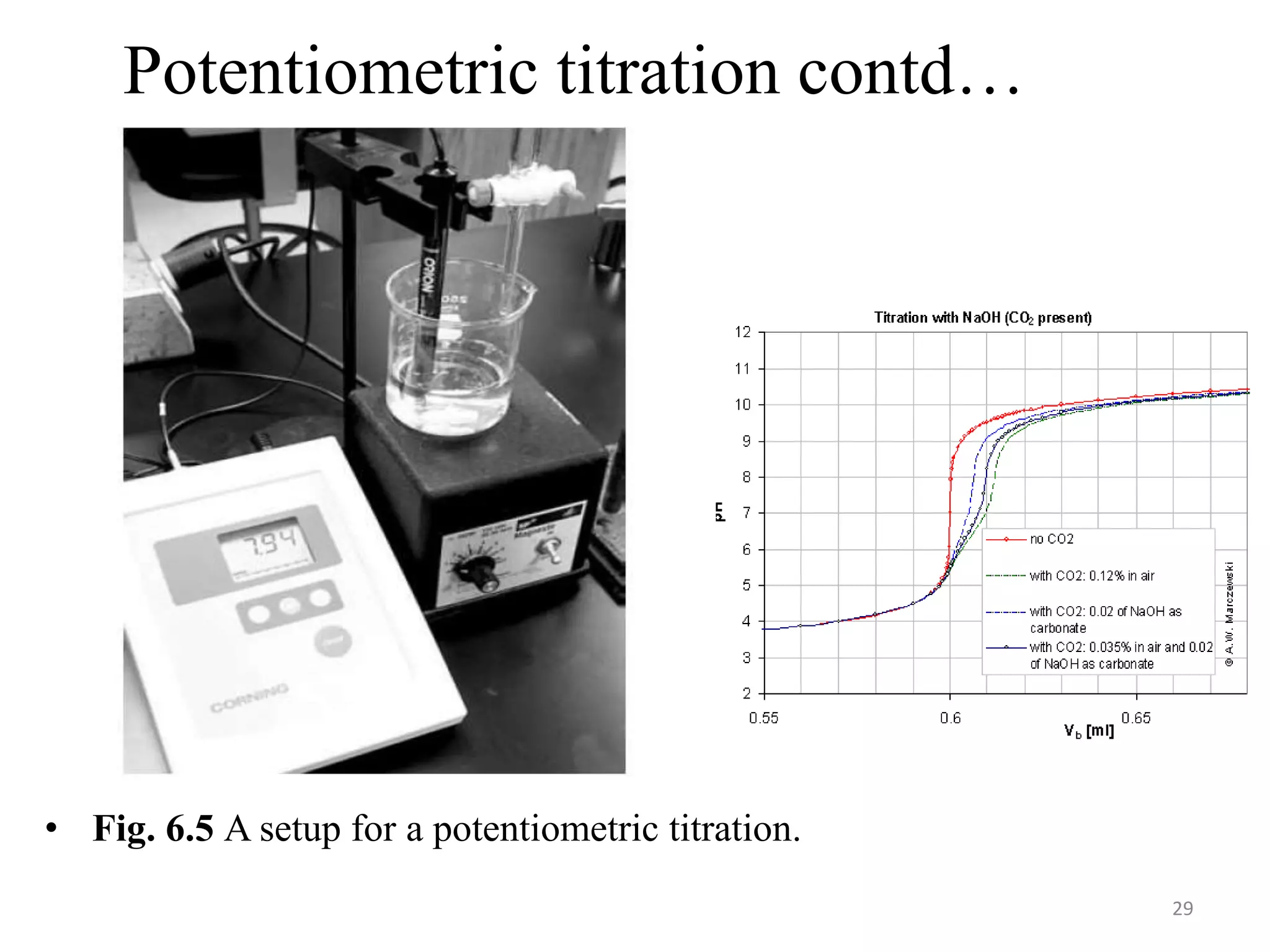
Potentiometry involves measuring the potential (voltage) between an indicator electrode and a reference electrode immersed in a solution. The potential measurement provides information about the concentration of an analyte in the solution. Common reference electrodes include the saturated calomel electrode (SCE) and silver-silver chloride electrode, which maintain a constant potential. pH electrodes function as indicator electrodes, with their potential directly proportional to the pH of the solution. The potential measurement is made against the reference electrode using a pH meter, which can be calibrated using buffer solutions.




