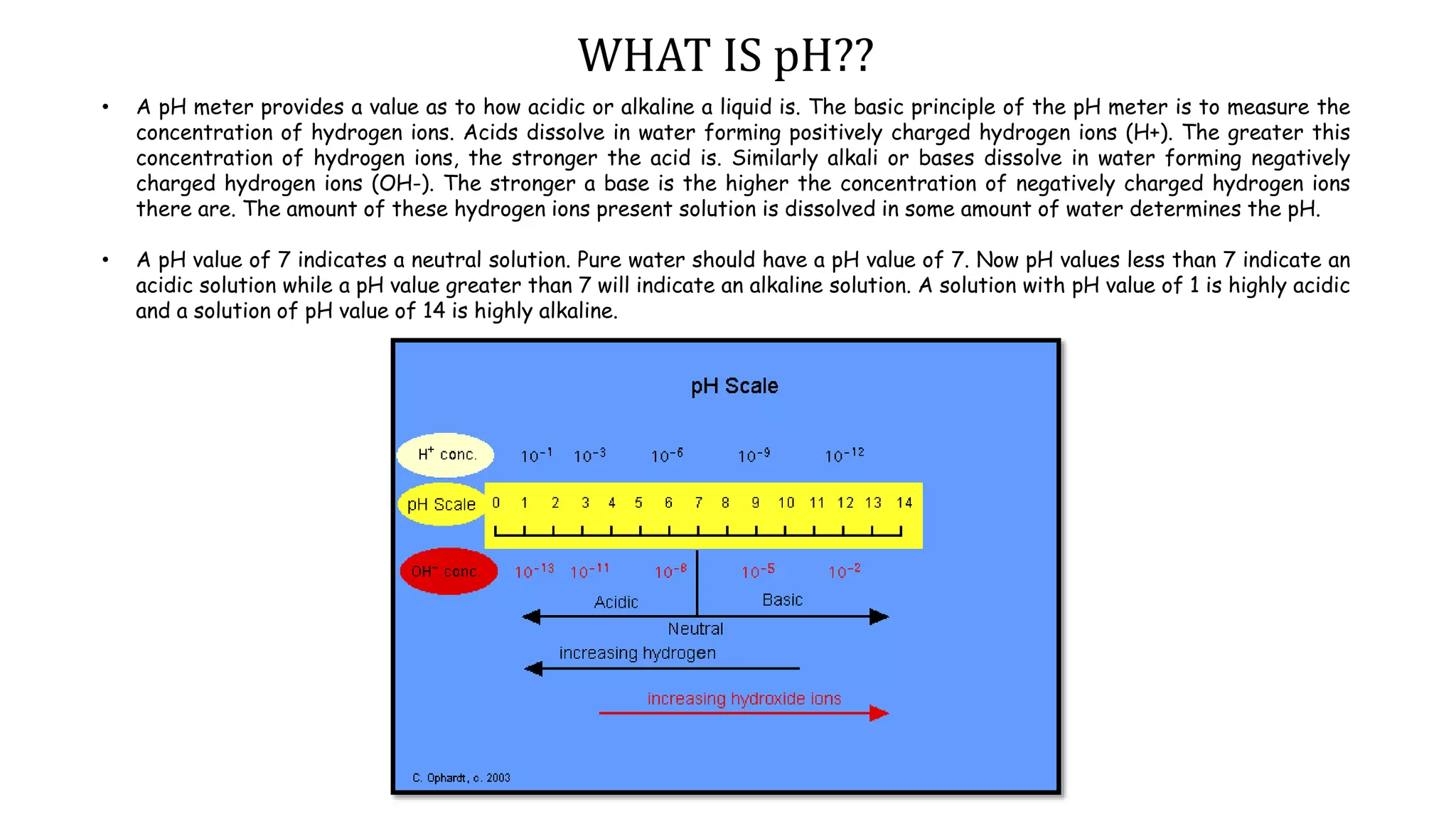
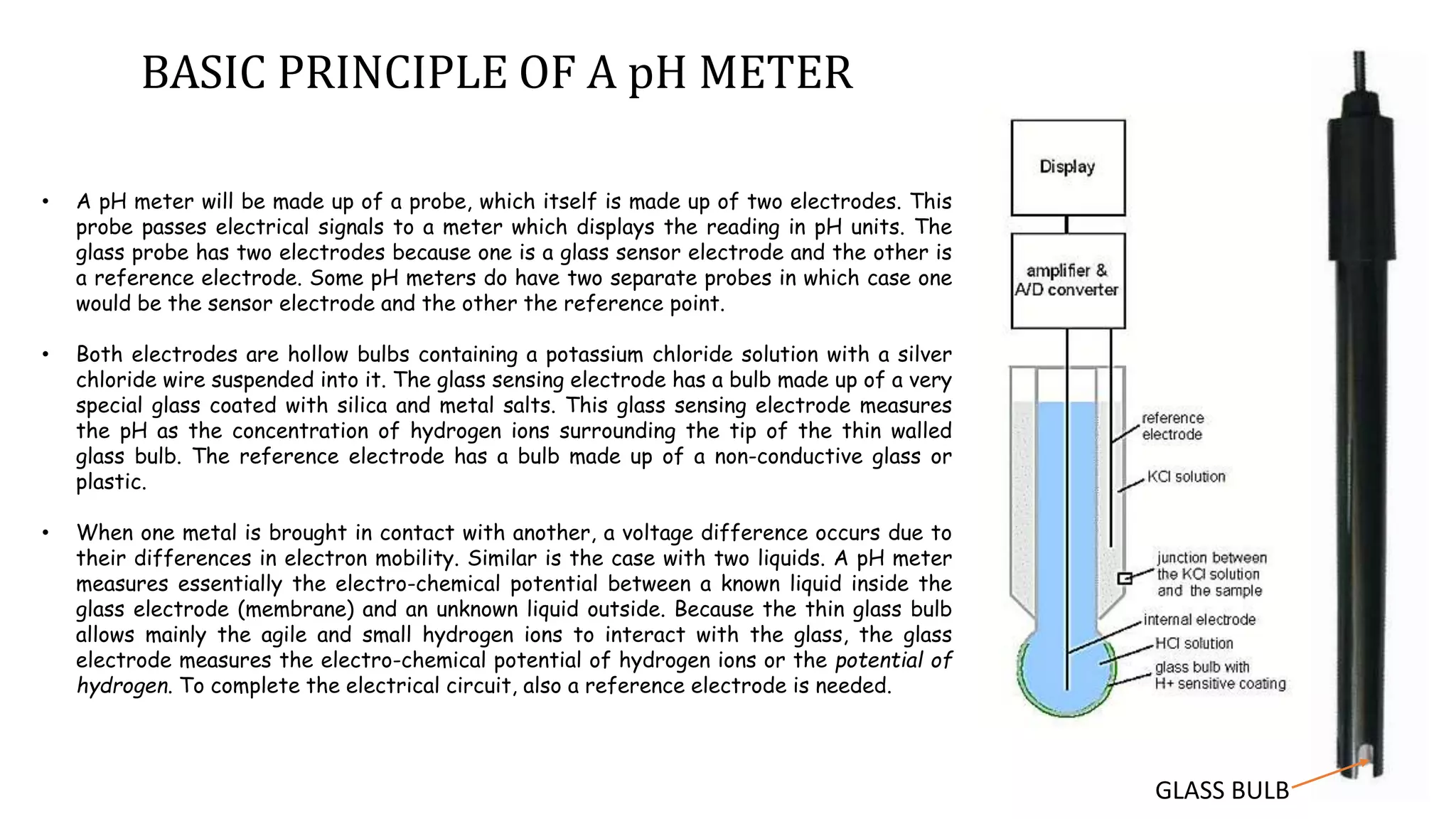
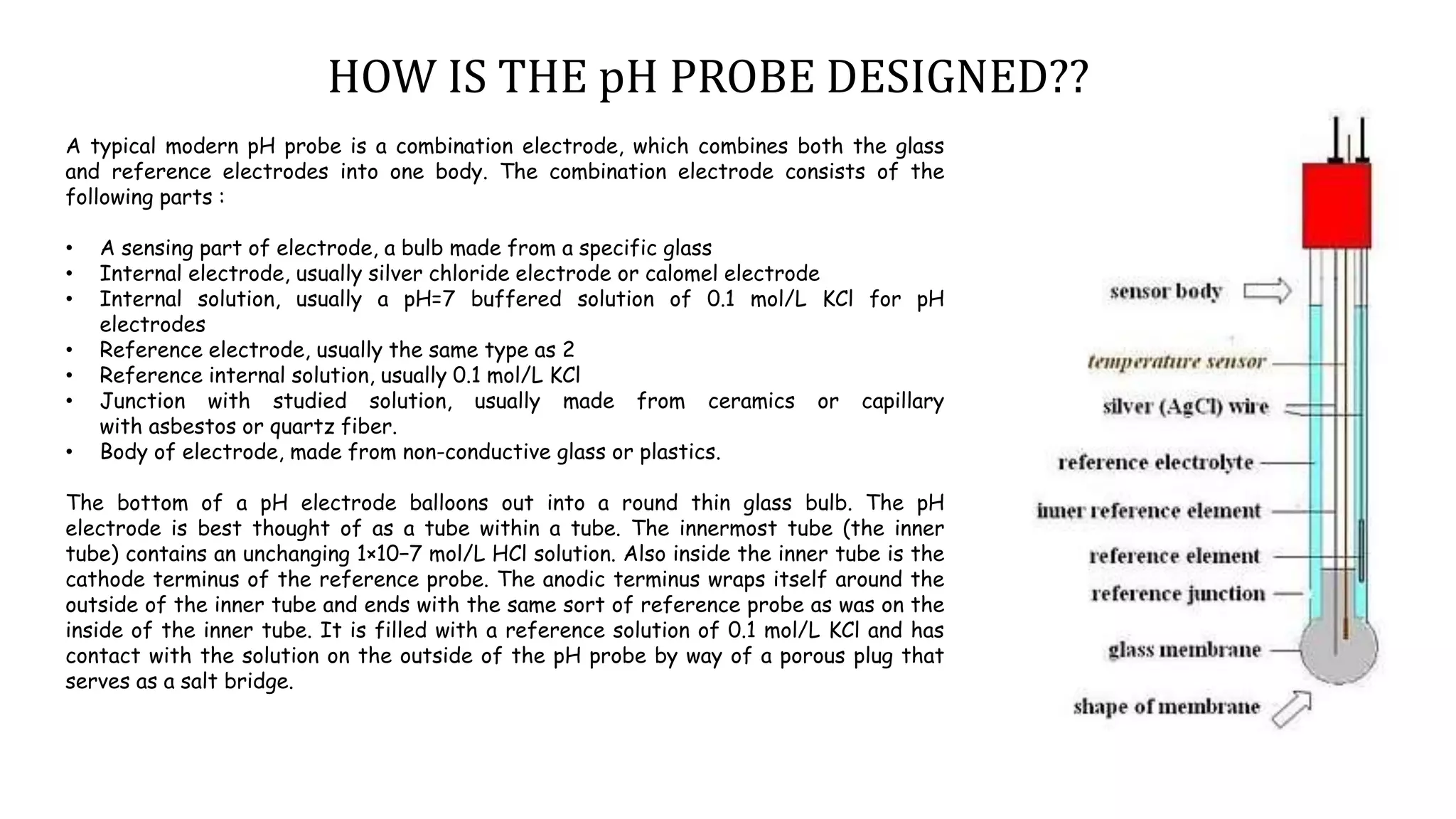
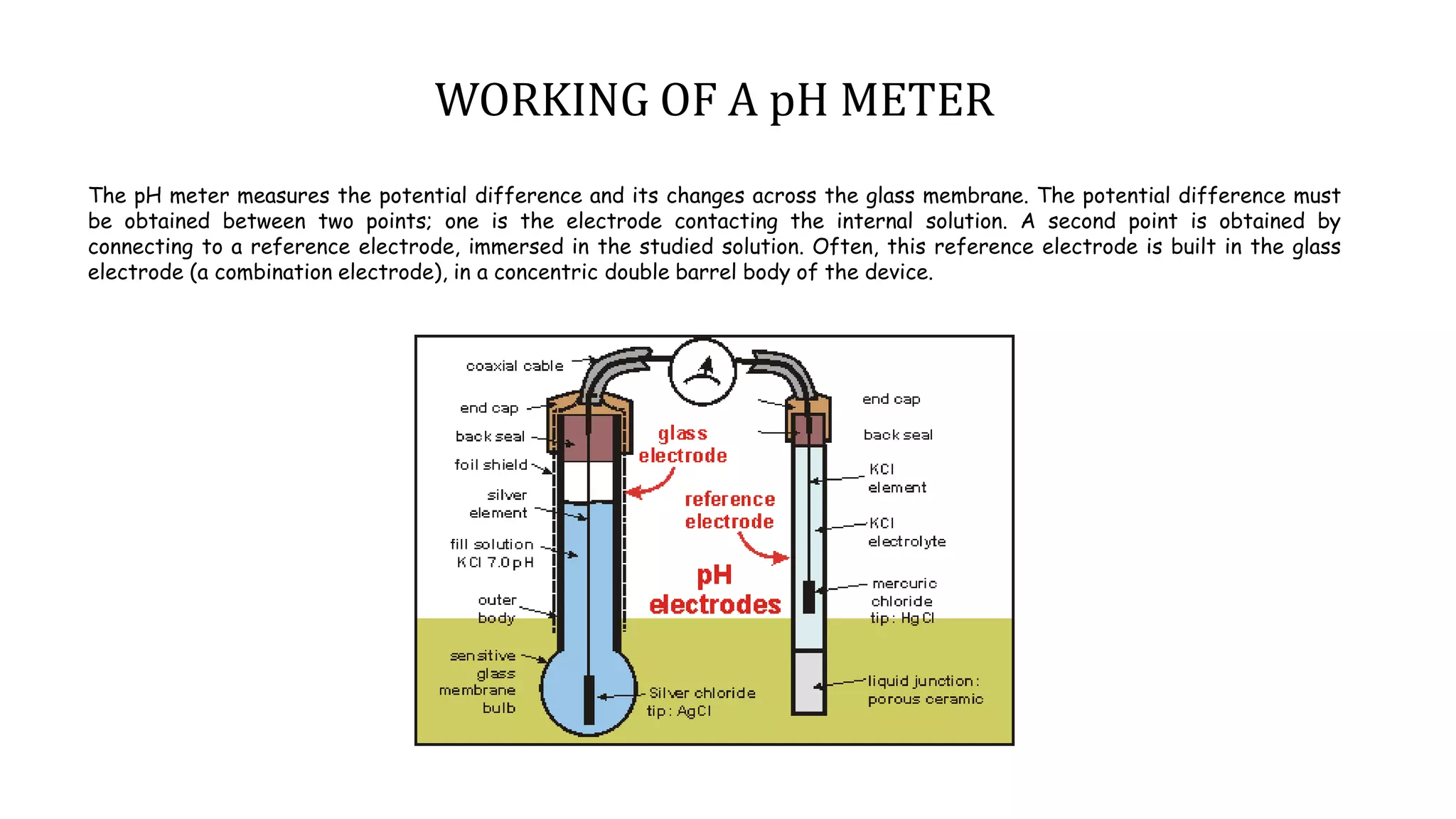
A pH meter measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution to determine if it is acidic or alkaline. It works by measuring the potential difference between a glass electrode that senses the hydrogen ions and a reference electrode in contact with a reference solution. The glass electrode contains a special glass bulb that allows hydrogen ions to interact with it, changing the electrochemical potential. This potential difference is measured by the pH meter and converted to a pH value. A silver chloride electrode is commonly used as the reference electrode due to its stable and reproducible reaction.