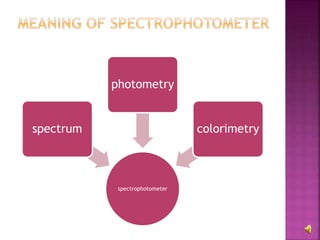
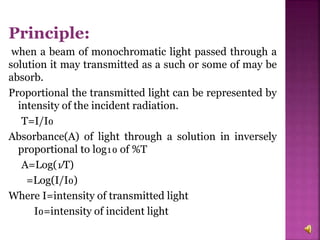
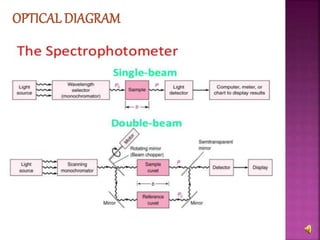
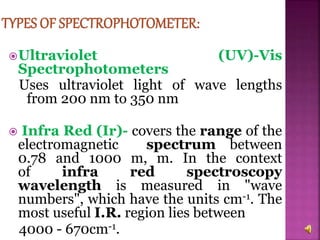
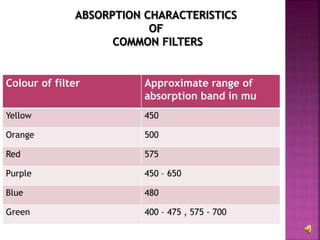
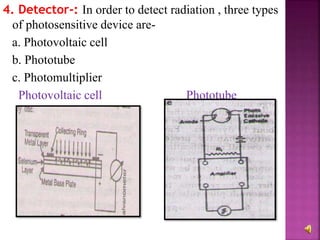
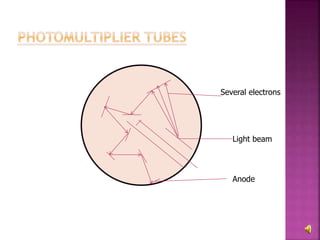
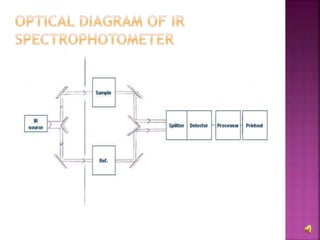
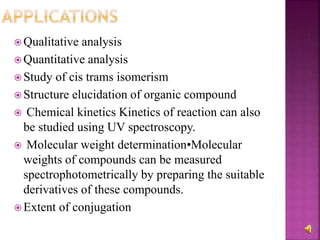
The document explains the function and principles of spectrophotometers, instruments that measure light intensity based on wavelength to determine the concentration of substances in a solution. It covers types of spectrophotometers, including UV-Vis and infrared, their components, and the application of Beer's and Lambert's laws in quantitative analysis. Additionally, it discusses the various detectors and methodologies used in both qualitative and quantitative assessments in spectroscopy.