![Cont…
Within the inner tube is mercury metal and a paste-like material
known as calomel.
Calomel is made by thoroughly mixing mercury metal (Hg) with
mercurous chloride (Hg2Cl2), a white solid.
When in use, the ff half-cell rxn occurs:
The Nernst equation for this rxn is
Obviously the only variable on which the potential depends is [Cl–]
The saturated KCl present provides the [Cl–] for the rxn, and, since
it is a saturated so/n, [Cl–] is a constant at a given temperature
represented by the solubility of KCl at that temperature.
If [Cl–] is constant, the potential of this half-cell, dependent only
on the [Cl–], is therefore also a constant.
As long as KCl is kept saturated and the temperature kept constant,
the SCE is useful as a reference against which all other potential
measurements can be made.
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-5-2048.jpg)

![Cont…
The Nernst equation for this is
The standard reduction potential for this half-rxn is +0.22233 V.
The potential is dependent only on the [Cl–], as was the potential of
the SCE, & once again [Cl–] is constant because the so/n is saturated.
Thus this electrode is also appropriate for use as a reference
electrode.
Fig. 6.2. A drawing of a commercial Ag–AgCl reference electrode. 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-7-2048.jpg)
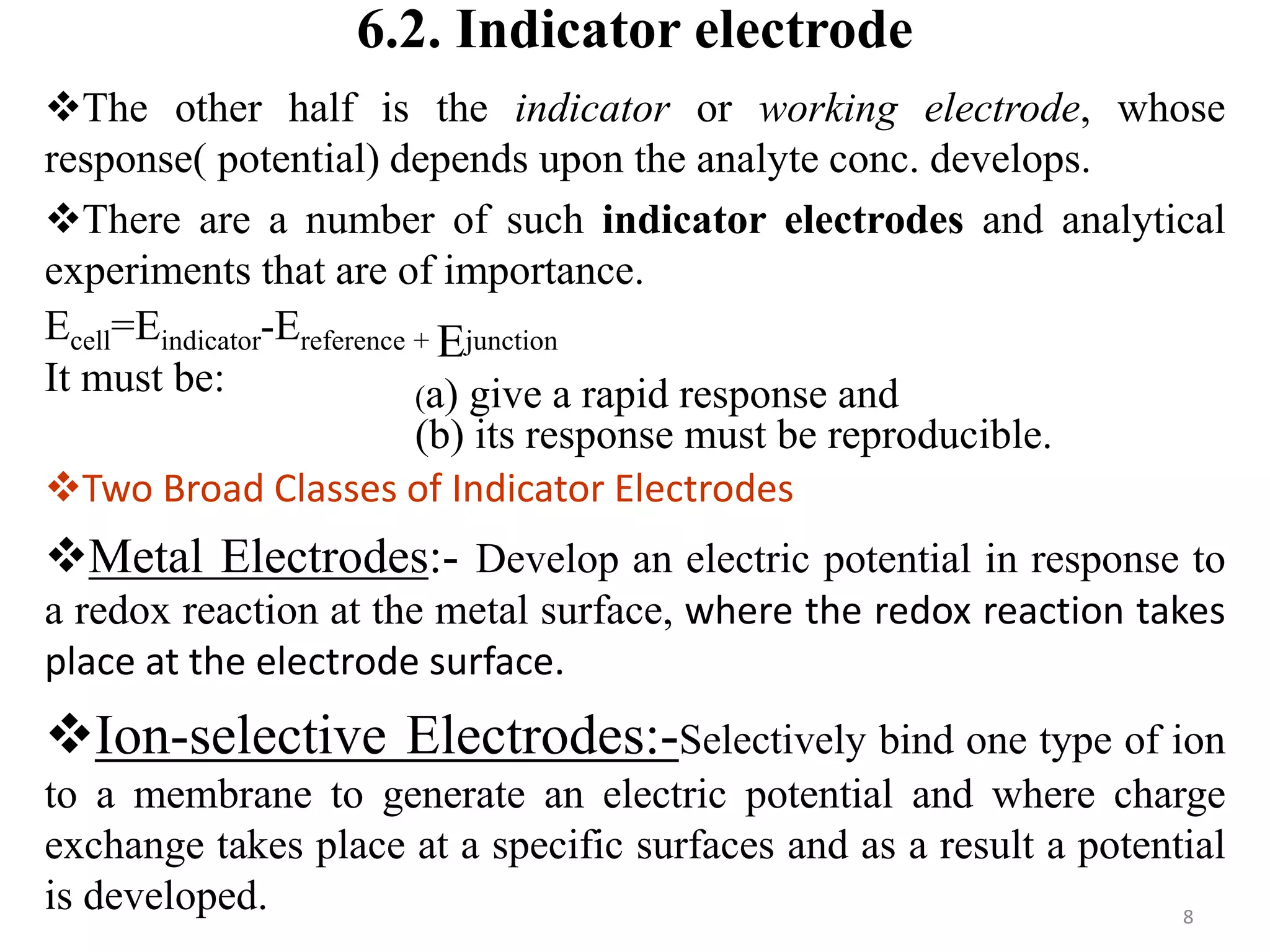
![Metal Electrodes
a- First-order electrodes for cations:
e.g. in determination of Ag+ a rode or wire of silver metal is the
indicator electrode, it is potential is:
It is used for determination of Ag+ with Cl-, Br- and CN-. Copper,
lead, cadmium, and mercury
b) Second order electrodes for anions
A metal electrode is also indirectly responsive to anions that form
