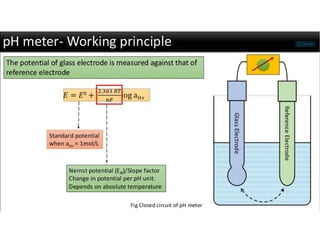
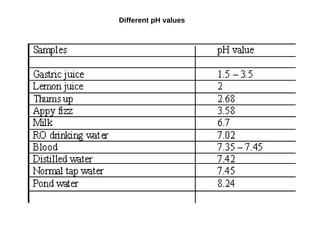
This document discusses the principles and components of a pH meter. It begins by defining pH as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration. A pH meter measures pH by using a glass electrode and a reference electrode, such as a silver-silver chloride or saturated calomel electrode. The glass electrode selectively binds hydrogen ions and generates an electric potential based on the hydrogen ion concentration difference across its membrane. Various pH values correspond to different applications in fields like medicine, agriculture, manufacturing and more.


![PH Meter
Principle
pH is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration.
pH= -log [ H+ ]
p = power
H = hydrogen
[H+ ] = hydrogen ion concentration
The pH of a solution can be measured by the pH meter. The glass
electrode is an half cell and the calomel electrode is another half cell.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmeters-171222095713/85/pH-Meter-3-320.jpg)



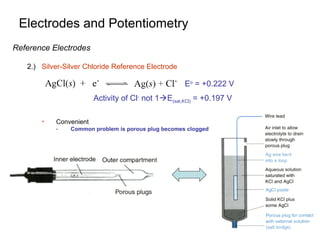

![Electrodes and Potentiometry
Reference Electrodes
3.) Saturated Calomel Reference Electrode (S.C.E)
Saturated KCl maintains constant [Cl-
] even with
some evaporation
Standard hydrogen electrodes are cumbersome
- Requires H2 gas and freshly prepared Pt surface
Eo
= +0.268 V
Activity of Cl-
not 1E(sat,KCl) = +0.241 V](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmeters-171222095713/85/pH-Meter-10-320.jpg)
![Electrodes and Potentiometry
pH Electrodes
1.) pH Measurement with a Glass Electrode
Glass electrode is most common ion-selective electrode
Combination electrode incorporates both glass and reference
electrode in one body
Ag(s)|AgCl(s)|Cl-
(aq)||H+
(aq,outside) H+
(aq,inside),Cl-
(aq)|AgCl(s)|Ag(s)
Outer reference
electrode
[H+
] outside
(analyte solution)
[H+
] inside Inner reference
electrode
Glass membrane
Selectively binds H+
Electric potential is generated by [H+
] difference across glass membrane](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmeters-171222095713/85/pH-Meter-11-320.jpg)
![Electrodes and Potentiometry
pH Electrodes
1.) pH Measurement with a Glass Electrode
Glass electrode is most common ion-selective electrode
Combination electrode incorporates both glass and reference
electrode in one body
Ag(s)|AgCl(s)|Cl-
(aq)||H+
(aq,outside) H+
(aq,inside),Cl-
(aq)|AgCl(s)|Ag(s)
Outer reference
electrode
[H+
] outside
(analyte solution)
[H+
] inside Inner reference
electrode
Glass membrane
Selectively binds H+
Electric potential is generated by [H+
] difference across glass membrane](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phmeters-171222095713/85/pH-Meter-12-320.jpg)