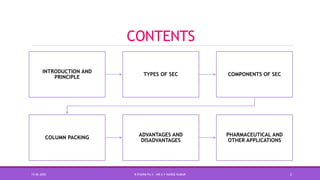
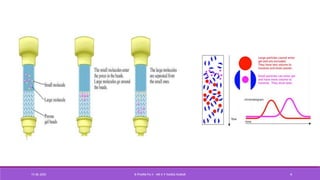
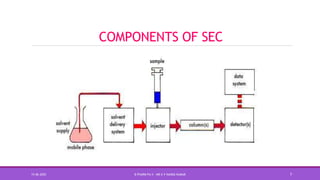
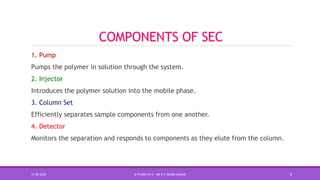
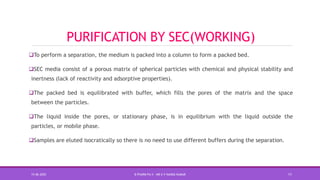
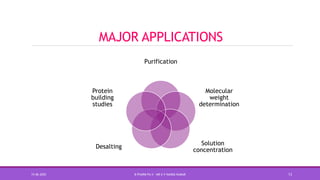
Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) is a method used to separate molecules based on their size by filtering through a gel with specific pore sizes. The document outlines the principles, types (gel permeation and gel filtration), components, and applications of SEC, highlighting its effectiveness in purifying biomolecules and determining molecular weights. It also discusses the setup, including a packed column, the use of pumps and detectors, and various applications such as desalting and protein studies.