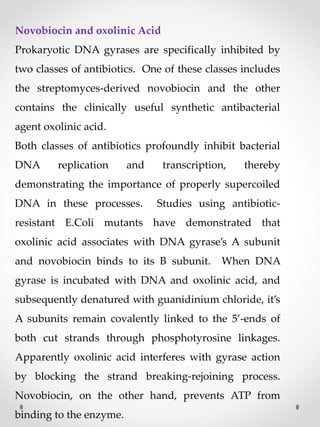
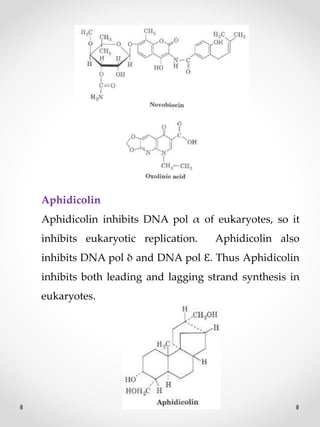
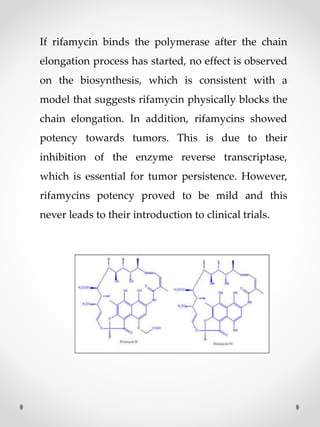
DNA replication is the process where one original DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules. It occurs through semiconservative replication where each strand of the original DNA serves as a template for the production of the complementary strand. The replication fork forms during DNA replication through the unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicases. It has two branching prongs that serve as templates for the leading and lagging strands which are synthesized by DNA polymerase.