This document discusses antibiotic sensitivity testing and provides updates from 2017. It describes various antibiotic classes and the major mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. It then covers the key methods for testing antibiotic sensitivity, including disk diffusion, E test, and broth dilution. Quality control and preparation of bacteria are also outlined. The document concludes by discussing specific resistant bacteria such as MRSA, ESBLs, and mechanisms of beta-lactamase production.



















![Extended Spectrum BetaExtended Spectrum Beta
LactamaseLactamase
[ESBL][ESBL]
Enzymes produced by Enteric Gram negative bacilliEnzymes produced by Enteric Gram negative bacilli
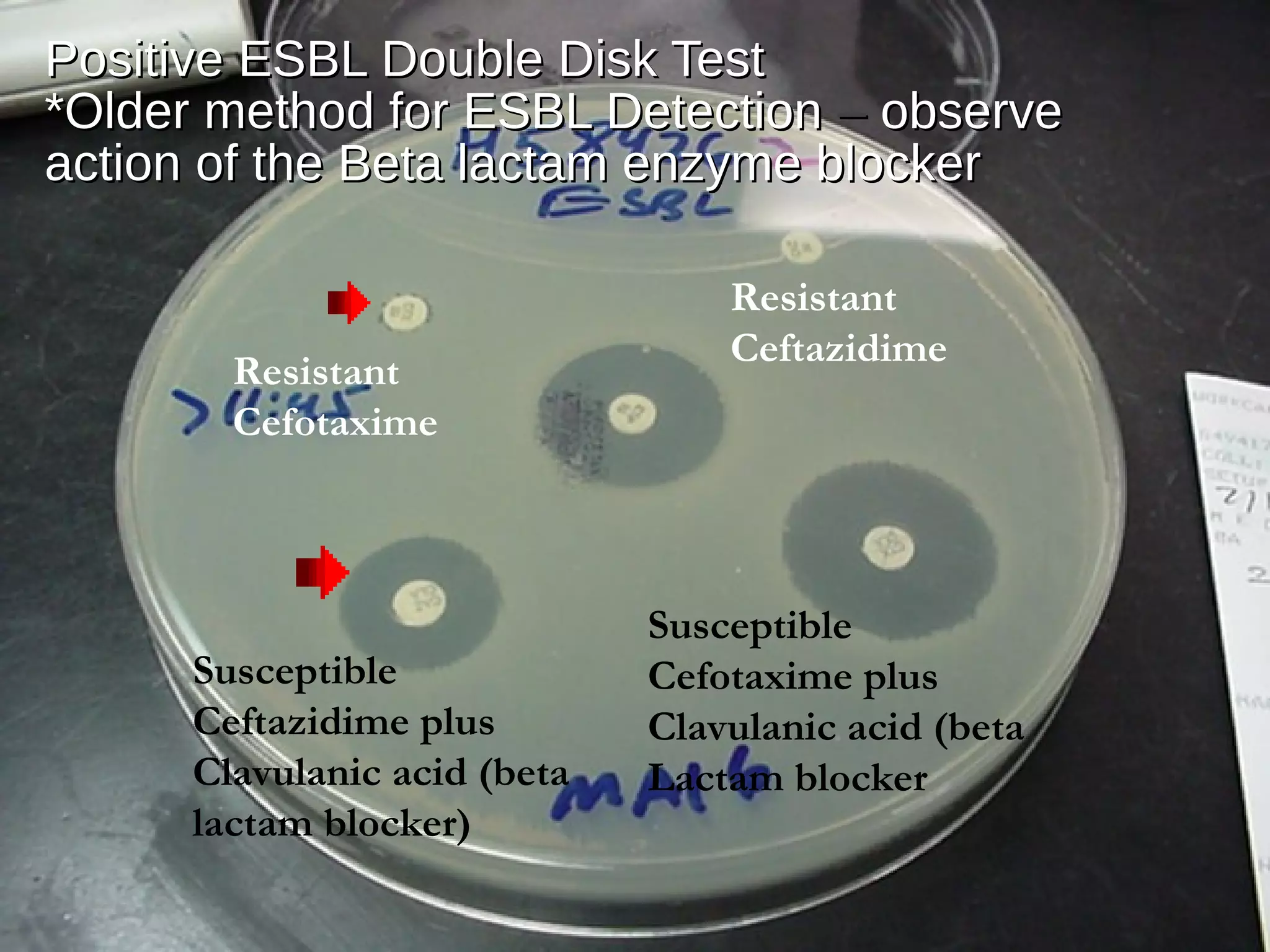
◦Confer resistance to Cephalosporins, Penicillins andConfer resistance to Cephalosporins, Penicillins and
Monobactam (Aztreonam) by opening the beta lactam ringMonobactam (Aztreonam) by opening the beta lactam ring
and inactivating the antibioticand inactivating the antibiotic
◦ESBLs do not attack Cephamycin (cefoxitin, cefotetan) or theESBLs do not attack Cephamycin (cefoxitin, cefotetan) or the
Carbapenem antibiotic classesCarbapenem antibiotic classes
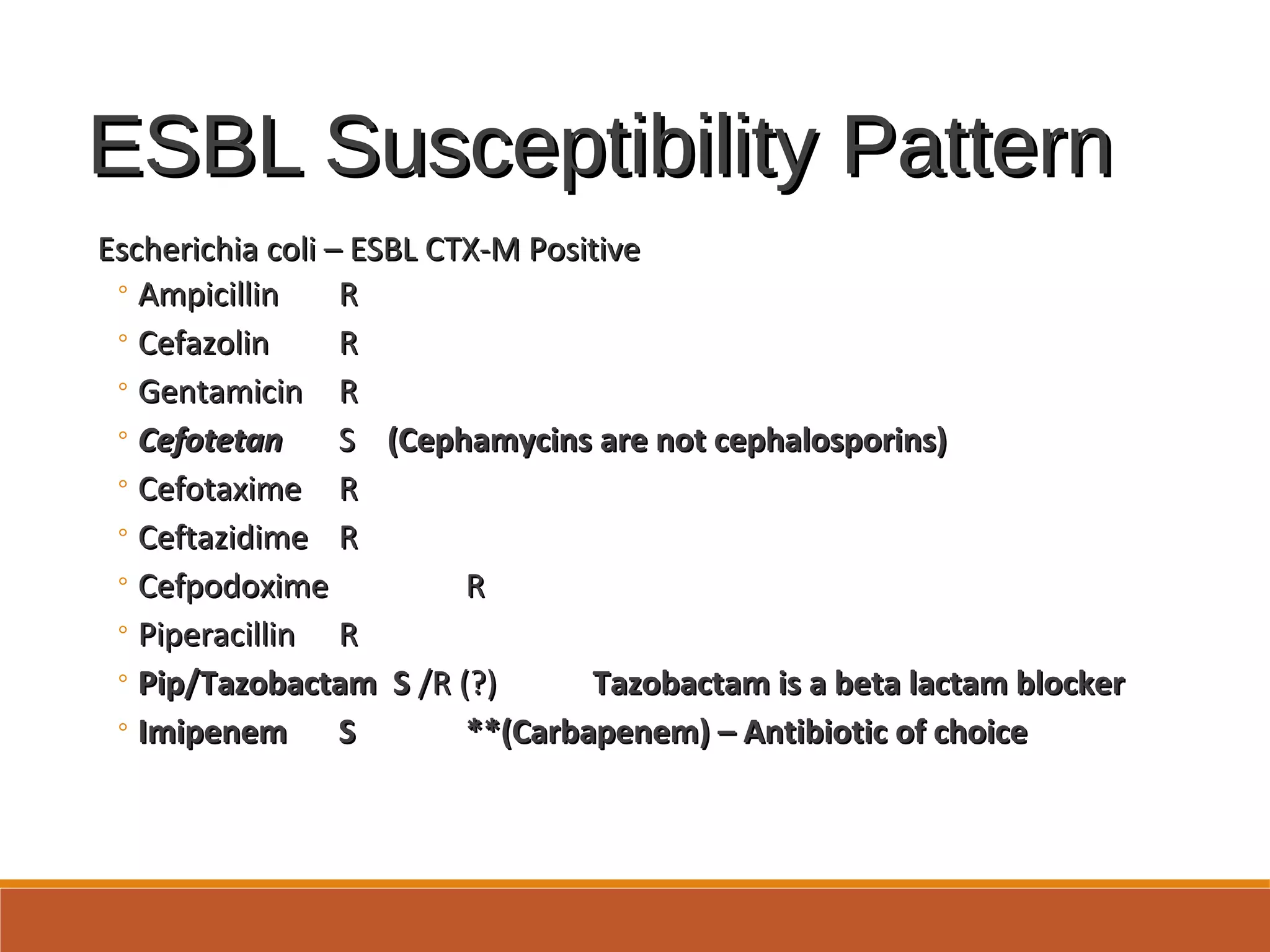
