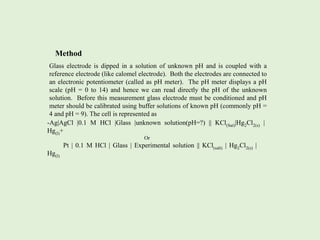
pH metry involves measuring the pH of a solution using an electrochemical cell and potentiometer or pH meter. The pH can be determined using a hydrogen electrode, quinhydrone electrode, or glass electrode. The hydrogen electrode is highly accurate but difficult to use, while the quinhydrone electrode has fewer disadvantages but cannot be used in alkaline solutions above pH 8. The glass electrode is simple to use and can measure a wide pH range but its bulb is fragile.

![pH Metry
Measurement of pH of a solution by constructing a suitable electrochemical cell
and measuring its EMF is defined as pH metry.
pH is the unit of measure that describes the degree of acidity or alkalinity.
It is measured on a scale of 0 to 14.
pH is defined as negative logarithm ( to the base 10) of activity of H+ ions
i.e. pH= - log10aH+. For dilute solution the activity of H+ ions may be replaced
by molar concentration of hydrogen ions , hence pH= - log10 [H+].
pH of a solution can be experimentally determined by combining an indicator
electrode which is reversible to H+ ions with a reference electrode and measuring
the EMF of cell with the help of potentiometer or pH meter.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmetry-230421101559-30eb78ee/85/pH-metry-pptx-2-320.jpg)

![The half cell reaction and single electrode reduction potential
2H+ + 2e– H2(g)(1 atm)
Platinum does not take part in the electrochemical reaction and it acts only as the
site for the transfer of electrons. The reduction potential of hydrogen electrode
is given by the Nernst equation.
For this electrode
At 25 0 C,
The electrode potential is given by
, n=2, PH2 =1 atm
E(H+,H2) = E0( H+, H2) -
E(H+,H2) = 0-
= -
= 0.0591 log[H+]
= -0.0591pH as pH = -log[H+]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmetry-230421101559-30eb78ee/85/pH-metry-pptx-4-320.jpg)



![The reduction potential of the quinhydrone electrode is given by the Nernst
equation.
For this electrode
E0
Q = 0.6996 V at 25°C
n = 2
At 25°C,
Now in aq. Solution of quinhydrone, [H2Q] = [Q]
At 25°C, EQ = 0.6996 – 0.0591 pH
Thus, reduction potential of Quinhydrone electrode is a function of pH of
the solution.
2.303 RT/ F = 0.0591](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmetry-230421101559-30eb78ee/85/pH-metry-pptx-8-320.jpg)


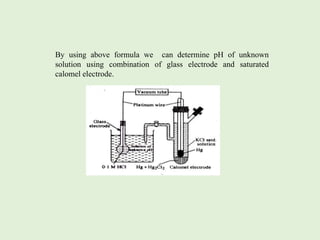
![Determination of pH by using Glass Electrode :
Haber and Klemensiewiez (1909) observed that when two solutions of different
pH are separated by a glass membrane of low melting and high conductivity
glass, potential is developed across the membrane. When such a glass bulb is
filled with 0.1 M HCl and is immersed in another solution containing H+ ions,
the potential of such electrode depends on the pH of outer solution. Thus, such
a glass electrode can be used for the measurement of pH of outer solution.
Construction of Glass Electrode and Single Electrode Potential
Glass electrode is made of a thin glass bulb or a special quality glass which is
attached to a glass tube. The glass bulb is filled with 0.1 M HCl solution and a
silver wire coated with AgCl (or Pt wire) is immersed in it.
Single electrode potential or a glass electrode is given by
EG = E°G + 0.0591 log [H+]
or EG = E°G - 0.0591 pH
Where E°G = A constant for the given glass electrode called as asymmetry
potential. Value of E°G may be determined by using a buffer solution of known
pH.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmetry-230421101559-30eb78ee/85/pH-metry-pptx-11-320.jpg)