slightly soluble precipitates or stable complexes with its cation.
The electrode reaction is AgCl + e = Ag+ + Cl-, and the electrode
potential is given by:
E25 = EoAg/AgCl - 0.059 log [Cl-]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-9-2048.jpg)





![Measurement of pH (cont.)
Hg2Cl2(s) + H2(g) 2Hg(l) + 2H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq)
• What if we let [H+] vary?
Q H
2
Cl
2
Ecell = E°cell - (0.0591/2)log(Q)
Ecell = E°cell - (0.0591/2)(2log[H+] + 2log[Cl-])
Ecell = E°cell - (0.0591)(log[H+] + log[Cl-])
saturate
constant](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-15-2048.jpg)
![Measurement of pH (cont.)
Ecell = E°cell - (0.0591)log[H+] + constant
• Ecell is directly proportional to log [H+]
electrode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-16-2048.jpg)

![Cont…
o Since the glass membrane at the tip is thin, a potential develops due
to the fact that the chemical composition inside is different from the
chemical composition outside.
o Specifically, it is the difference in the conc of the H-ions on
opposite sides of the membrane that causes the potential (the
membrane potential) to develop.
o There is no half-cell rxn involved.
The Nernst equation is
or, since the internal [H+] is a constant, it can be combined with Eo,
which is also a constant, giving a modified Eo, E*, and eliminating
[H+](internal): E = E* - 0.0592 log [H+](external)
In addition, we can recognize that pH = –log [H+] and substitute this
into the above equation: E = E* + 0.0592 pH
The beauty of this electrode is that the measured potential (measured
against a reference electrode) is thus directly proportional to the pH
of the so/n into which it is dipped.