Plasmid mediated CTX-M beta lactamases are the mostPlasmid mediated CTX-M beta lactamases are the most
common in the US currently, but many more ESBL typescommon in the US currently, but many more ESBL types
worldwideworldwide
Therapy for ESBL producing gram negative rods:Therapy for ESBL producing gram negative rods:
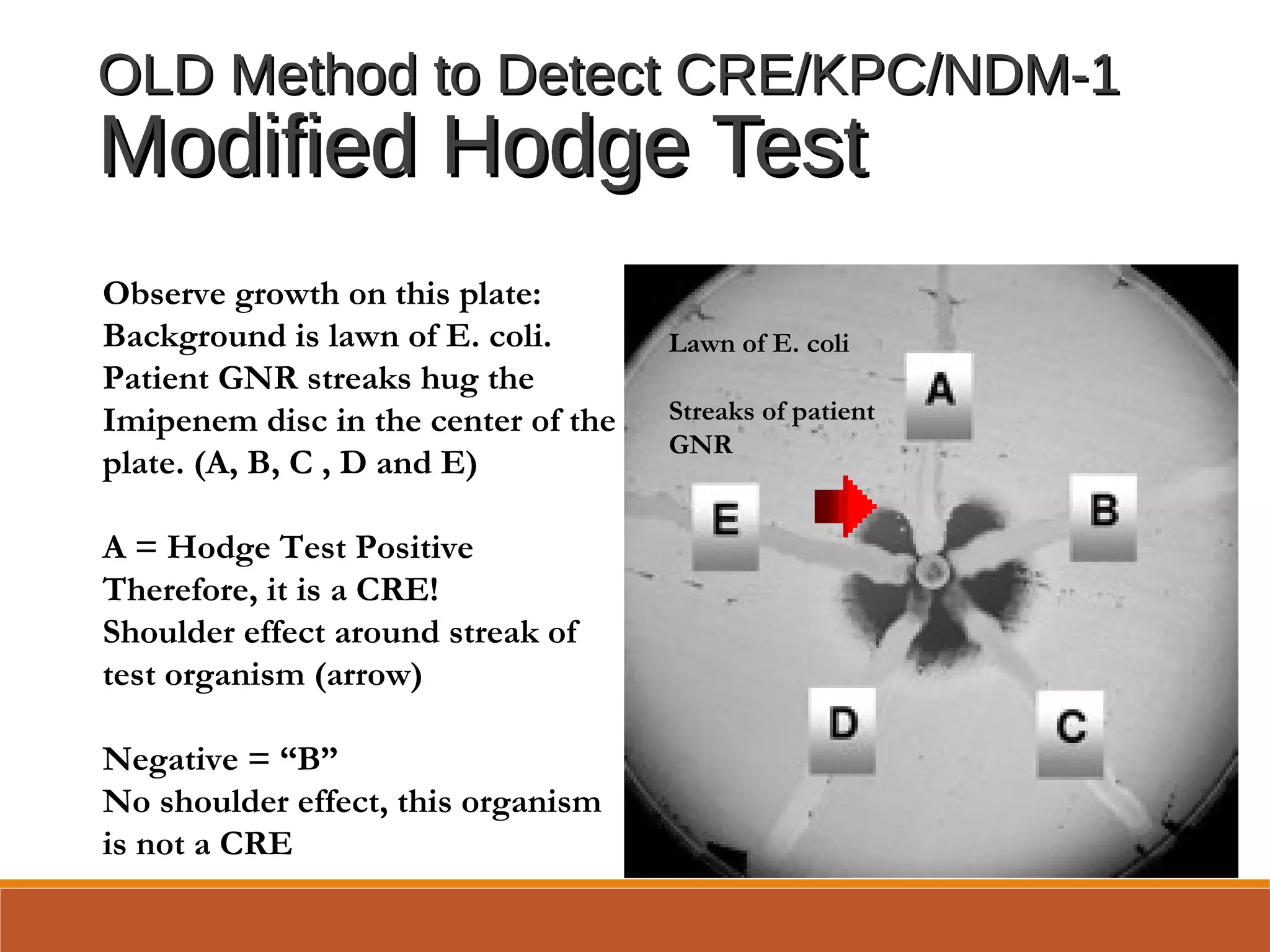
◦Carbapenems: Imipenem, Meropenem, Doripenem,Carbapenems: Imipenem, Meropenem, Doripenem,
ErtapenemErtapenem](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antibioticsenstivitytesting2017update-170323135636/75/Antibiotic-Senstivity-Testing-2017-Update-27-2048.jpg)