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-18-2048.jpg)

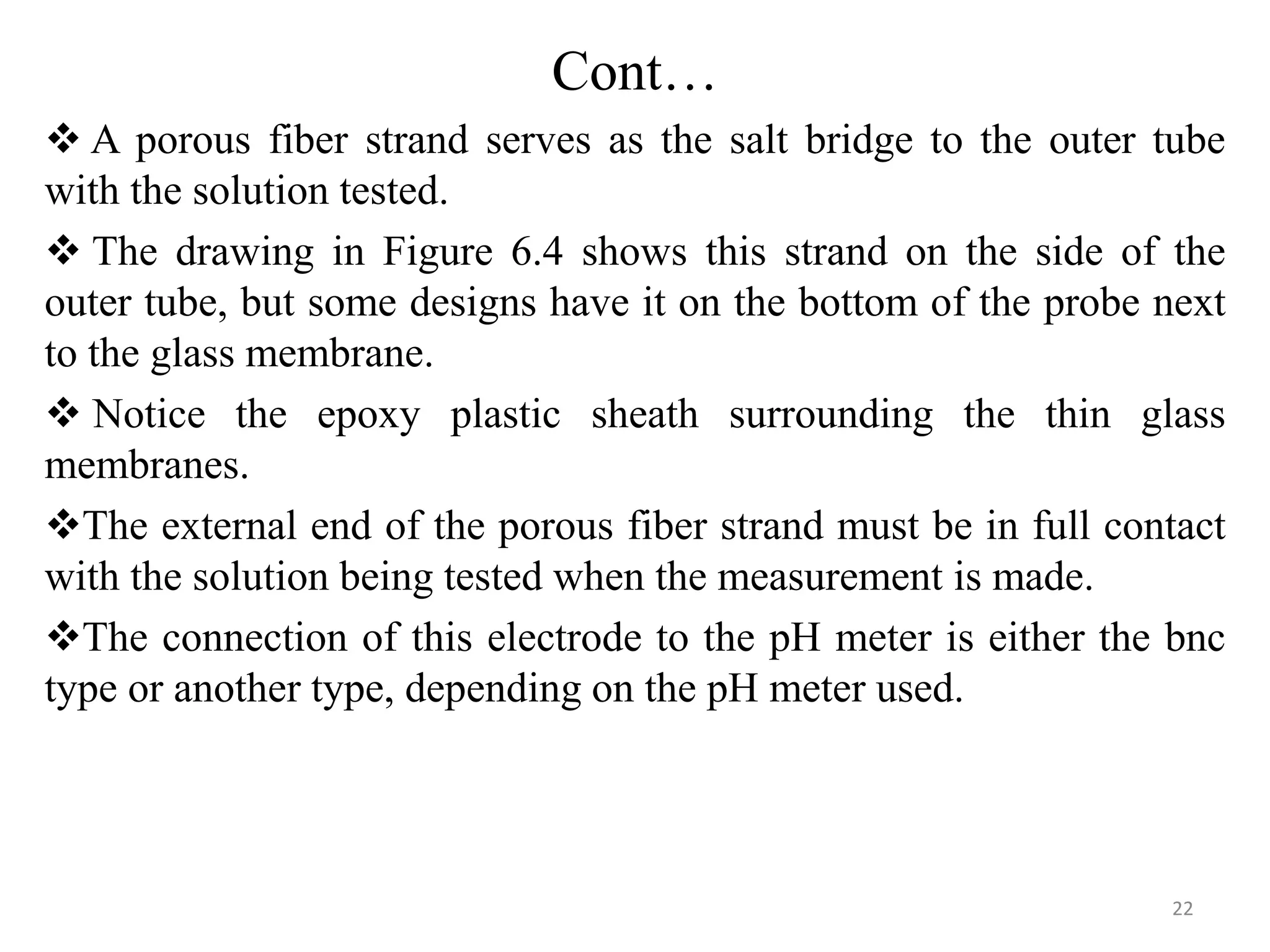
![Cont…
Fig. 6.4. A drawing of a commercial
Combination pH Electrode.
o The pH electrode is found in the center of the probe as shown.
o It is identical to the pH electrode described above a Ag wire coated
with AgCl immersed in a so/n saturated with AgCl and having a [H+]
of 1.0 M.
o This solution is in contact with a thin glass membrane at the tip.
o The RE is in an outer tube concentric with the inner pH electrode.
o It has a Ag wire coated with AgCl in contact with a so/n saturated
with silver chloride and potassium chloride. 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-21-2048.jpg)



![Cont…
As the gases diffuse in, the pH of the so/n constituting the thin film
changes, and thus the response of the pH electrode changes
proportionally to the amount of gas diffusing in.
Calibration of ion-selective electrodes for use in quantitative
analysis is usually done by preparing a series of standards as in most
other instrumental analysis methods, since the measured potential is
proportional to the logarithm of the concentration.
The relationship is
in which z is the signed charge on the ion.
The analyst can measure the potential of the electrode immersed in
each of the standards and the sample (vs. the SCE or silver–silver
chloride reference), plot E vs. log [ion], and find the unknown
concentration from the linear regression procedures.
26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitsixed-200103101810/75/potentiometry-26-2048.jpg)